What Is a Trust Fund and How Does It Work?
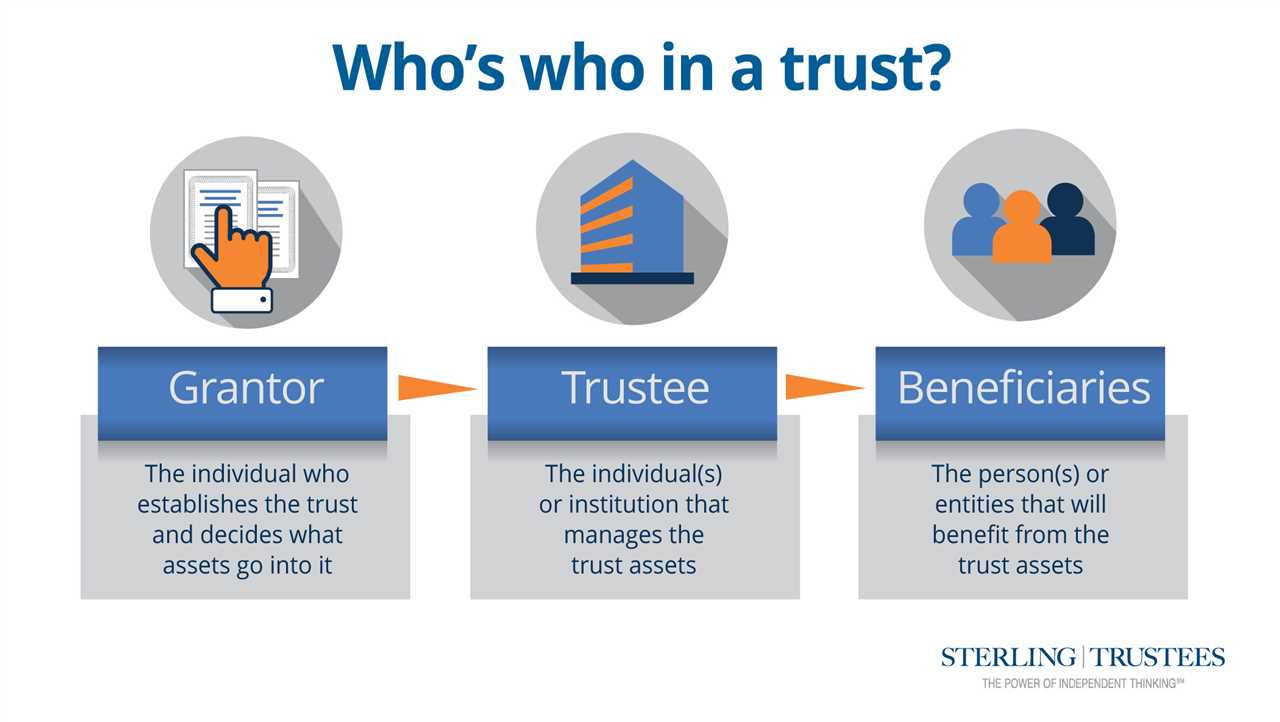
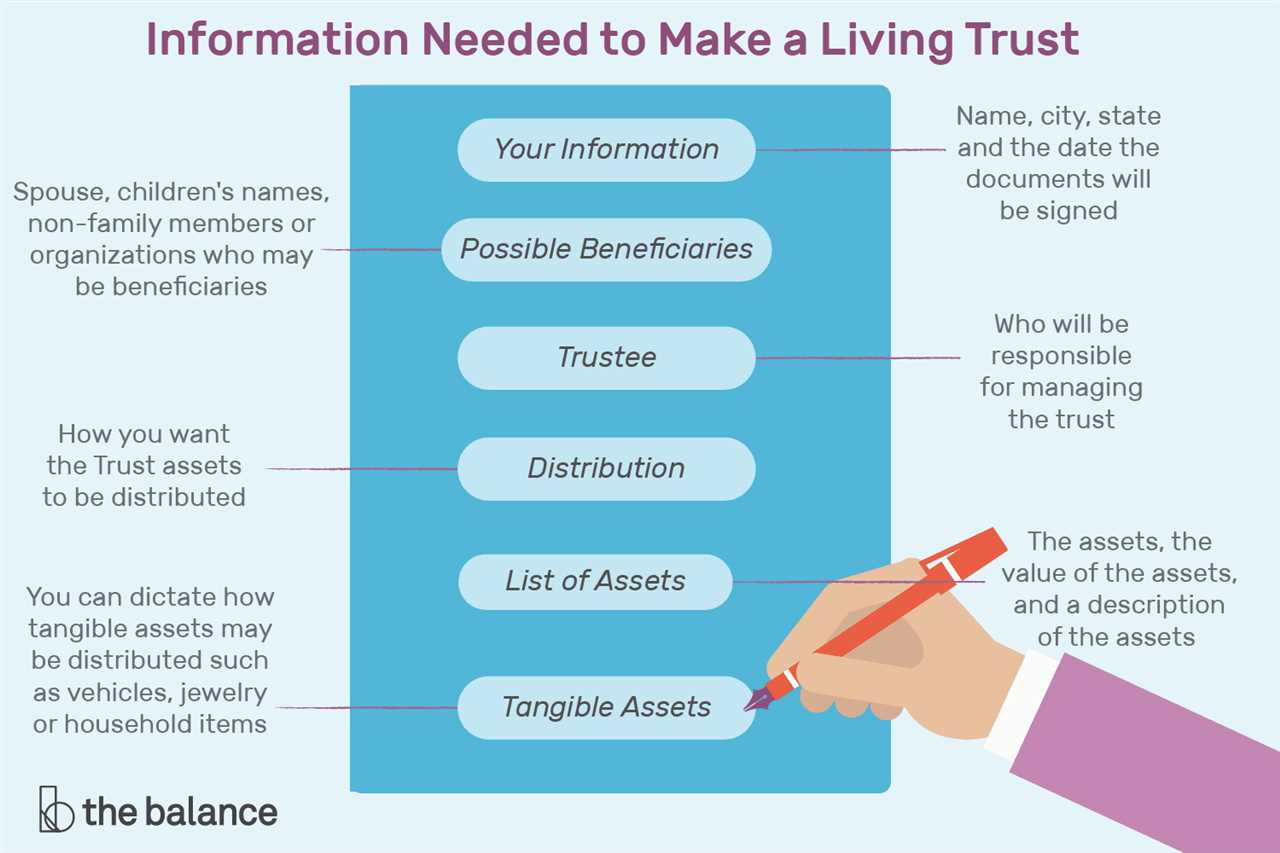
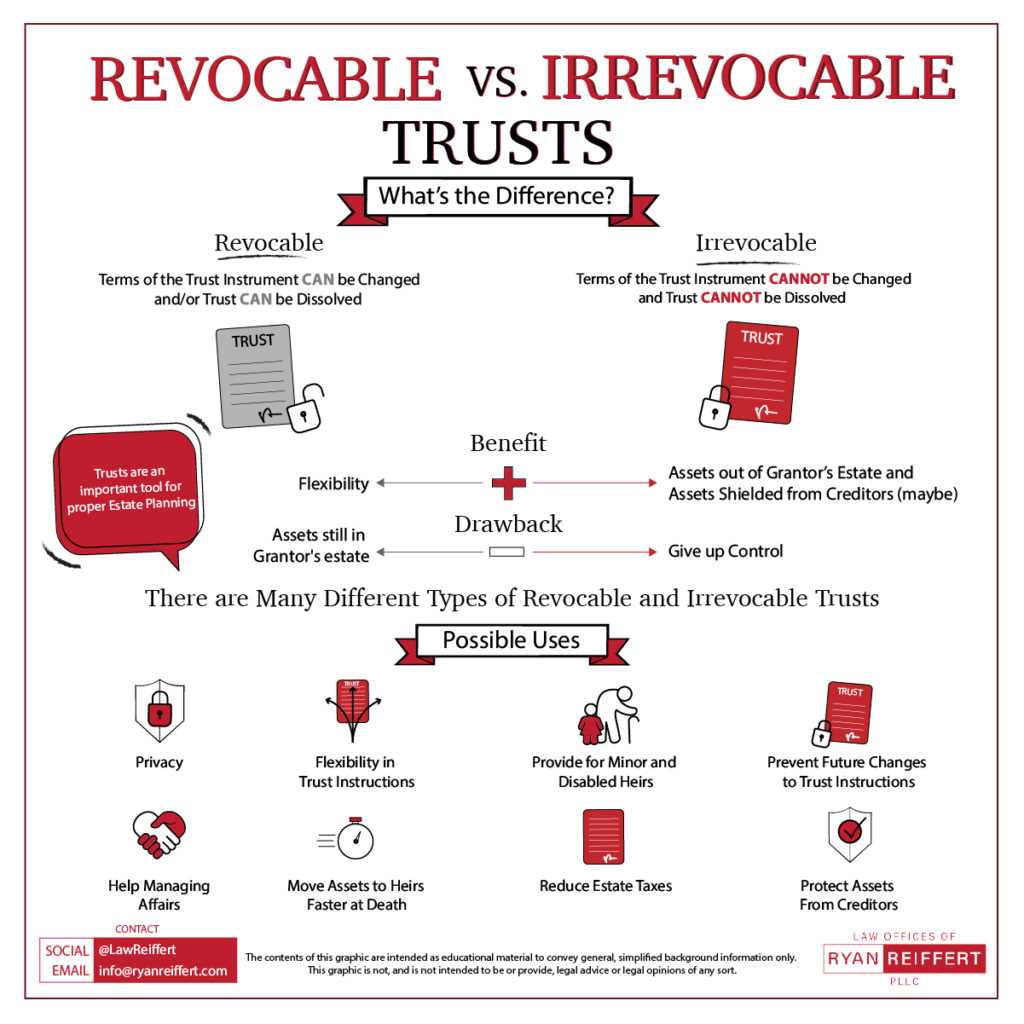
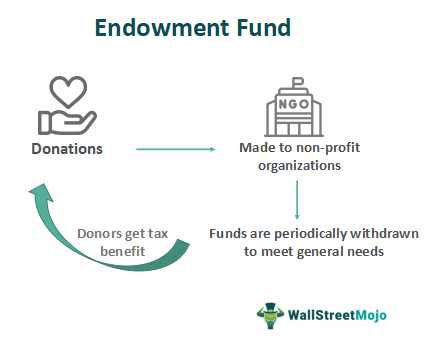
What Is a Trust Fund? A trust fund is a legal entity that holds assets on behalf of a beneficiary or beneficiaries. It is created by a grantor, who transfers assets into the trust, and managed by a trustee, who has a fiduciary duty to act in the best interest … …