Financial Analysis: Definition, Importance, Types, and Examples

One of the key objectives of financial analysis is to assess the company’s ability to generate profits and cash flows, as well as its ability to meet its financial obligations. By analyzing financial statements, investors, creditors, and other stakeholders can make informed decisions about whether to invest in or lend to the company.
There are several types of financial analysis that can be performed, depending on the specific needs and objectives. These include:
1. Ratio Analysis: This involves calculating and interpreting various financial ratios, such as profitability ratios (e.g., gross profit margin, net profit margin), liquidity ratios (e.g., current ratio, quick ratio), and solvency ratios (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio, interest coverage ratio). Ratio analysis helps in assessing the company’s financial performance and comparing it with industry benchmarks.
3. Comparative Analysis: This involves comparing the financial performance of the company with its competitors or industry peers. It helps in benchmarking the company’s performance and identifying areas of strength and weakness.
4. Cash Flow Analysis: This involves analyzing the company’s cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities. It helps in assessing the company’s ability to generate cash and meet its short-term and long-term cash needs.
Financial analysis is crucial for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, management, and regulators. It provides valuable insights into the company’s financial health and performance, which can be used for decision-making and strategic planning.
For example, investors can use financial analysis to evaluate the company’s growth potential and profitability before making investment decisions. Creditors can use it to assess the company’s ability to repay loans and interest. Management can use it to identify areas for improvement and make informed business decisions. Regulators can use it to monitor the financial stability and compliance of the company.
What is Financial Analysis?
Financial analysis is the process of evaluating a company’s financial performance and position by analyzing its financial statements. It involves assessing the company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency to make informed decisions about its financial health and future prospects.
Importance of Financial Analysis
Financial analysis is crucial for various stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and managers, as it provides valuable insights into a company’s financial condition. Here are some key reasons why financial analysis is important:
1. Assessing Performance: Financial analysis helps assess a company’s past and current performance by analyzing its financial statements. It allows stakeholders to evaluate the company’s profitability, growth, and efficiency over time.
2. Identifying Trends: By analyzing financial data, trends and patterns can be identified, which can help stakeholders understand the company’s financial performance and make predictions about its future prospects.
3. Making Investment Decisions: Investors use financial analysis to evaluate the potential returns and risks associated with investing in a particular company. It helps them make informed investment decisions based on the company’s financial health and growth potential.
4. Assessing Financial Health: Financial analysis helps assess a company’s financial health by examining its liquidity and solvency. It provides insights into the company’s ability to meet short-term obligations and its long-term financial stability.
5. Comparing Competitors: Financial analysis allows for the comparison of a company’s financial performance with its competitors. This helps stakeholders understand the company’s relative position in the industry and identify areas for improvement.
Types of Financial Analysis
There are different types of financial analysis that focus on various aspects of a company’s financial performance:
1. Ratio Analysis: Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios to assess a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and efficiency. It helps identify strengths and weaknesses in a company’s financial position.
2. Trend Analysis: Trend analysis involves comparing financial data over multiple periods to identify trends and patterns. It helps stakeholders understand the company’s financial performance over time and make predictions about its future performance.
3. Comparative Analysis: Comparative analysis involves comparing a company’s financial performance with that of its competitors or industry benchmarks. It helps identify areas where the company is outperforming or underperforming relative to its peers.
Examples of Financial Analysis
Here are some examples of financial analysis:
1. Profitability Analysis: Calculating and analyzing profitability ratios, such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, and return on investment, to assess a company’s profitability.
2. Liquidity Analysis: Evaluating a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations by analyzing liquidity ratios, such as current ratio and quick ratio.
3. Solvency Analysis: Assessing a company’s long-term financial stability and ability to meet its long-term obligations by analyzing solvency ratios, such as debt-to-equity ratio and interest coverage ratio.
4. Efficiency Analysis: Analyzing a company’s efficiency in utilizing its assets and resources by calculating efficiency ratios, such as asset turnover ratio and inventory turnover ratio.
The Importance of Financial Analysis
Financial analysis plays a crucial role in the success of any business. It involves the examination and interpretation of financial statements to gain insights into the financial health and performance of a company. By analyzing financial data, businesses can make informed decisions, identify areas of improvement, and assess their overall financial stability.
1. Assessing Financial Performance
Financial analysis allows businesses to evaluate their financial performance over a specific period. By comparing financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, companies can assess their profitability, liquidity, and solvency. This information helps them identify areas where they are excelling and areas that need improvement.
2. Identifying Trends and Patterns
Financial analysis helps businesses identify trends and patterns in their financial data. By analyzing historical financial statements, companies can identify recurring patterns and trends in their revenue, expenses, and cash flow. This information can be used to forecast future financial performance and make strategic decisions.
