Insurance: Definition and Importance
Insurance is a financial product that provides protection against potential financial losses. It is a contract between the insured and the insurance company, where the insured pays a premium in exchange for the promise of compensation in the event of a covered loss.
Definition of Insurance
Insurance can be defined as a risk management tool that helps individuals and businesses mitigate the financial impact of unexpected events. It provides a sense of security by transferring the risk of potential losses to the insurance company.
Insurance policies are designed to cover various types of risks, such as property damage, liability, health issues, and even loss of life. The terms and conditions of each policy may vary, depending on the type of coverage and the insurance company.
Importance of Insurance
Insurance plays a crucial role in protecting individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. Here are some key reasons why insurance is important:
1. Financial Protection:
Insurance provides financial protection against unexpected events, such as accidents, natural disasters, or illnesses. It helps individuals and businesses recover from financial losses and avoid bankruptcy.
2. Peace of Mind:
Having insurance coverage gives peace of mind, knowing that one is protected against potential risks. It allows individuals to focus on their daily lives and business operations without constantly worrying about the financial consequences of unforeseen events.
3. Risk Management:
Insurance helps individuals and businesses manage risks by transferring them to the insurance company. By paying a relatively small premium, policyholders can protect themselves from significant financial losses that could otherwise be devastating.
In many cases, insurance is a legal requirement. For example, auto insurance is mandatory in most countries to ensure that drivers can cover the costs of damages or injuries caused by accidents. Similarly, businesses may be required to have liability insurance to protect against potential lawsuits.
5. Social Stability:
Insurance contributes to social stability by providing a safety net for individuals and businesses. It helps prevent individuals from falling into poverty due to unexpected events and ensures that businesses can continue to operate even after significant losses.
What is Insurance and Why is it Important?
Insurance is a financial arrangement that provides protection against potential losses or damages. It involves transferring the risk of these losses or damages from an individual or organization to an insurance company. In exchange for regular premium payments, the insurance company agrees to compensate the policyholder in the event of a covered loss or damage.
Insurance is important because it helps individuals and businesses manage risk and protect themselves from financial hardship. By having insurance coverage, individuals and businesses can transfer the potential financial burden of unexpected events to an insurance company. This can provide peace of mind and financial security.
There are several reasons why insurance is important:
1. Protection against financial loss: Insurance provides financial protection in the event of a loss or damage. For example, if a person’s house is damaged by a fire, their homeowner’s insurance policy can help cover the cost of repairs or rebuilding.
2. Risk management: Insurance allows individuals and businesses to manage risk by transferring it to an insurance company. By paying a relatively small premium, policyholders can protect themselves against potentially large financial losses.
3. Legal requirements: In some cases, insurance is required by law. For example, auto insurance is mandatory in many countries to protect other drivers and pedestrians in the event of an accident.
4. Peace of mind: Knowing that you have insurance coverage can provide peace of mind. It can help alleviate worries about potential financial losses and allow individuals and businesses to focus on other aspects of their lives or operations.
5. Business continuity: For businesses, insurance can help ensure continuity in the event of a loss or damage. It can provide the necessary funds to repair or replace damaged assets, cover liability claims, and continue operations.
How Insurance Works
Insurance is a financial arrangement that provides protection against potential risks and uncertainties. It works by transferring the risk of loss from an individual or organization to an insurance company in exchange for regular premium payments.
When you purchase an insurance policy, you enter into a contract with the insurance company. The policy outlines the terms and conditions of coverage, including the types of risks that are covered, the amount of coverage provided, and the premium amount you need to pay.
In the event of a covered loss or event, you can file a claim with the insurance company. The claims process involves notifying the insurance company of the loss, providing any necessary documentation or evidence, and cooperating with the company’s investigation. Once the claim is approved, the insurance company will provide compensation or benefits as outlined in the policy.
Insurance works on the principle of risk pooling. The insurance company collects premiums from many policyholders, which creates a pool of funds to pay for potential claims. Not all policyholders will experience a loss at the same time, so the premiums collected from those who do not have a claim help to cover the costs of those who do.
Insurance also operates on the principle of risk assessment. Insurance companies use various factors, such as age, health, driving record, and location, to assess the risk of a policyholder experiencing a loss. Based on this assessment, they determine the premium amount that the policyholder needs to pay. Those who are considered to have a higher risk will typically have to pay a higher premium.
Insurance provides financial protection and peace of mind. It helps individuals and organizations mitigate the financial impact of unexpected events, such as accidents, illnesses, natural disasters, or property damage. By transferring the risk to an insurance company, policyholders can protect themselves from significant financial losses.
Overall, insurance works by pooling risks, assessing individual risks, and providing compensation or benefits in the event of a covered loss. It is an essential tool for managing uncertainties and protecting against potential financial hardships.
The Process of Obtaining Insurance Coverage
Obtaining insurance coverage is an important step in protecting yourself, your assets, and your loved ones from unexpected events. Whether it’s for your car, home, health, or life, insurance provides financial security and peace of mind.
