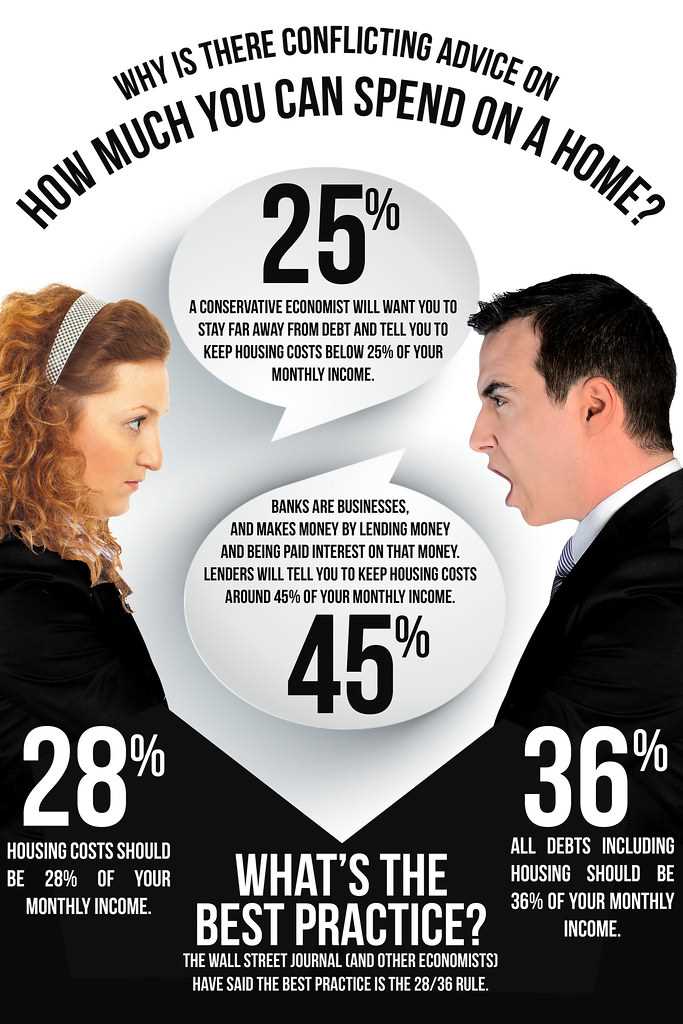
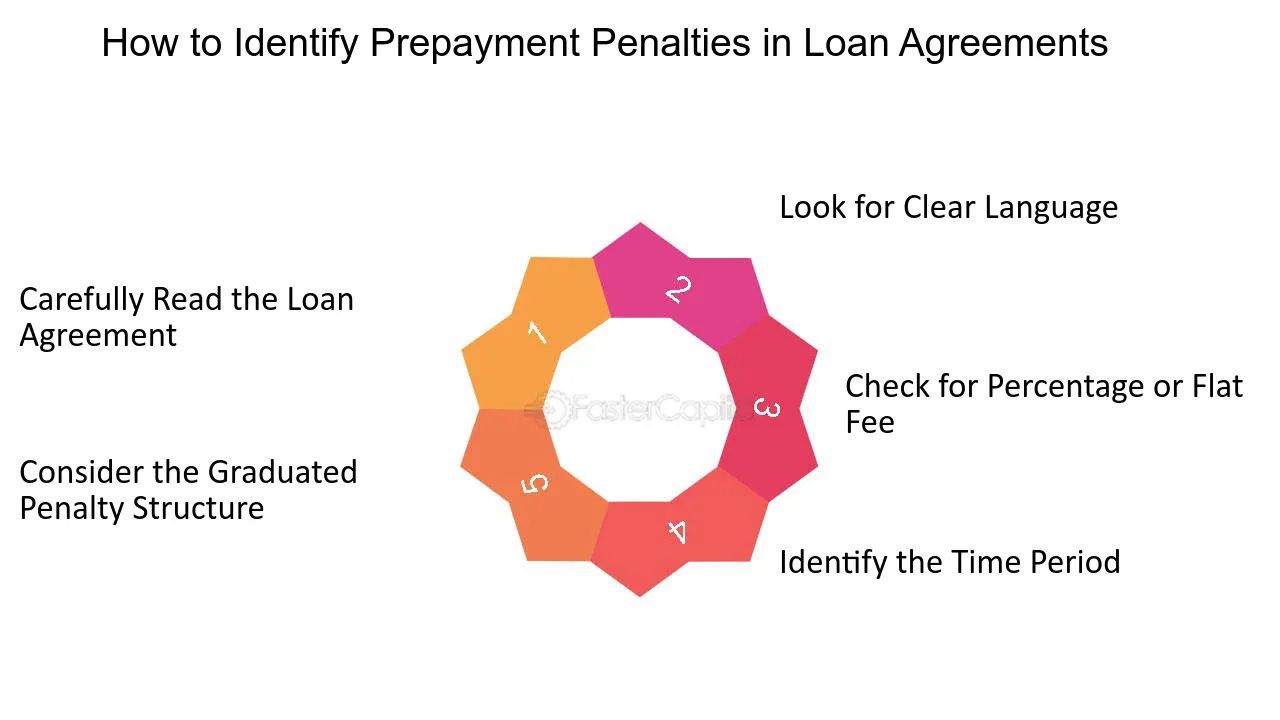
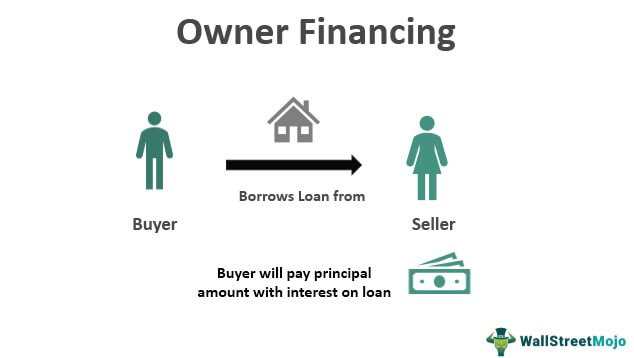
Purchase-Money Mortgages: Definition, Types, And Benefits
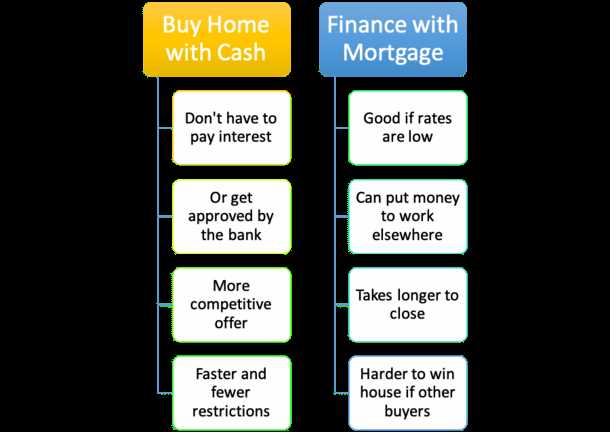
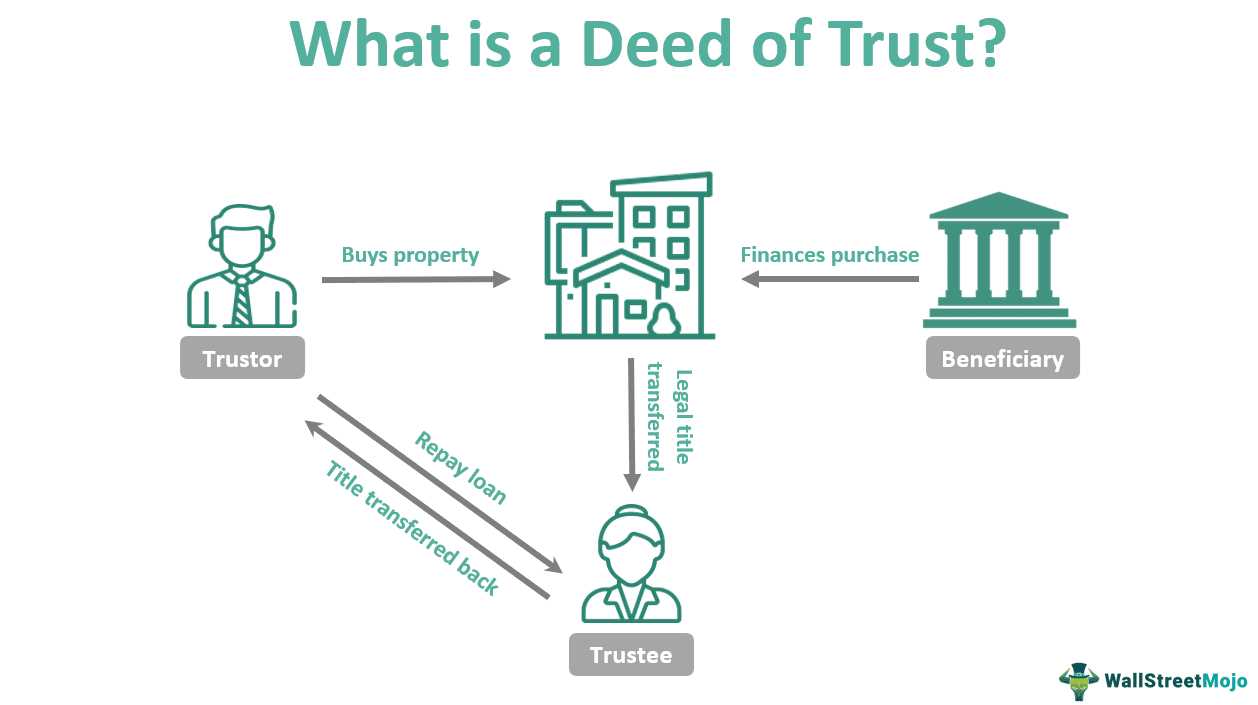
What is a Purchase-Money Mortgage? One of the key features of a purchase-money mortgage is that it is typically used when the buyer does not have enough cash on hand to purchase the property outright or when they are unable to secure traditional financing from a bank or mortgage lender. … …