What is an Income Statement?
The income statement is important because it shows how much money a company has made or lost during a particular period. It provides valuable information about the company’s financial performance and helps investors, creditors, and other stakeholders assess its profitability and financial health.
Components of an Income Statement
An income statement typically consists of the following components:
- Revenue: This represents the total amount of money generated from the sale of goods or services. It includes sales revenue, interest income, and any other income earned by the company.
- Expenses: These are the costs incurred by the company in order to generate revenue. They can include the cost of goods sold, operating expenses (such as salaries, rent, and utilities), interest expenses, and taxes.
- Gross Profit: This is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the revenue. It represents the profit generated from the company’s core operations before deducting operating expenses.
- Operating Income: This is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the company’s core operations after deducting all operating expenses.
- Net Income: This is the final result after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest, from the revenue. It represents the company’s overall profitability.
Interpreting the Income Statement
Interpreting the income statement involves analyzing the various components and ratios to assess the company’s financial performance. Key metrics that can be derived from the income statement include gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin.
The gross profit margin indicates the percentage of revenue that is left after deducting the cost of goods sold. It measures the company’s ability to generate profit from its core operations.
The operating profit margin measures the company’s ability to generate profit from its core operations after deducting all operating expenses. It indicates the company’s efficiency in managing its costs.
The net profit margin represents the company’s overall profitability after deducting all expenses, including taxes and interest. It shows how much profit the company is able to generate from its revenue.
Importance of the Income Statement
The income statement is important for several reasons:
- It helps investors and creditors assess the company’s profitability and financial health.
- It provides insights into the company’s revenue sources and expense categories.
- It allows for comparison of financial performance over different periods.
- It helps in making informed business decisions and setting financial goals.
Utilizing the Income Statement for Financial Analysis
The income statement can be used for financial analysis in several ways:
- Comparing the income statement of different periods to identify trends and patterns in revenue and expenses.
- Comparing the income statement of different companies in the same industry to assess their relative profitability.
- Calculating financial ratios, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, to assess the company’s financial performance.
- Using the income statement as a basis for forecasting future revenue and expenses.
By utilizing the income statement for financial analysis, investors, creditors, and other stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions.
Components of an Income Statement
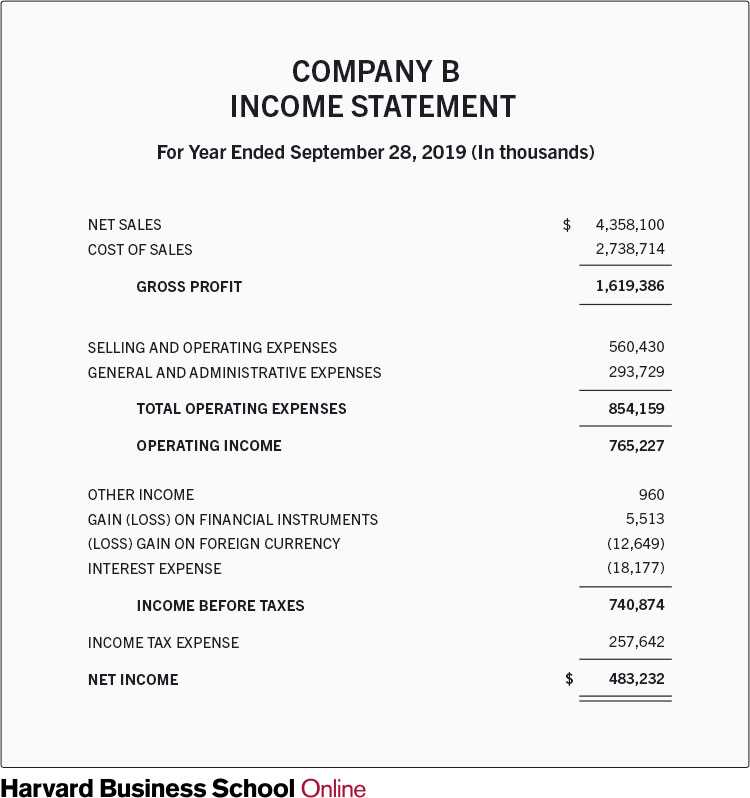
The income statement consists of several components that provide a comprehensive view of a company’s financial results. These components include:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Revenue | This component represents the total amount of money generated from the sale of goods or services. It includes sales revenue, interest income, and any other income earned by the company. |
| Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | This component represents the direct costs associated with producing or delivering the goods or services sold by the company. It includes the cost of raw materials, labor, and overhead expenses. |
| Gross Profit | This component is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the revenue. It represents the profit made by the company before deducting operating expenses. |
| Operating Expenses | This component includes all the expenses incurred by the company in its day-to-day operations. It includes salaries, rent, utilities, marketing expenses, and other administrative expenses. |
| Operating Income | This component is calculated by subtracting the operating expenses from the gross profit. It represents the profit made by the company from its core operations. |
| Non-Operating Income and Expenses | This component includes income and expenses that are not directly related to the company’s core operations. It includes interest income, interest expense, gains or losses from investments, and other non-operating items. |
| Net Income | This component is calculated by subtracting the non-operating income and expenses from the operating income. It represents the final profit or loss made by the company after considering all revenues and expenses. |
By analyzing the components of an income statement, investors and analysts can gain insights into a company’s revenue sources, cost structure, profitability, and overall financial health. This information is crucial for making investment decisions, assessing the company’s ability to generate profits, and evaluating its financial performance compared to competitors.
