Debt Issue: Definition, Process, And Costs
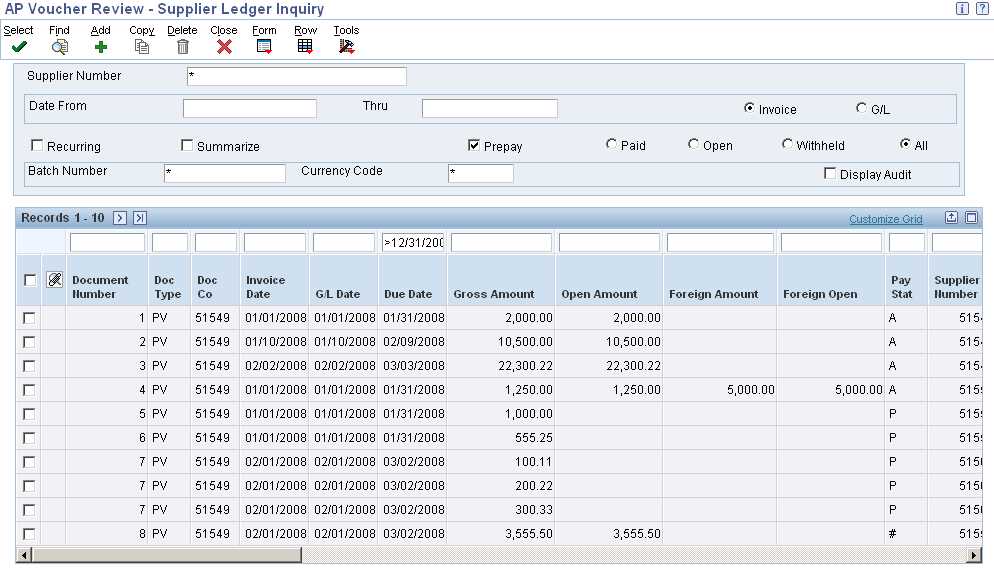
Definition of Debt Issue A debt issue refers to the process of raising funds by a company through the issuance of debt securities to investors. Debt securities can take various forms, such as bonds, notes, or debentures, and they represent a contractual obligation for the company to repay the borrowed … …