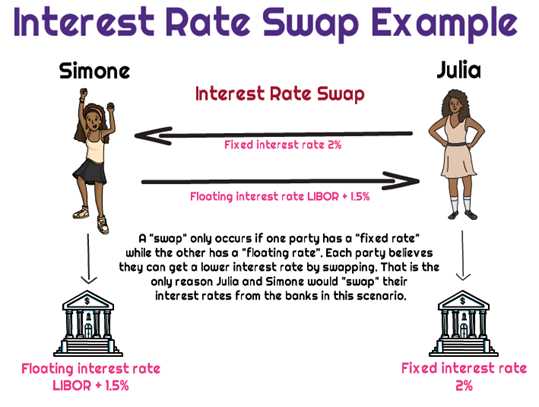
Interest Rate Swap Definition Types and Real-World Example
Interest Rate Swap: Definition, Types, and Real-World Example An interest rate swap is a financial derivative instrument that allows two parties to exchange interest rate payments on a specified notional amount over a set period of time. It is a popular tool used by businesses and investors to manage their … …