Intertemporal Choice: A Key Decision-Making Concept For Businesses And Individuals
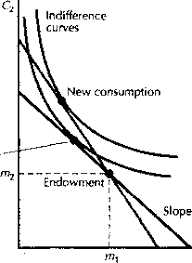
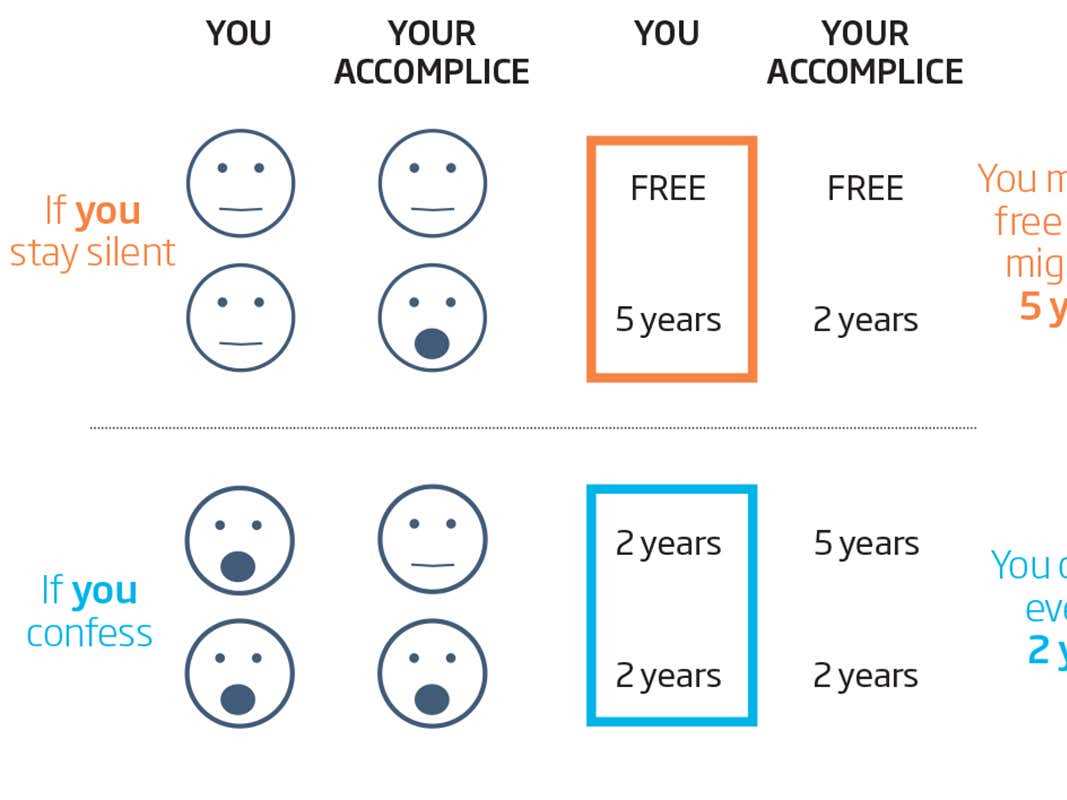
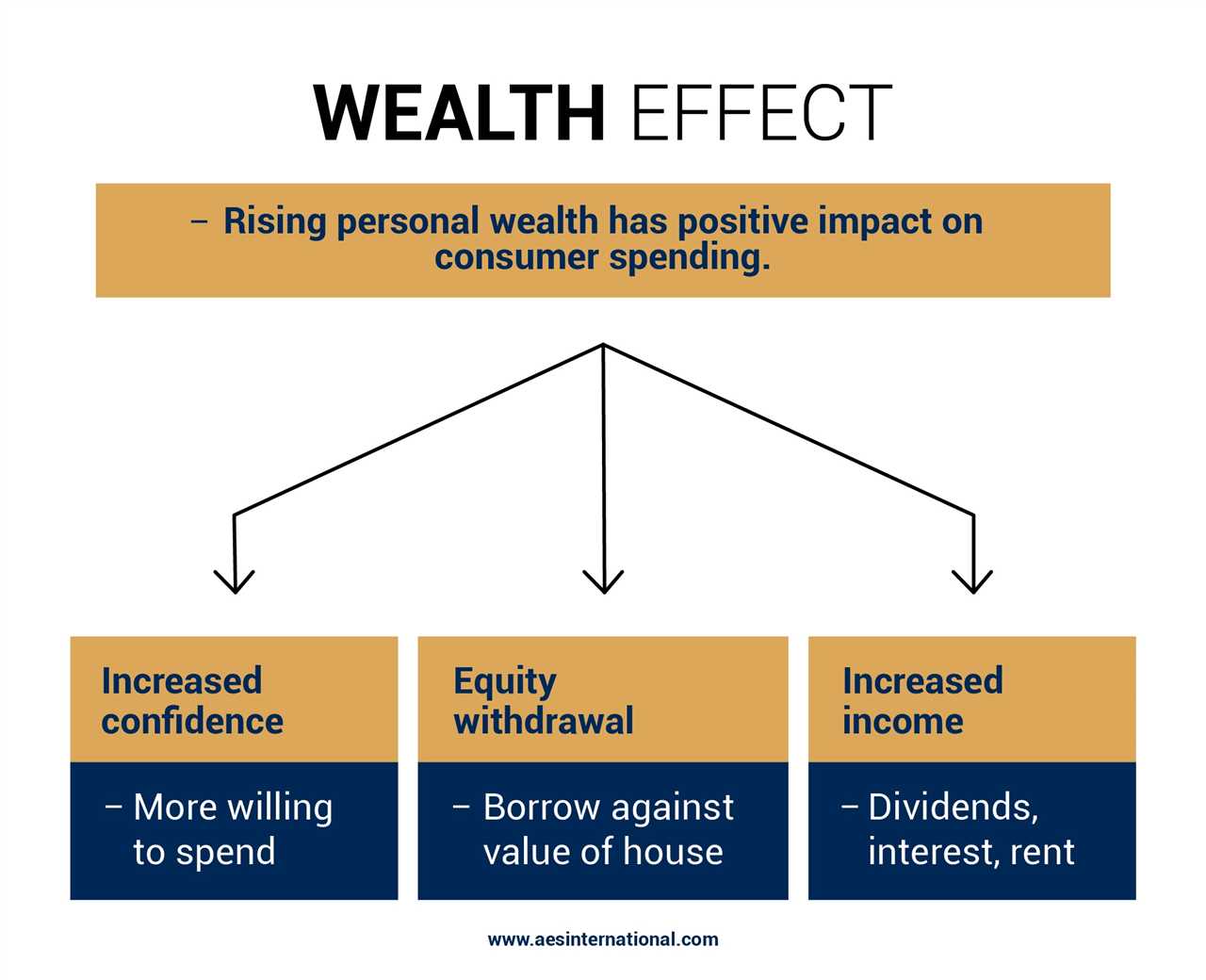
