Unregistered Shares Meaning Overview Considerations
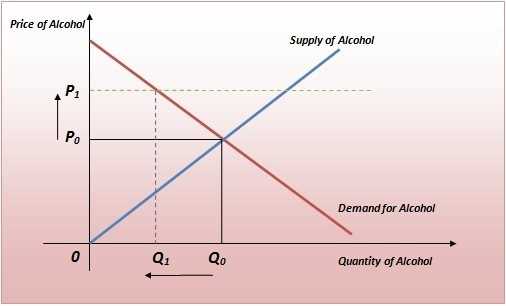
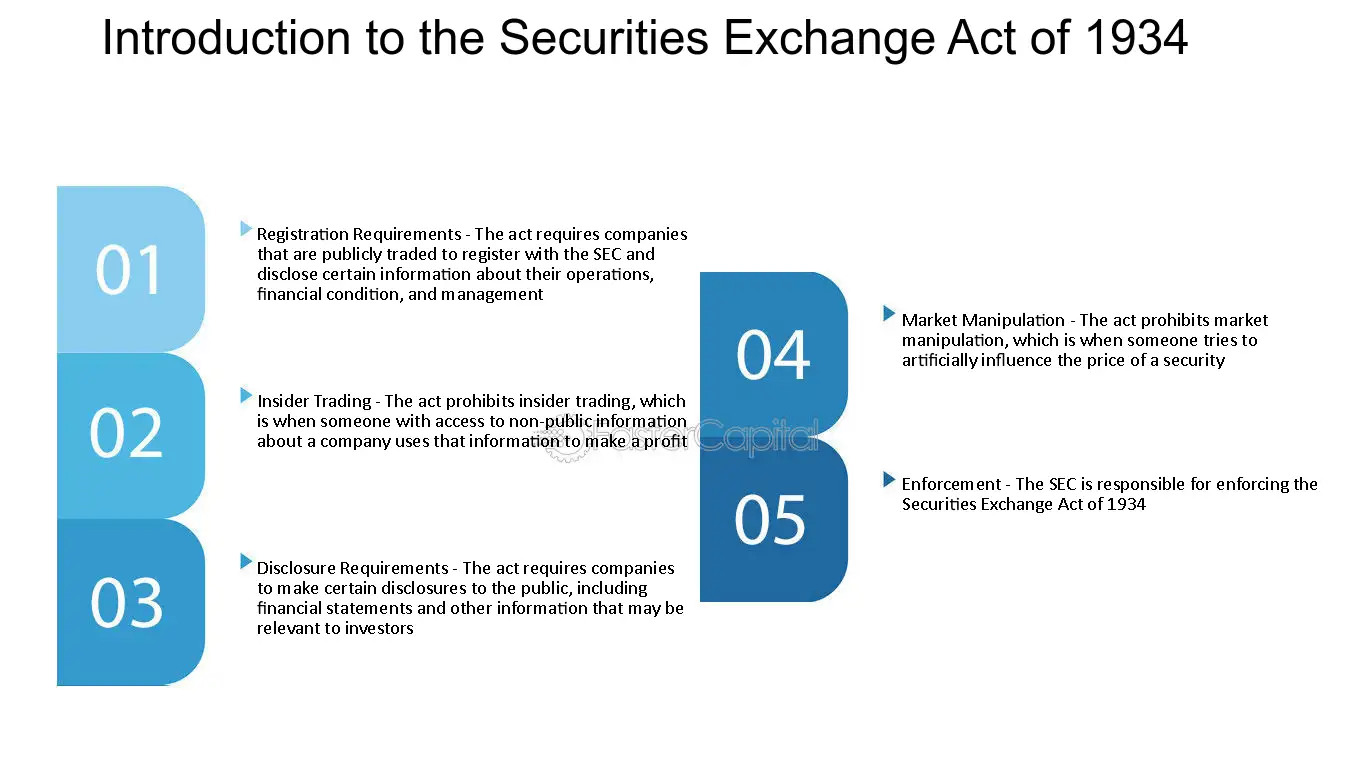
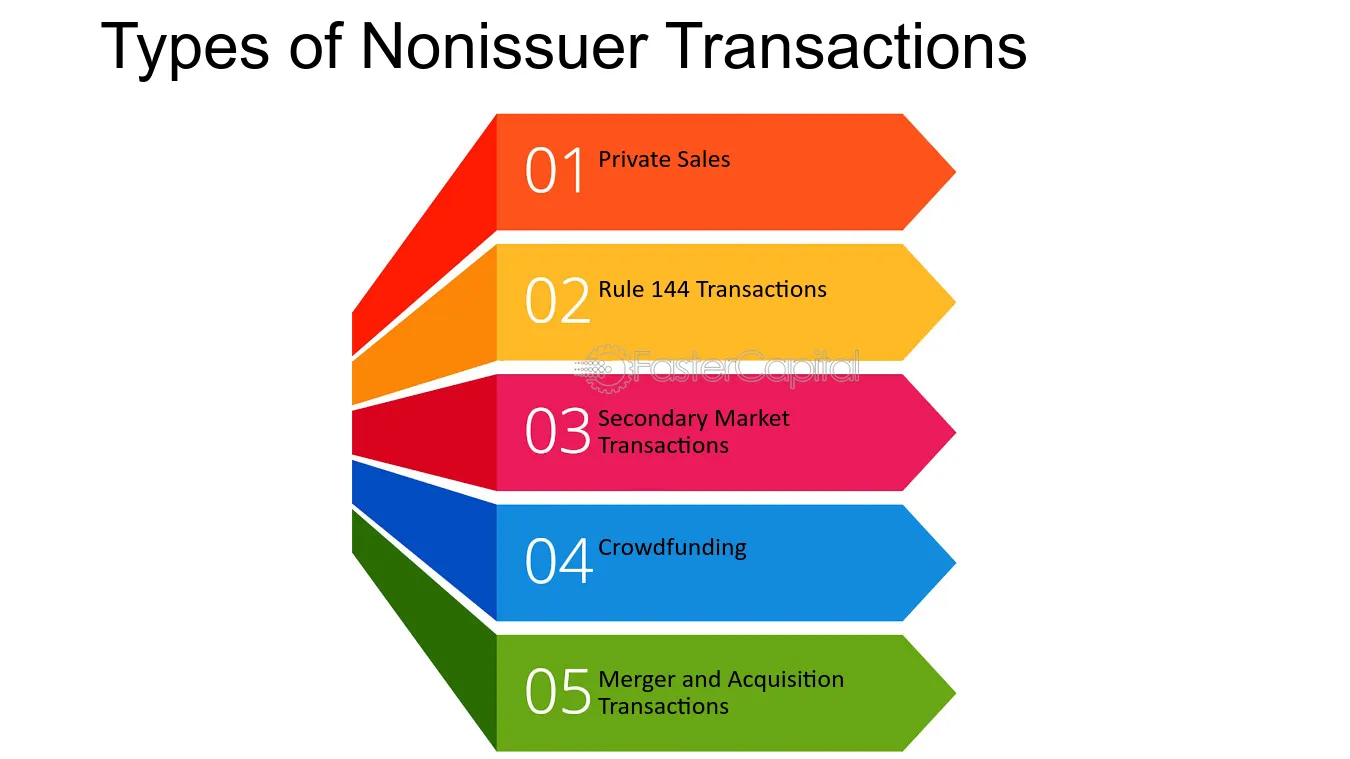
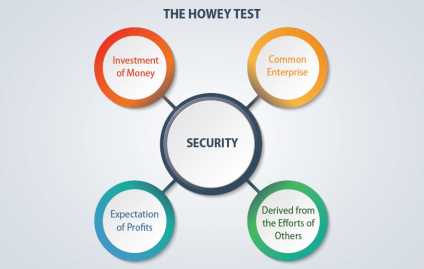
Unregistered Shares: Meaning and Overview Unregistered shares refer to shares of stock that have not been registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). When a company wants to offer its shares to the public, it must typically register those shares with the SEC. However, there are certain circumstances in … …