What is a Broker?
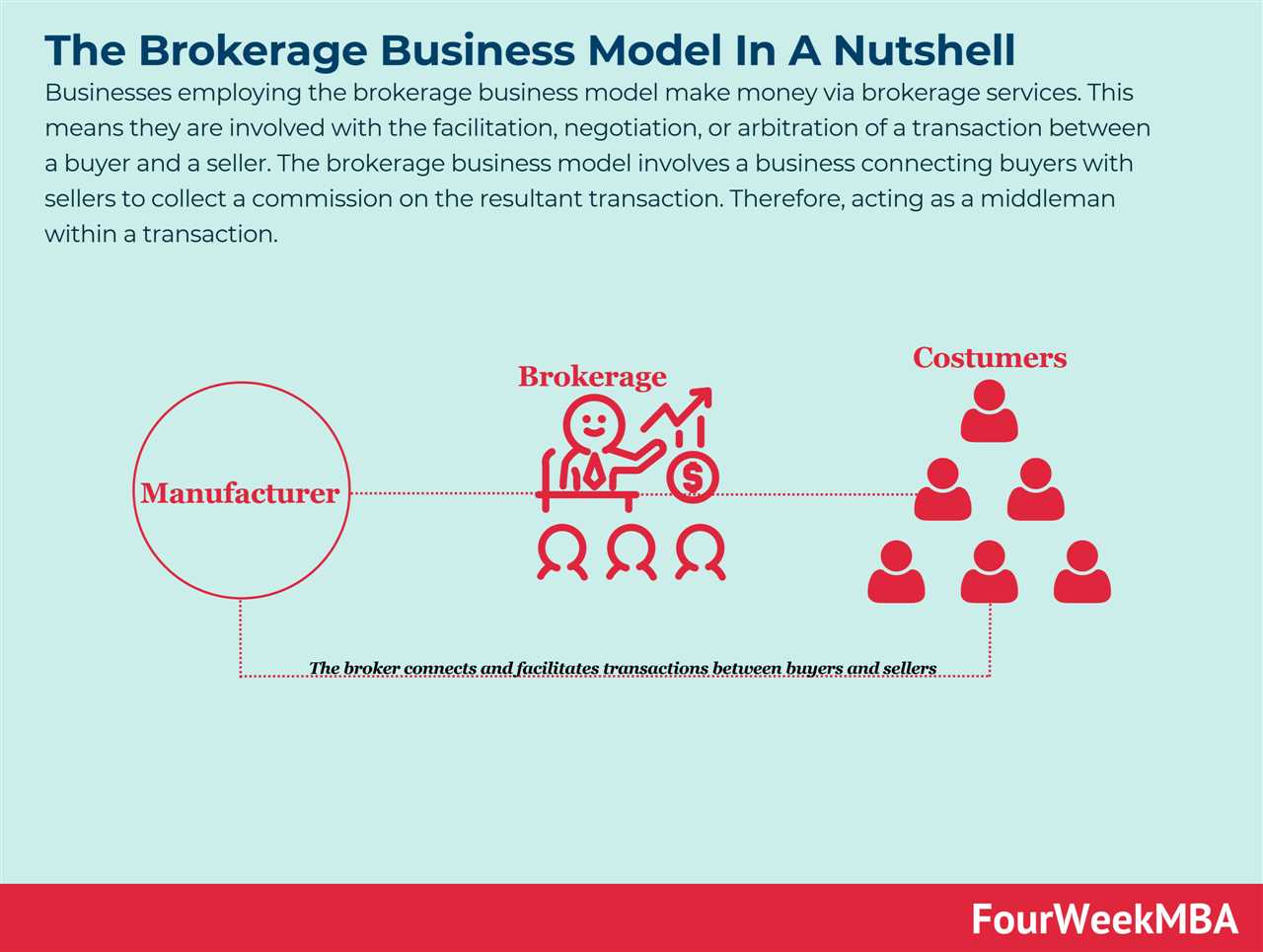
A broker is a financial intermediary who facilitates the buying and selling of various financial instruments on behalf of their clients. They act as a bridge between buyers and sellers, executing trades and providing valuable advice and guidance.
Brokers play a crucial role in the financial markets, helping individuals and institutions access a wide range of investment opportunities. They provide a platform for investors to trade stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, and other financial products.
Types of Brokers
There are several types of brokers, each specializing in a specific area of the financial markets:
1. Stockbrokers: These brokers facilitate the buying and selling of stocks and other securities on stock exchanges. They provide investors with access to a wide range of stocks and help execute trades.
2. Forex Brokers: Forex brokers enable individuals and institutions to trade currencies in the foreign exchange market. They offer trading platforms and tools to execute currency trades and provide leverage to amplify potential profits.
3. Commodities Brokers: Commodities brokers facilitate the trading of physical commodities such as gold, oil, agricultural products, and more. They connect buyers and sellers in the commodities market and help execute trades.
4. Real Estate Brokers: Real estate brokers assist buyers and sellers in the purchase and sale of properties. They help clients find suitable properties, negotiate deals, and handle the paperwork involved in real estate transactions.
Regulation of Brokers

Brokers are typically regulated by financial authorities to ensure fair and transparent trading practices. Regulatory bodies set rules and guidelines that brokers must adhere to, protecting the interests of investors and maintaining market integrity.
