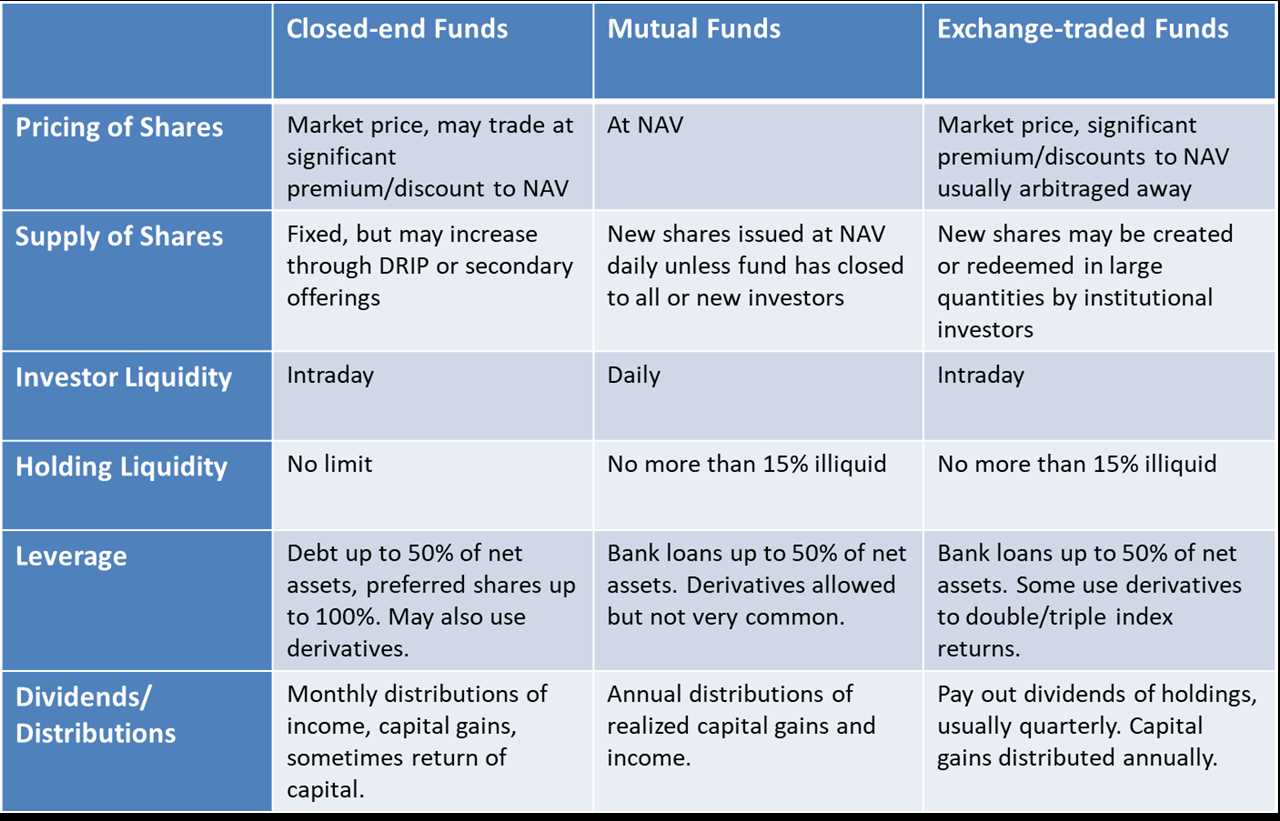
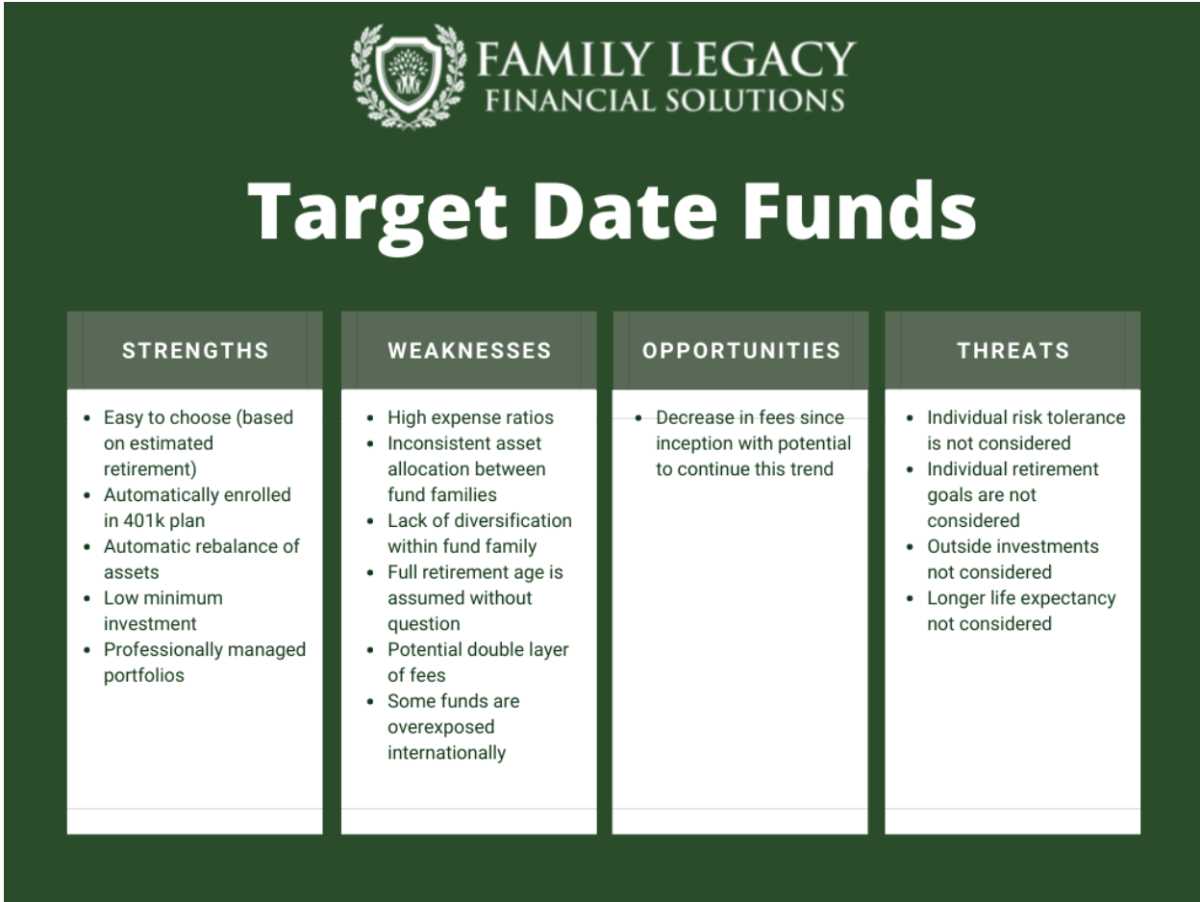
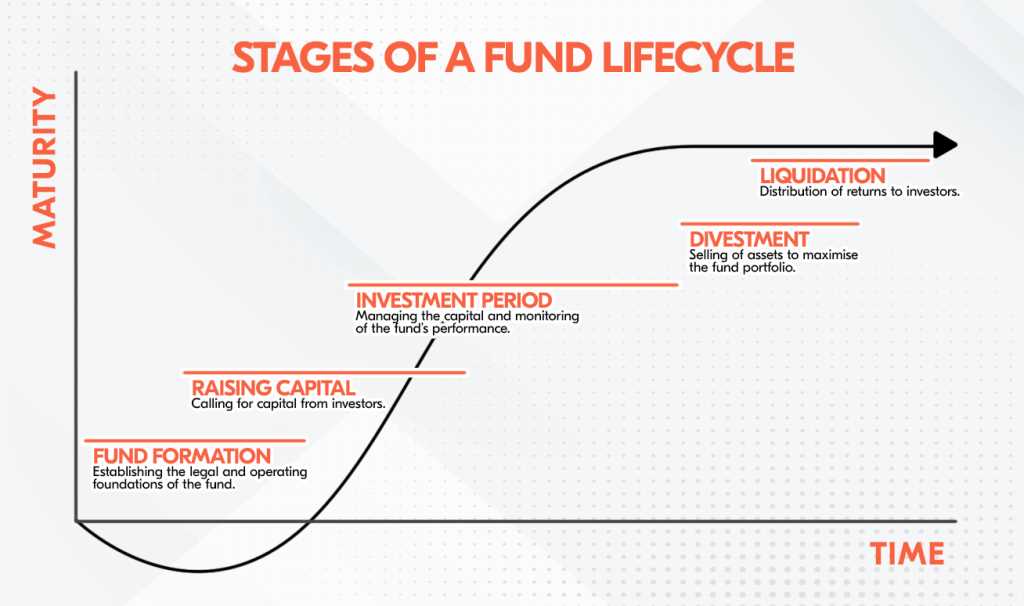
