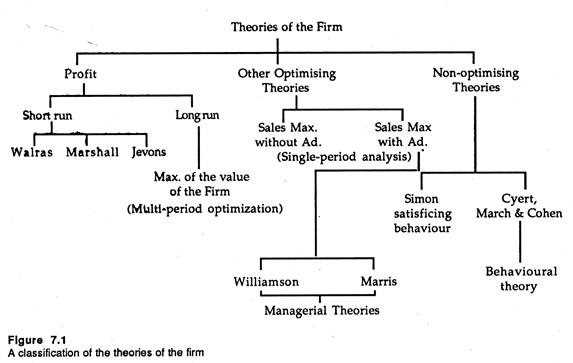
Understanding Productivity: A Comprehensive Guide to Measurement
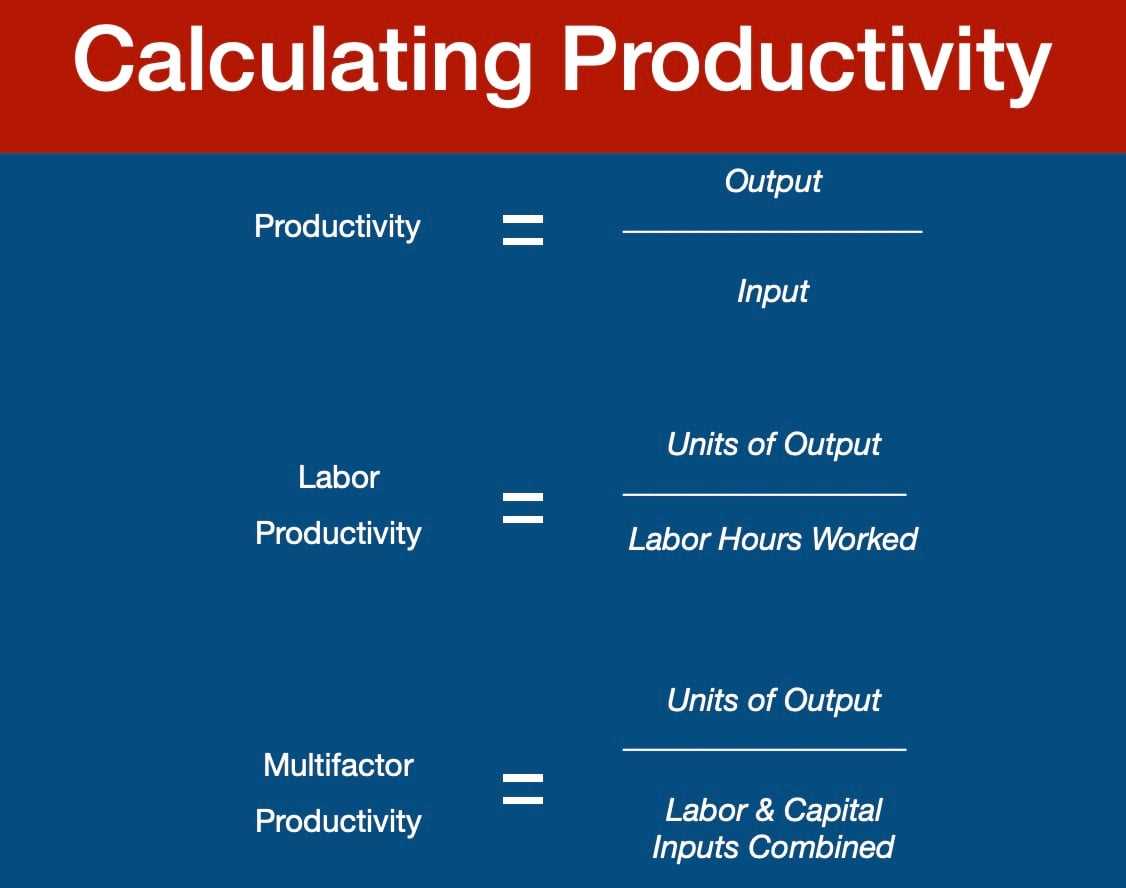
The Importance of Productivity Measurement 1. Assessing Performance: Productivity measurement allows businesses to assess their performance and compare it to industry benchmarks or competitors. It provides a quantitative measure of how efficiently resources are being utilized and how effectively outputs are being produced. This information helps businesses identify areas where … …