What is a Hedge?
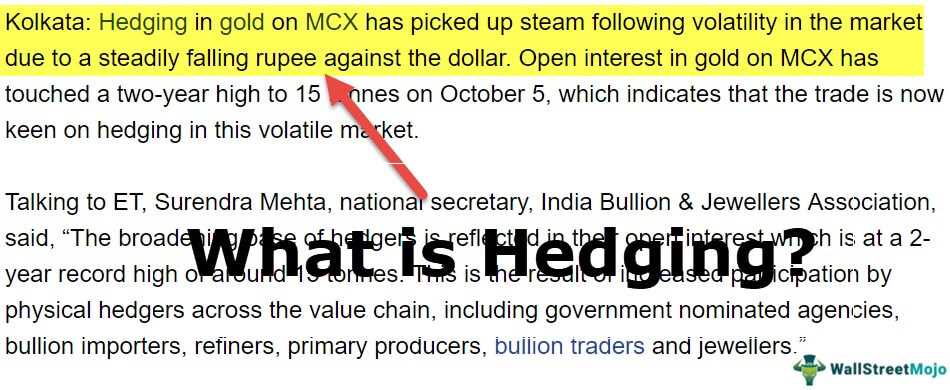
A hedge is an investment strategy that is used to reduce or offset the risk of adverse price movements in an asset. It involves taking an offsetting position in a related security or derivative, such as options or futures contracts, to protect against potential losses.
Hedging is commonly used by investors and businesses to manage their risk exposure. By hedging, they can protect themselves from potential losses and volatility in the market. It allows them to maintain a more stable financial position and minimize the impact of adverse price movements.
There are various types of hedges that can be used, depending on the specific circumstances and objectives of the investor or business. Some common types of hedges include:
– Equity hedges: These involve taking positions in stocks or stock options to offset potential losses in a portfolio.
– Currency hedges: These involve taking positions in foreign currencies or currency derivatives to protect against fluctuations in exchange rates.
– Commodity hedges: These involve taking positions in commodities or commodity derivatives to hedge against price volatility.
– Interest rate hedges: These involve taking positions in interest rate derivatives to protect against changes in interest rates.
Advanced Strategies and Instruments for Hedging
1. Options
Options are one of the most commonly used instruments for hedging. They give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specific time frame. By purchasing put options, investors can protect against a decline in the price of an asset, while buying call options can provide protection against a rise in price.
2. Futures Contracts

Futures contracts are another popular instrument for hedging. These contracts allow investors to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price on a future date. By entering into a futures contract, investors can lock in a price for an asset, protecting themselves against price fluctuations.
3. Swaps

Swaps are financial agreements between two parties to exchange cash flows based on predetermined conditions. They can be used to hedge against interest rate risk, currency risk, or commodity price risk. For example, a company that has borrowed money at a variable interest rate may enter into an interest rate swap to convert that variable rate into a fixed rate, protecting themselves against potential interest rate increases.
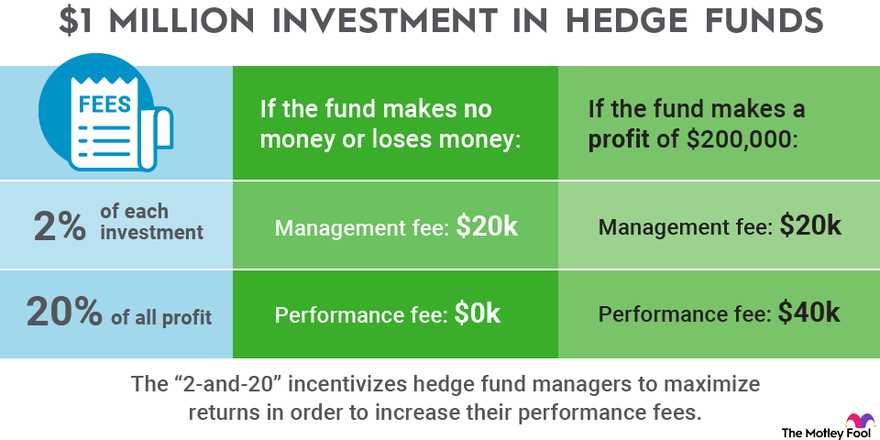
Overall, these advanced strategies and instruments provide investors with a range of options for hedging their investments. By utilizing these tools effectively, investors can mitigate risk and protect their portfolios from potential losses in the market.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