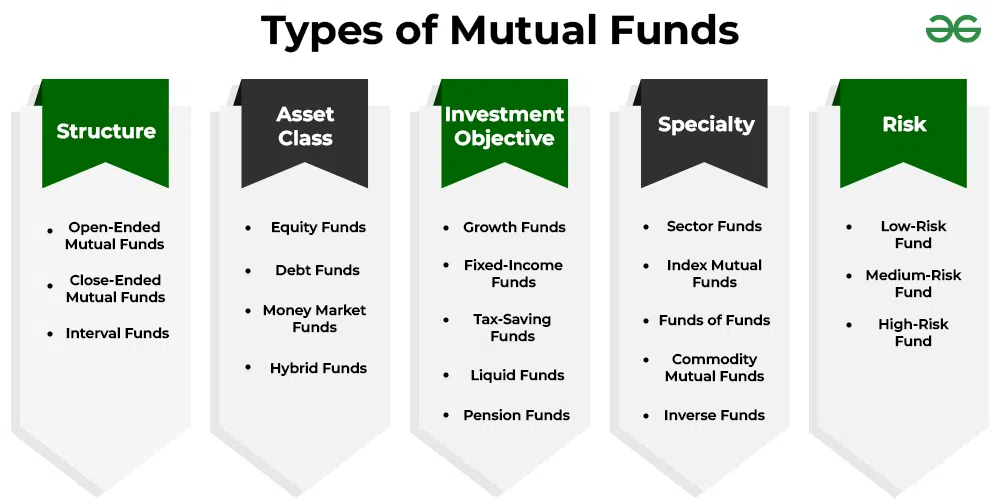
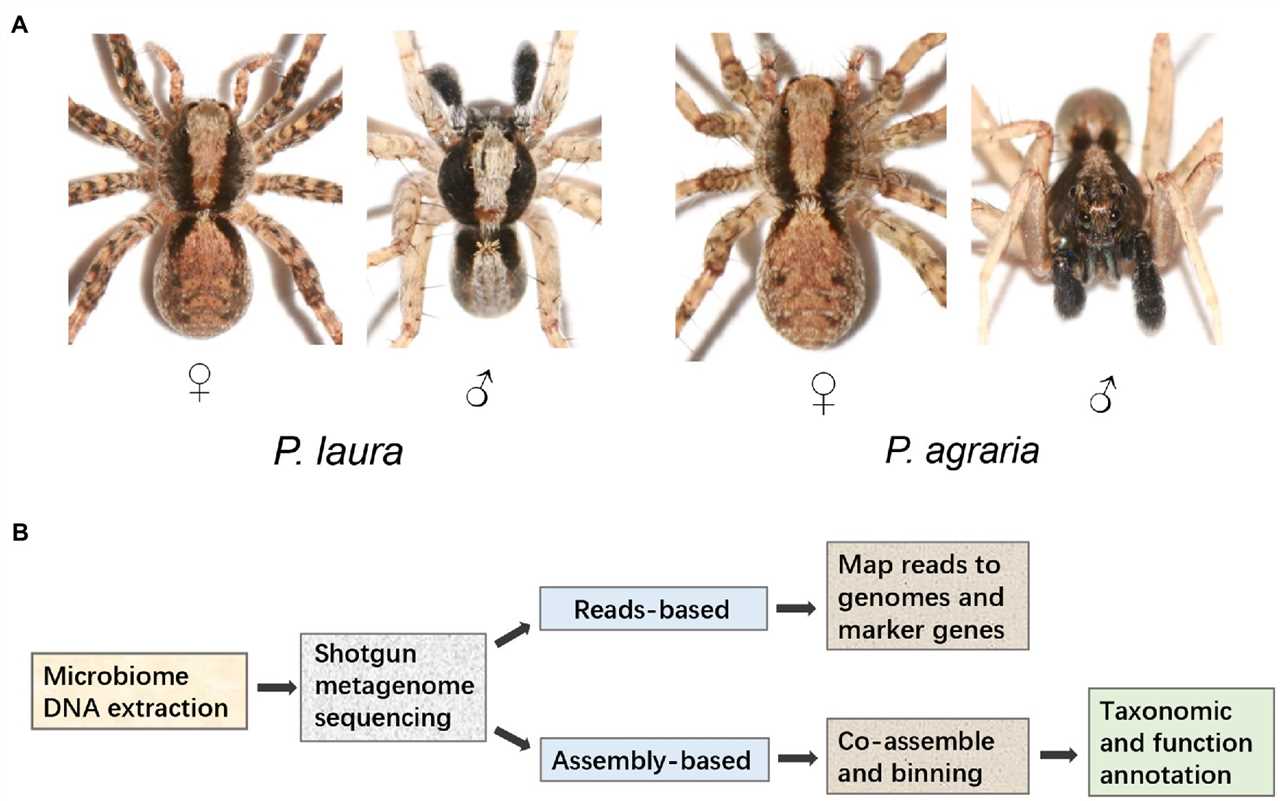
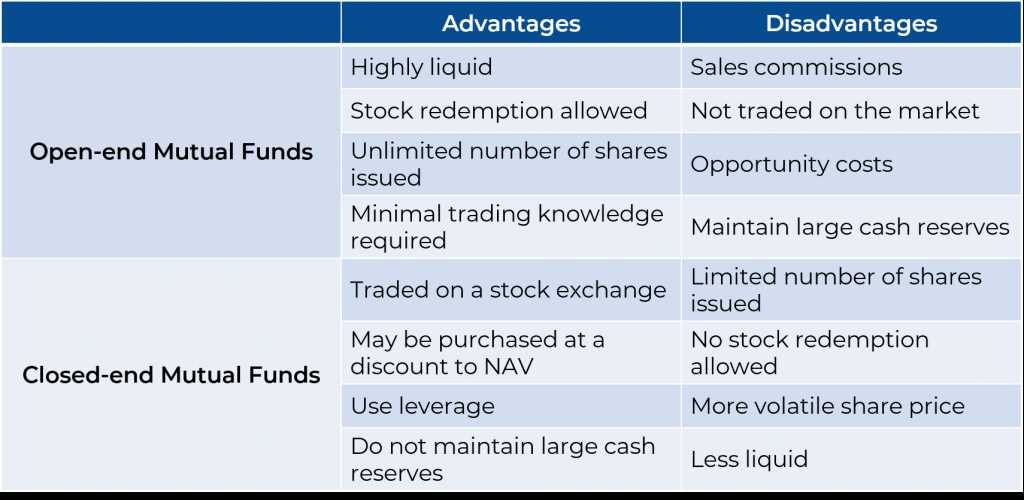
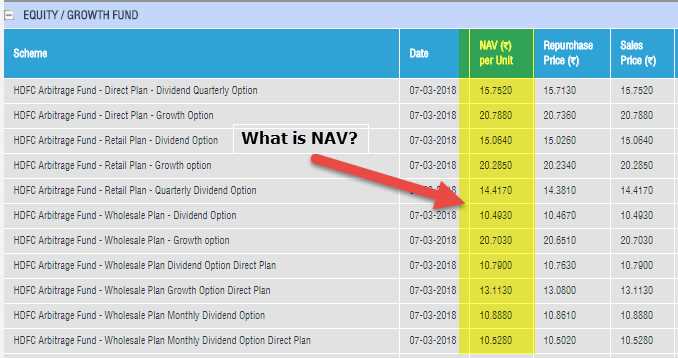