3. Making Informed Decisions
Financial analysis provides businesses with the necessary information to make informed decisions. By analyzing financial data, companies can evaluate the potential risks and rewards of various business opportunities. This analysis helps them determine whether to invest in new projects, expand their operations, or make changes to their existing strategies.
4. Assessing Financial Stability
Financial analysis helps businesses assess their financial stability and sustainability. By examining financial ratios such as liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and solvency ratios, companies can determine their ability to meet short-term and long-term financial obligations. This analysis is essential for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders who need to assess the financial health of a company before making investment or lending decisions.
5. Benchmarking and Comparison
Financial analysis allows businesses to benchmark their performance against industry standards and competitors. By comparing their financial ratios and performance indicators with those of similar companies, businesses can identify areas where they are lagging and take necessary measures to improve their performance.
Types of Financial Analysis
Financial analysis is a crucial tool for evaluating the financial health and performance of a company. There are different types of financial analysis that provide valuable insights into various aspects of a company’s operations and financial position. These types of analysis include:
1. Ratio Analysis: Ratio analysis involves the calculation and interpretation of various financial ratios to assess a company’s liquidity, profitability, efficiency, and solvency. Common ratios used in ratio analysis include the current ratio, return on equity, and debt-to-equity ratio.
3. Comparative Analysis: Comparative analysis involves comparing a company’s financial performance with that of its competitors or industry benchmarks. This analysis helps in evaluating a company’s relative performance and identifying areas of strength or weakness.
4. Cash Flow Analysis: Cash flow analysis focuses on the movement of cash in and out of a company. It helps in assessing a company’s ability to generate cash, meet its financial obligations, and invest in future growth.
5. Risk Analysis: Risk analysis involves evaluating the potential risks and uncertainties that may impact a company’s financial performance. This analysis helps in identifying and managing risks related to market conditions, regulatory changes, and other external factors.
6. Valuation Analysis: Valuation analysis is used to determine the intrinsic value of a company’s stock or business. It involves analyzing various factors such as earnings, cash flows, and market conditions to estimate the fair value of a company.
Each type of financial analysis provides unique insights into different aspects of a company’s financial performance. By utilizing a combination of these analyses, investors, analysts, and managers can make informed decisions and assess the overall financial health of a company.
Examples of Financial Analysis
Financial analysis is a crucial tool for businesses and investors to assess the financial health and performance of a company. By analyzing financial statements and other relevant data, financial analysts can gain insights into a company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. Here are some examples of financial analysis techniques commonly used:
1. Ratio Analysis
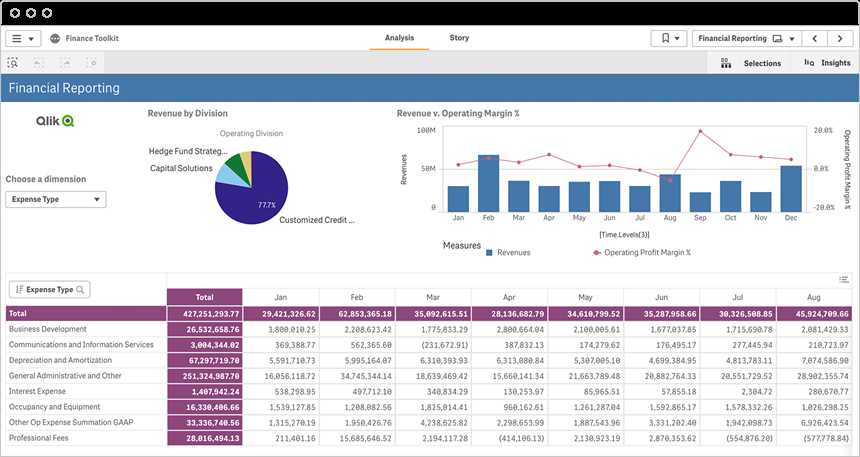
Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting various financial ratios to evaluate a company’s financial performance. These ratios can provide insights into a company’s profitability, efficiency, liquidity, and leverage. Some commonly used ratios include:
- Profitability ratios: such as gross profit margin, net profit margin, return on assets, and return on equity.
- Liquidity ratios: such as current ratio, quick ratio, and cash ratio.
- Solvency ratios: such as debt-to-equity ratio, debt ratio, and interest coverage ratio.
- Efficiency ratios: such as inventory turnover ratio, accounts receivable turnover ratio, and asset turnover ratio.
