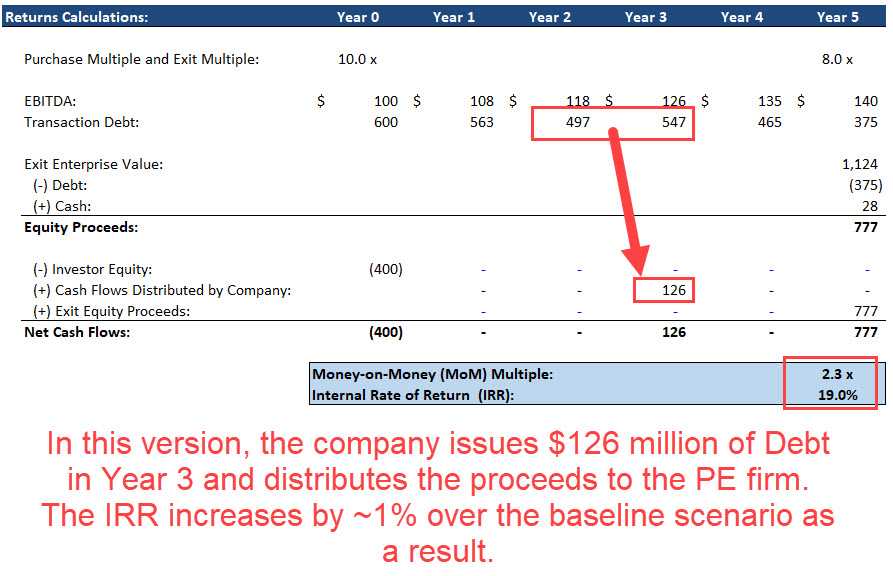
Dividend Recapitalization With Example
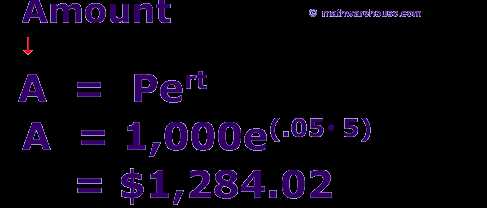
Overview of Dividend Recapitalization Dividend recapitalization is a financial strategy that involves a company borrowing money to pay a special dividend to its shareholders. This strategy allows the company to distribute excess cash to shareholders while also increasing its debt levels. During a dividend recapitalization, the company typically issues new … …