The process of obtaining insurance coverage typically involves several steps:
1. Assessing Your Needs
2. Researching Insurance Providers
Once you’ve identified your insurance needs, the next step is to research insurance providers. Look for reputable companies with a strong financial standing and a good track record of customer service. Read reviews and compare quotes from multiple providers to find the best coverage options and rates.
After researching insurance providers, it’s time to choose the right policy. Consider factors such as coverage limits, deductibles, and premiums. Make sure the policy meets your specific needs and provides adequate protection. For example, if you’re getting health insurance, check if your preferred doctors and hospitals are in-network.
4. Applying for Coverage
Once you’ve selected a policy, you’ll need to fill out an application form. Provide accurate and complete information about yourself, your assets, and your health. Insurance companies use this information to assess the risk and determine the premium. Be honest and transparent to avoid any issues during the claims process.
5. Underwriting and Approval
After submitting your application, the insurance company will review it through a process called underwriting. During underwriting, the company evaluates the risk associated with insuring you and decides whether to approve or deny your application. They may request additional information or medical exams to assess your risk accurately.
6. Paying Premiums
If your application is approved, you’ll need to pay the premiums to activate your coverage. Premiums can be paid monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the policy and the insurance provider. Set up automatic payments or reminders to ensure you don’t miss any payments and maintain continuous coverage.
7. Policy Issuance
Once you’ve paid the premiums, the insurance company will issue your policy. The policy document outlines the terms, conditions, and coverage details. Read it carefully and keep a copy for your records. Familiarize yourself with the claims process and the steps to take in case of an incident.
Remember, insurance is a contract between you and the insurance company. It’s essential to understand the terms and conditions of your policy to ensure you’re adequately protected. Review your coverage periodically and make updates as needed to adapt to any changes in your life or assets.
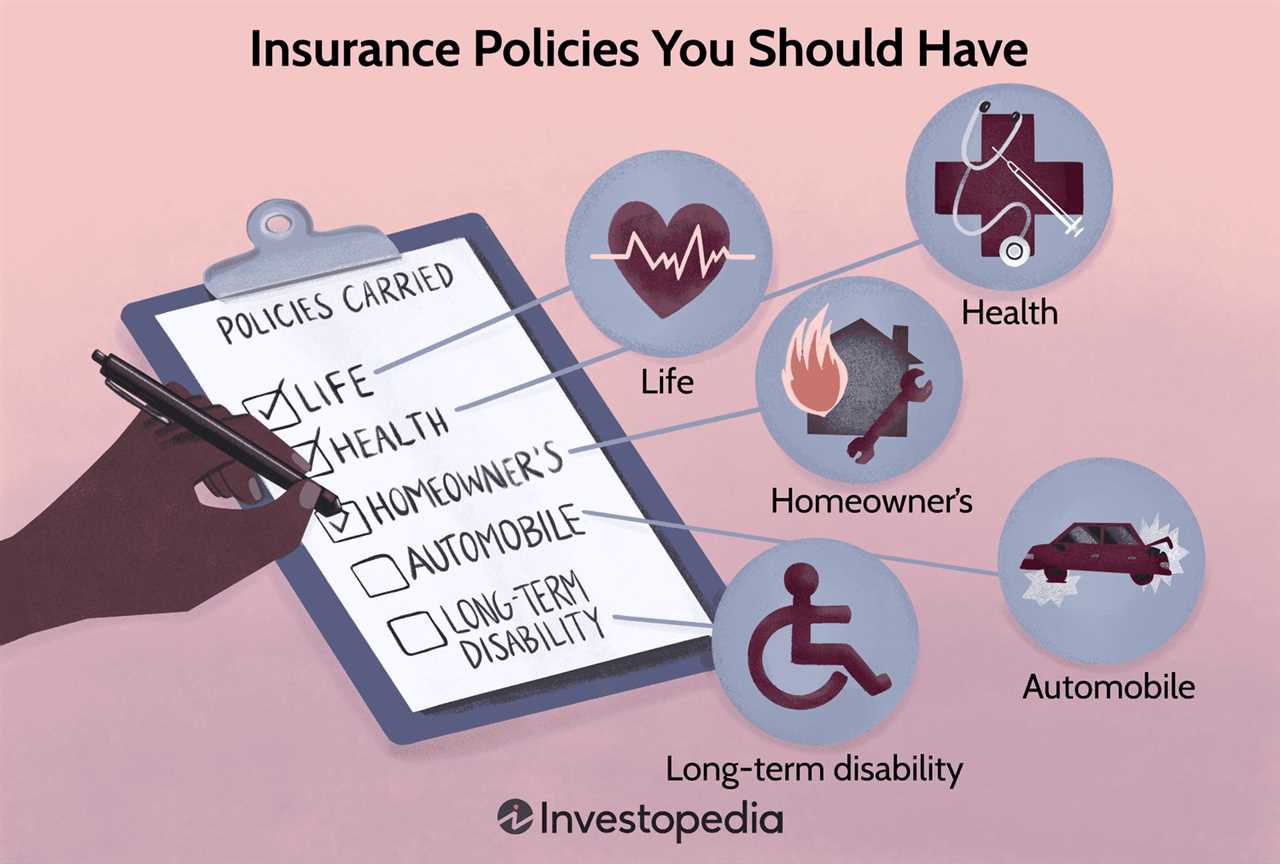
Main Types of Insurance Policies
Insurance policies are contracts between an insurance company and an individual or organization that provide financial protection against specific risks. There are several main types of insurance policies that individuals and businesses can purchase to protect themselves and their assets. These policies include:
1. Auto Insurance: Auto insurance provides coverage for damages and injuries caused by an accident involving a vehicle. It can also provide coverage for theft, vandalism, and other types of damage to the vehicle.
2. Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance protects homeowners against losses and damages to their property and belongings. It can provide coverage for damage caused by fire, theft, natural disasters, and other events.
3. Renters Insurance: Renters insurance is similar to homeowners insurance but is designed for individuals who rent their homes or apartments. It provides coverage for personal belongings and liability protection.
4. Health Insurance: Health insurance provides coverage for medical expenses and can help individuals pay for doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription medications, and other healthcare services.
5. Life Insurance: Life insurance provides financial protection for the policyholder’s loved ones in the event of their death. It can help cover funeral expenses, outstanding debts, and provide income replacement for dependents.
6. Disability Insurance: Disability insurance provides income replacement for individuals who are unable to work due to a disability. It can help cover living expenses and medical bills while the individual is unable to earn an income.
7. Business Insurance: Business insurance provides coverage for businesses against various risks, including property damage, liability claims, and interruption of business operations.
8. Liability Insurance: Liability insurance provides protection against claims of negligence or wrongdoing that result in bodily injury or property damage to others. It can help cover legal expenses and damages awarded in a lawsuit.
Life Insurance: Protecting Your Loved Ones
Life insurance is a crucial financial tool that provides protection and financial security to your loved ones in the event of your untimely death. It ensures that your family members or beneficiaries are financially supported and can maintain their standard of living even after you are gone.
There are various types of life insurance policies available, including term life insurance and whole life insurance. Term life insurance provides coverage for a specific period, usually 10, 20, or 30 years, while whole life insurance provides coverage for the entire lifetime of the insured individual.
When you purchase a life insurance policy, you pay regular premiums to the insurance company. In return, the insurance company promises to pay a death benefit to your beneficiaries upon your death. This death benefit can be used to cover funeral expenses, pay off debts, replace lost income, or provide financial support for your dependents.
Life insurance is especially important if you have dependents who rely on your income to meet their financial needs. It can help ensure that your children can continue their education, your spouse can pay off the mortgage, and your family can maintain their current lifestyle.
Additionally, life insurance can also be used as an estate planning tool. It can provide liquidity to your estate, allowing your beneficiaries to pay estate taxes or other expenses without having to sell assets, such as a family home or business.
Health Insurance: Ensuring Your Well-being
Health insurance is a crucial aspect of financial planning and personal well-being. It provides coverage for medical expenses, ensuring that individuals and families can access necessary healthcare services without facing significant financial burdens.
Importance of Health Insurance
Health insurance plays a vital role in safeguarding individuals and families from the high costs of medical treatments and hospitalizations. Without insurance, even minor illnesses or injuries can lead to substantial medical bills, causing financial strain and potentially leading to debt.
Having health insurance ensures that individuals can receive timely and appropriate medical care, including preventive services, routine check-ups, and necessary treatments. It promotes early detection and intervention, which can significantly improve health outcomes and reduce the risk of developing serious health conditions.
How Health Insurance Works
Health insurance operates on the principle of risk-sharing. Policyholders pay regular premiums to the insurance company, and in return, the insurance company covers a portion of their medical expenses. The specific coverage and benefits vary depending on the policy and the insurance provider.
When individuals require medical services, they present their health insurance card to the healthcare provider. The provider then submits a claim to the insurance company, detailing the services provided and the associated costs. The insurance company reviews the claim and pays the provider directly for the covered services, while the policyholder may be responsible for any deductibles, co-pays, or out-of-pocket expenses.
Types of Health Insurance Policies
There are several types of health insurance policies available, including:
- Employer-sponsored health insurance: Many employers offer health insurance coverage as part of their employee benefits package.
- Individual health insurance: Individuals can purchase health insurance plans directly from insurance companies or through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
- Medicaid: A government program that provides health insurance for low-income individuals and families.
- Medicare: A federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities.
It is essential to carefully review and compare different health insurance policies to determine the coverage, premiums, deductibles, and other factors that best meet individual or family needs.
Overall, health insurance is a vital component of financial security and well-being. It provides individuals and families with access to necessary healthcare services, protects against high medical costs, and promotes overall health and wellness.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