Regulation varies depending on the jurisdiction and the type of financial instrument being traded. Brokers may need to obtain licenses and meet certain capital requirements to operate legally.
Examples of Brokers
Some well-known examples of brokers include:
1. Charles Schwab: A prominent stockbroker that provides a wide range of investment services and tools.
2. OANDA: A popular forex broker that offers online currency trading services to individuals and institutions.
3. CME Group: A leading commodities broker that operates one of the largest derivatives exchanges in the world.
4. Sotheby’s International Realty: A renowned real estate broker specializing in luxury properties.
Types of Brokers
Brokers can be classified into various types based on the financial markets they operate in and the services they provide. Here are some of the most common types of brokers:
- Stockbrokers: These brokers specialize in buying and selling stocks on behalf of their clients. They provide investment advice, execute trades, and help clients navigate the stock market.
- Forex Brokers: Forex brokers facilitate trading in the foreign exchange market. They provide access to currency pairs and allow individuals and institutions to trade currencies.
- Commodity Brokers: Commodity brokers deal with the trading of commodities such as gold, oil, agricultural products, and more. They help clients buy and sell these physical goods or trade commodity futures contracts.
- Real Estate Brokers: Real estate brokers assist in buying, selling, and renting properties. They connect buyers and sellers, negotiate deals, and help clients navigate the complex real estate market.
- Insurance Brokers: Insurance brokers act as intermediaries between insurance companies and individuals or businesses seeking insurance coverage. They help clients choose the right insurance policies and negotiate terms.
- Mortgage Brokers: Mortgage brokers help individuals and businesses secure loans for purchasing real estate. They work with various lenders to find the best mortgage rates and terms for their clients.
- Online Brokers: Online brokers operate exclusively through online platforms, allowing individuals to trade stocks, bonds, commodities, and other financial instruments from the comfort of their own homes.
- Discount Brokers: Discount brokers offer trading services at lower commission rates compared to full-service brokers. They provide basic trading functionalities without personalized investment advice.
- Full-Service Brokers: Full-service brokers offer a wide range of services, including investment advice, research, financial planning, and more. They cater to high-net-worth individuals and provide personalized investment strategies.
Regulation of Brokers
Brokers operate in a highly regulated industry to ensure the protection of investors and maintain fair and transparent markets. The regulation of brokers varies by country and jurisdiction, but there are common regulatory bodies and frameworks that govern their activities.
Regulatory Bodies
One of the primary regulatory bodies for brokers is the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States. The SEC is responsible for enforcing federal securities laws and regulating the securities industry, including brokers and brokerage firms.
In addition to the SEC, there are other regulatory bodies around the world that oversee brokers and financial markets. For example, in the United Kingdom, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) is the main regulatory body for brokers and financial services companies.
Regulatory Frameworks
Regulatory frameworks are sets of rules and regulations that brokers must adhere to in order to operate legally and ethically. These frameworks outline the requirements for licensing, capital adequacy, client protection, disclosure of information, and more.
For example, brokers in the United States must comply with the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which requires them to register with the SEC and follow certain rules and regulations regarding trading practices, record-keeping, and disclosure of information to clients.
In the European Union, brokers must comply with the Markets in Financial Instruments Directive (MiFID II), which sets out rules for the provision of investment services and the operation of financial markets.
Benefits of Regulation
The regulation of brokers provides several benefits to investors and the overall financial system. It helps to ensure the integrity of markets, protect investors from fraud and misconduct, and promote fair competition among brokers.
Regulation also helps to establish trust and confidence in the financial industry, as investors can be assured that brokers are operating within a legal and ethical framework. It provides a level playing field for all market participants and contributes to the stability and efficiency of financial markets.
Overall, the regulation of brokers plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of the financial industry, protecting investors, and promoting fair and transparent markets.
Examples of Brokers
Brokers play a crucial role in various industries and sectors, facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers. Here are some examples of brokers in different fields:
| Industry | Example of Broker |
|---|---|
| Real Estate | Real estate brokers help individuals and businesses buy, sell, or rent properties. They assist clients in finding suitable properties, negotiating deals, and completing the necessary paperwork. |
| Stock Market | Stockbrokers act as intermediaries between investors and the stock market. They execute buy and sell orders on behalf of their clients and provide them with investment advice and market insights. |
| Insurance | Insurance brokers help individuals and businesses find suitable insurance policies that meet their specific needs. They work with multiple insurance companies to provide clients with a range of options and assist them in comparing coverage and premiums. |
| Forex Trading | Forex brokers facilitate currency trading for individuals and institutions. They provide access to the foreign exchange market, offer trading platforms, and assist clients in executing trades and managing their portfolios. |
| Freight and Logistics | Freight brokers connect shippers with carriers to facilitate the transportation of goods. They negotiate rates, arrange shipments, and ensure the smooth movement of cargo from one location to another. |
| Travel | Travel agents act as brokers between travelers and travel service providers. They help individuals and groups plan and book flights, accommodations, and other travel-related services, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable travel experience. |
These are just a few examples of the diverse roles that brokers play in various industries. They bring together buyers and sellers, provide expertise and guidance, and facilitate transactions, making them an essential part of the business ecosystem.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
