What Is a Sukuk Sharia-Compliant Bond-Like Financial Instruments
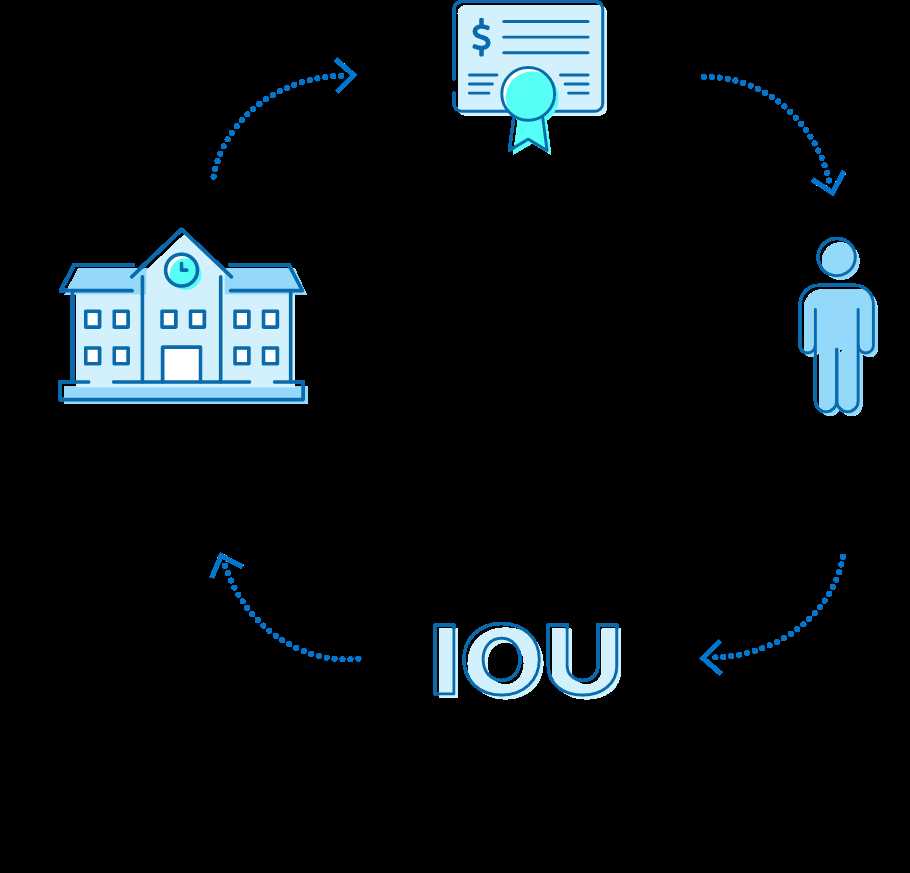
What are Sukuk? Sukuk are Islamic financial instruments that are similar to bonds. They are used to raise capital in a Sharia-compliant manner. Sukuk represent ownership in a tangible asset or a pool of assets, such as real estate, infrastructure projects, or commodities. Unlike traditional bonds, which represent debt, Sukuk … …