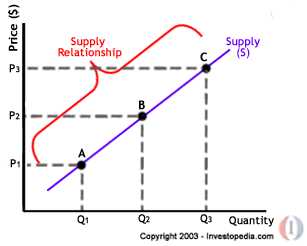
Weightless Economy: Understanding, Mechanics, And Examples
What is a Weightless Economy? A weightless economy refers to an economic system that is primarily based on intangible goods and services, rather than physical products. In a weightless economy, the value is derived from knowledge, information, and innovation, rather than from the production and distribution of tangible goods. This … …