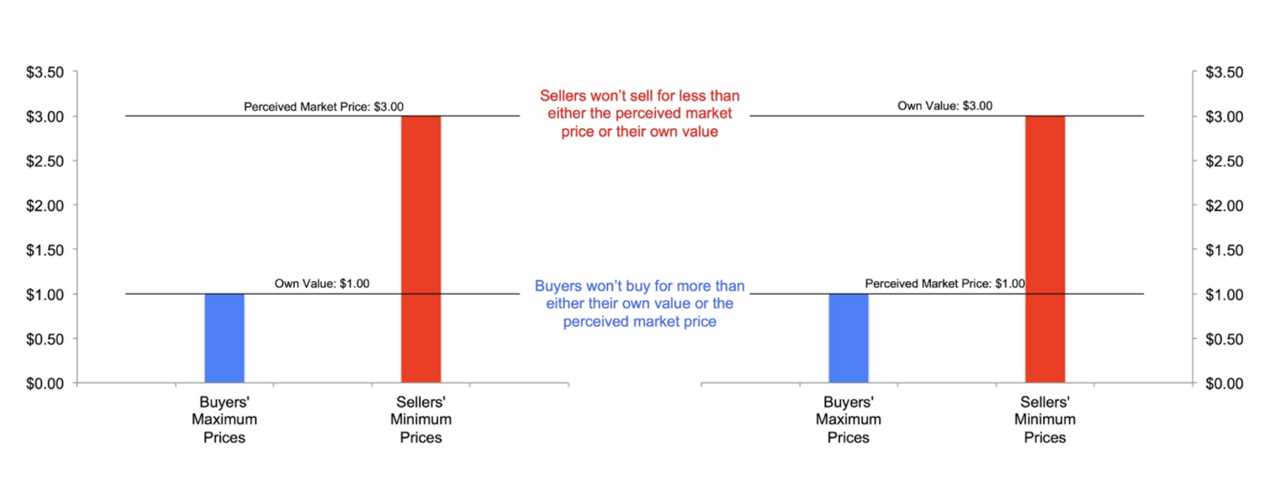
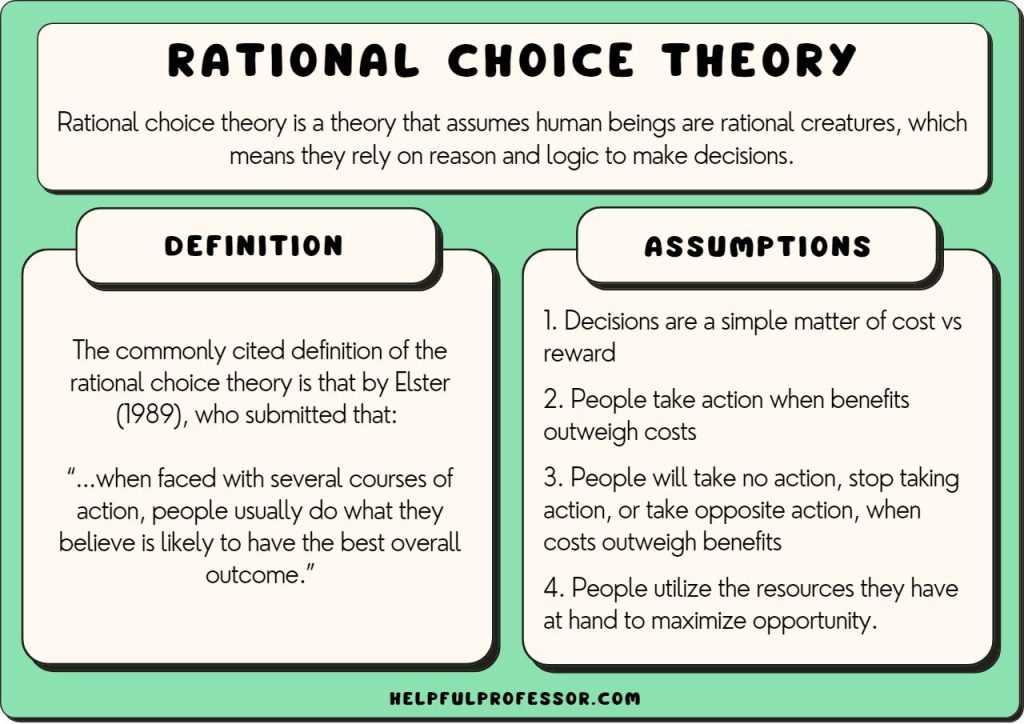
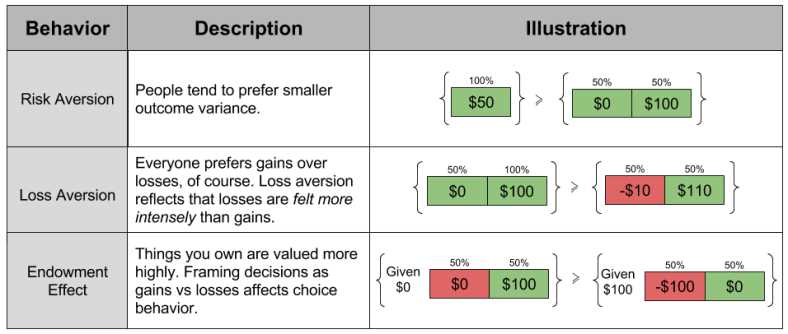
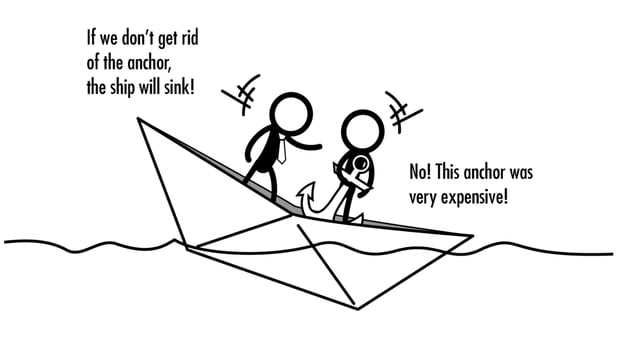
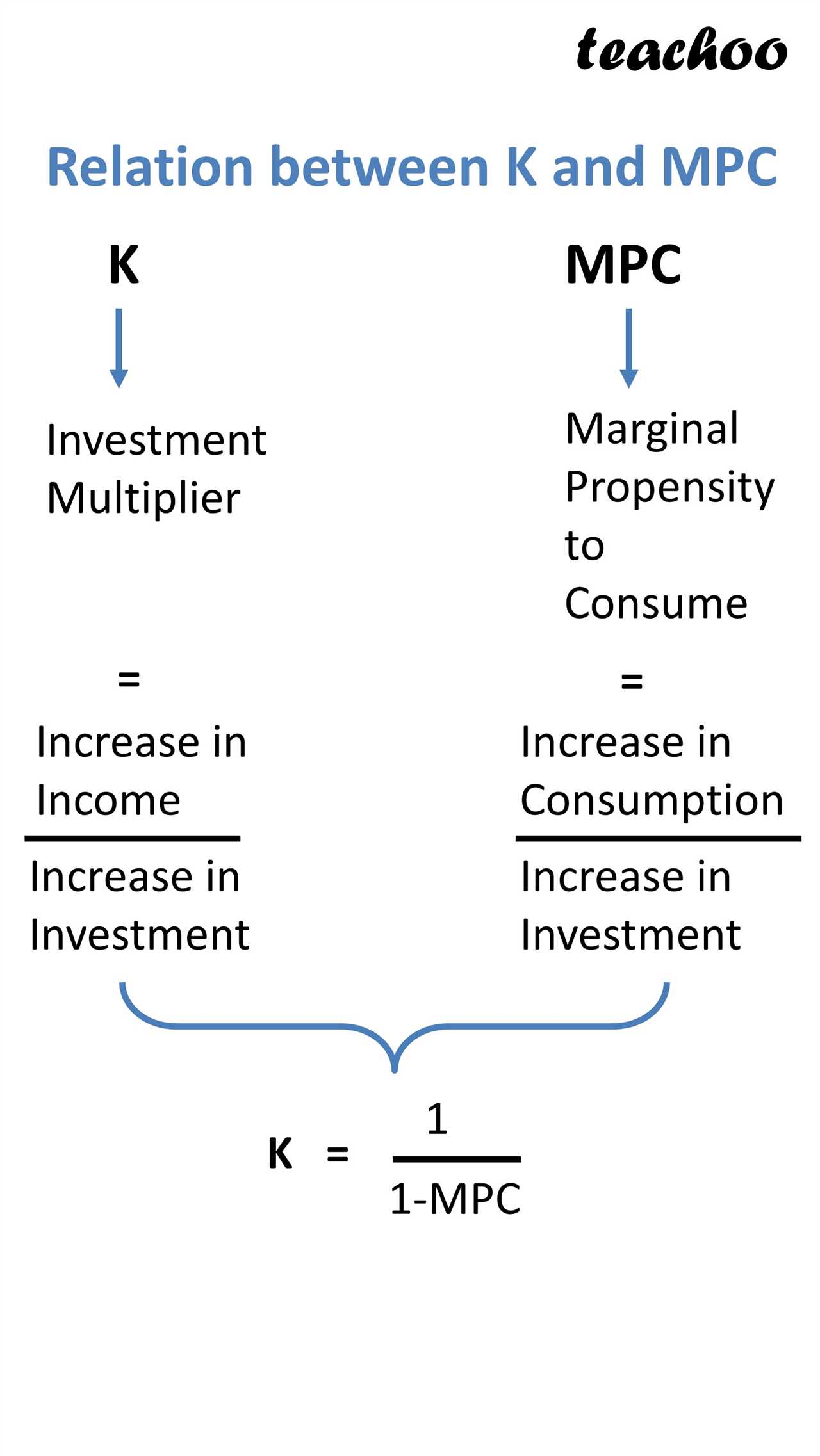
Importance of Intertemporal Choice in Behavioral Economics 1. Strategic Planning Intertemporal choice helps businesses in strategic planning by considering the trade-offs between short-term gains and long-term benefits. By evaluating the potential outcomes and consequences of different choices over time, businesses can develop effective strategies that align with their long-term goals. … …