2. Trend Analysis
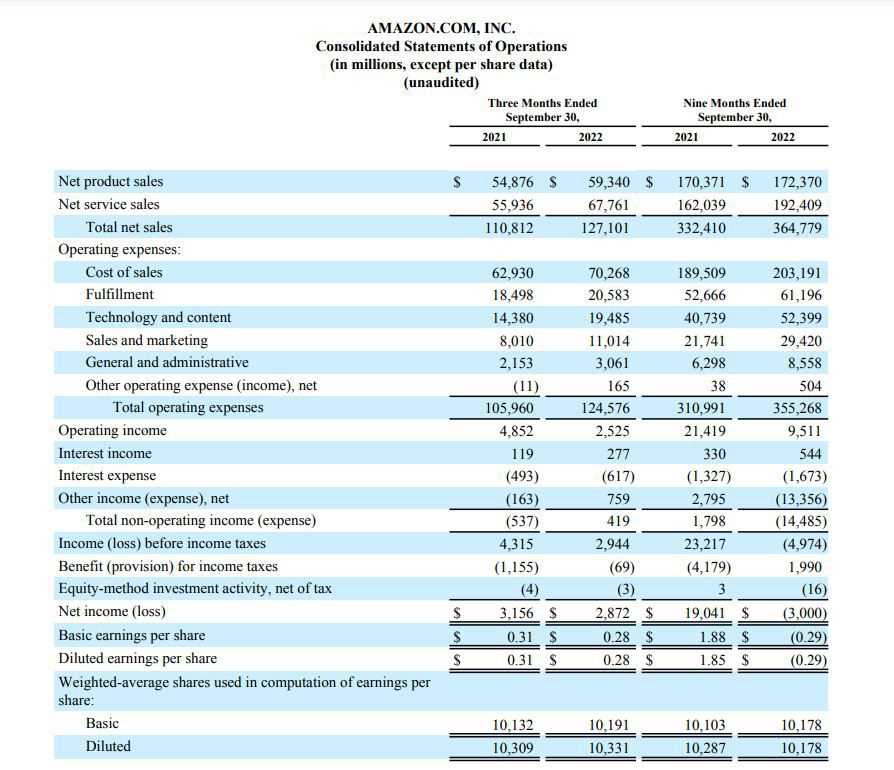
Trend analysis involves comparing financial data over a period of time to identify patterns and trends. By analyzing trends in key financial metrics, such as revenue, expenses, and profitability, analysts can assess a company’s financial performance and make predictions about its future prospects. Trend analysis can help identify growth opportunities, potential risks, and areas for improvement.
3. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis involves comparing a company’s financial performance to that of its competitors or industry benchmarks. By benchmarking against industry peers, analysts can assess a company’s relative performance and identify areas where it may be underperforming or outperforming. Comparative analysis can provide valuable insights into a company’s competitive position and help identify opportunities for improvement.
4. Cash Flow Analysis
Cash flow analysis involves examining a company’s cash inflows and outflows to assess its ability to generate and manage cash. By analyzing the cash flow statement, analysts can evaluate a company’s liquidity, cash flow generation, and cash flow sustainability. Cash flow analysis is particularly important for assessing a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations and fund its operations.
5. Break-Even Analysis
Break-even analysis involves calculating the point at which a company’s total revenue equals its total costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss. By conducting break-even analysis, analysts can determine the minimum level of sales or production volume required for a company to cover its costs. This analysis can help assess a company’s profitability and risk, as well as inform pricing and cost management decisions.
Financial Statements and Financial Analysis
Financial statements are important documents that provide a snapshot of a company’s financial performance. They include the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. These statements are prepared by companies to provide information to investors, creditors, and other stakeholders about the financial health and performance of the business.
The balance sheet shows the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time. It provides an overview of the company’s financial position and helps investors assess its solvency and liquidity.
The cash flow statement shows the company’s cash inflows and outflows from operating, investing, and financing activities. It provides information about the company’s ability to generate cash and its cash management practices.
Financial Analysis
Financial analysis involves the examination of a company’s financial statements to assess its financial performance and make informed decisions. It helps investors, creditors, and other stakeholders evaluate the company’s profitability, liquidity, solvency, and overall financial health.
There are several methods of financial analysis, including ratio analysis, trend analysis, and comparative analysis. Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting financial ratios, such as liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, and leverage ratios, to assess the company’s financial position and performance.
Trend analysis involves analyzing the company’s financial data over multiple periods to identify patterns and trends. It helps investors understand the company’s historical performance and predict its future financial performance.
Comparative analysis involves comparing the company’s financial performance to that of its competitors or industry benchmarks. It helps investors assess the company’s competitive position and identify areas for improvement.
Conclusion
Financial statements are essential tools for financial analysis. They provide valuable information about a company’s financial performance and help investors, creditors, and other stakeholders make informed decisions. By analyzing financial statements using various methods, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health and make sound investment decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