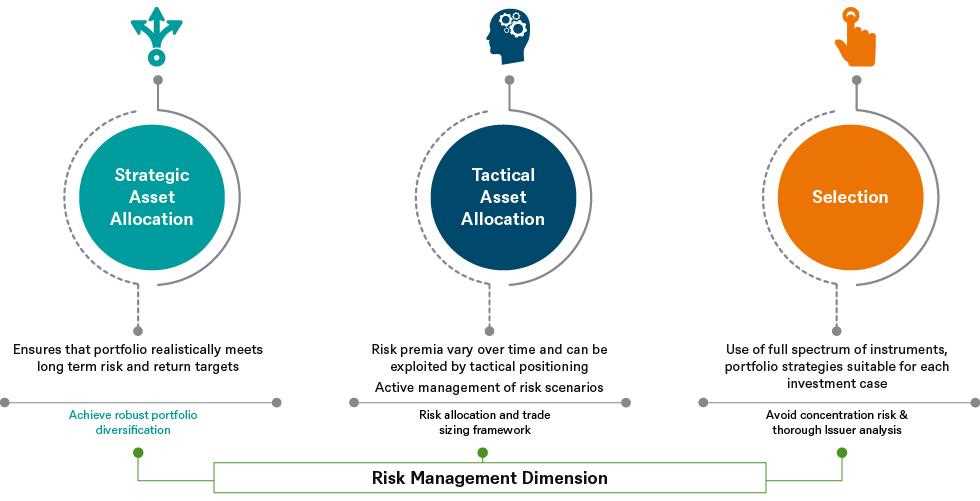
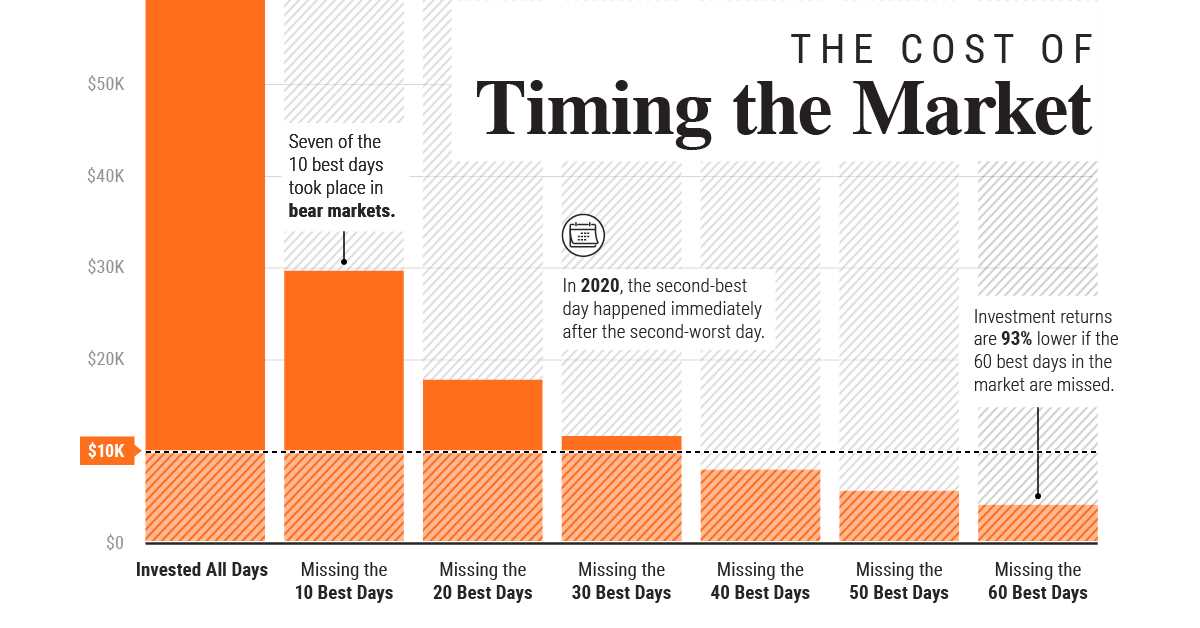
Understanding Turnover Ratio: Definition, Importance, and Analysis
Definition of Turnover Ratio The turnover ratio is a financial metric used to measure the rate at which a mutual fund buys and sells its portfolio holdings over a given period of time. It is calculated by dividing the total value of securities bought or sold by the average net … …