Production Externality: Definition, Measurement, And Real-World Examples
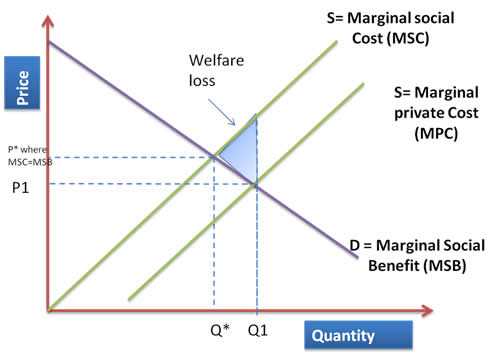
What is Production Externality? Production externality refers to the impact that a firm’s production activities have on third parties or the surrounding environment, which is not reflected in the firm’s costs or revenues. It occurs when the production of a good or service by one firm affects the well-being of … …