Interpreting the Income Statement
1. Revenue
The top line of the income statement represents the company’s revenue or sales. It includes all the money generated from the sale of goods or services. Analyzing the revenue section can help identify trends, growth rates, and the company’s ability to generate income.
2. Expenses
The expenses section of the income statement includes all the costs incurred to generate revenue. This includes costs of goods sold, operating expenses, interest expenses, and taxes. Analyzing the expenses section can help identify areas where the company is spending too much or where cost-saving measures can be implemented.
3. Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the revenue. It represents the profit generated from the core operations of the business. Analyzing the gross profit can help assess the company’s profitability and efficiency in producing goods or services.
4. Operating Income
Operating income is calculated by subtracting operating expenses from the gross profit. It represents the profit generated from the company’s core operations before considering interest and taxes. Analyzing the operating income can help evaluate the company’s ability to generate profit from its core business activities.
5. Net Income
When interpreting the income statement, it is important to compare the figures to previous periods, industry benchmarks, and competitors. This can provide insights into the company’s performance relative to others in the market and help identify areas for improvement.
Importance of the Income Statement
One of the primary reasons why the income statement is important is that it helps investors, analysts, and stakeholders understand a company’s financial performance. By examining the revenues and expenses, they can evaluate how well the company is generating profits and managing its costs. This information is crucial for making informed investment decisions and assessing the company’s overall financial health.
Evaluating Profitability
The income statement allows businesses to assess their profitability. By comparing the revenues and expenses, companies can determine their net income or loss. This information is essential for gauging the company’s ability to generate profits and sustain its operations. It also helps in identifying areas where cost reductions or revenue enhancements may be necessary to improve profitability.
Assessing Efficiency and Effectiveness
The income statement provides insights into a company’s efficiency and effectiveness in managing its resources. By analyzing the expenses, companies can identify areas where costs are high or increasing rapidly. This information can help in optimizing operations, reducing unnecessary expenses, and improving overall efficiency.
Comparing Performance
The income statement allows for the comparison of a company’s financial performance over different periods. By analyzing the revenues, expenses, and net income or loss, companies can identify trends and patterns in their financial performance. This information is crucial for assessing whether the company is improving or declining over time.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
| Benefits of the Income Statement |
|---|
| Provides insights into financial performance |
| Evaluates profitability |
| Assesses efficiency and effectiveness |
| Allows for performance comparison |
| Meets regulatory requirements |
Utilizing the Income Statement for Financial Analysis
The income statement is a crucial financial statement that provides valuable information about a company’s financial performance over a specific period of time. It presents the revenues, expenses, and net income or loss of a company, allowing analysts and investors to assess its profitability and financial health.
Financial analysis involves the interpretation and evaluation of financial statements to make informed decisions and predictions about a company’s future prospects. The income statement is a primary tool used in financial analysis, as it provides key insights into a company’s revenue sources, cost structure, and overall profitability.
One way to utilize the income statement for financial analysis is by calculating various financial ratios. These ratios help assess a company’s financial health, efficiency, and profitability. Some commonly used ratios include:
- Gross profit margin: This ratio measures the profitability of a company’s core operations by comparing gross profit to revenue. A higher gross profit margin indicates better efficiency in managing costs.
- Net profit margin: This ratio measures the overall profitability of a company by comparing net income to revenue. It indicates how effectively a company generates profit from its operations.
- Return on assets (ROA): This ratio measures the profitability of a company’s assets by comparing net income to total assets. It shows how efficiently a company utilizes its assets to generate profit.
- Return on equity (ROE): This ratio measures the profitability of a company’s shareholders’ equity by comparing net income to shareholders’ equity. It indicates how effectively a company generates profit for its shareholders.
In addition to calculating financial ratios, analysts can also use the income statement to compare a company’s performance over different periods or against industry benchmarks. This helps identify trends, strengths, and weaknesses, and provides insights into a company’s competitive position.
Furthermore, the income statement can be used to assess the impact of various business decisions on a company’s financial performance. For example, analysts can evaluate the profitability of new product launches, cost-cutting initiatives, or changes in pricing strategies by analyzing the corresponding changes in revenue and expenses.
Overall, the income statement is a powerful tool for financial analysis, providing valuable information about a company’s profitability and financial performance. By utilizing this statement effectively, analysts and investors can make informed decisions, assess risks, and evaluate the potential for future growth and success.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
