Austerity: Types Of Measures And Real-Life Examples
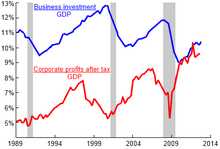
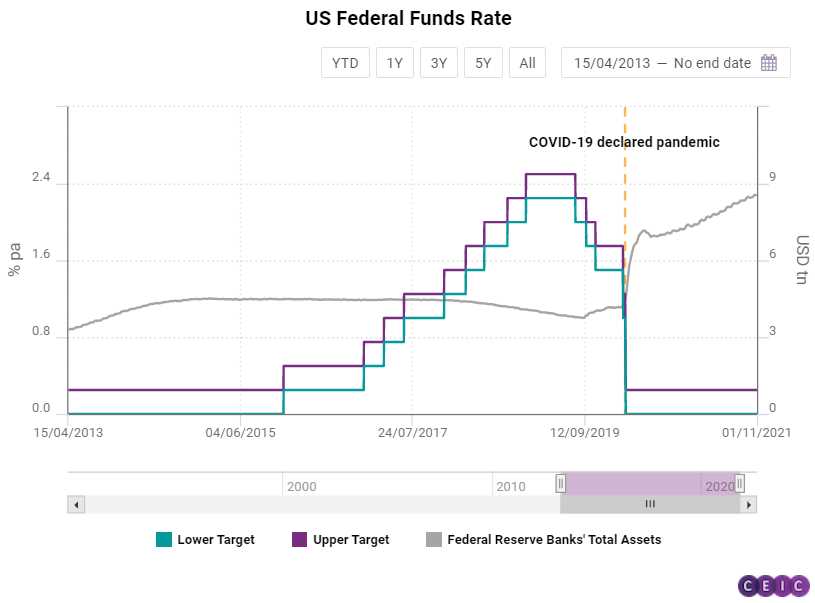
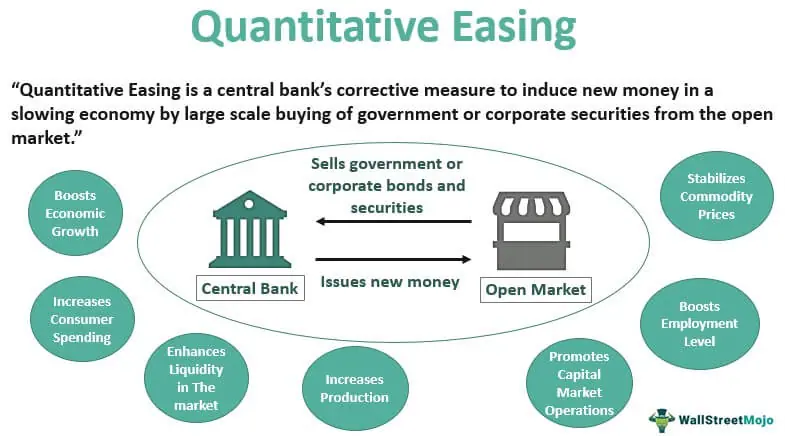
Fiscal Austerity Measures Fiscal austerity measures refer to the actions taken by governments to reduce their budget deficits and control public spending. These measures are typically implemented during times of economic crisis or when a country’s debt levels become unsustainable. The goal of fiscal austerity is to restore fiscal discipline … …