Tax Benefit Definition Types and IRS Rules
Definition of Tax Benefits
Tax benefits are provisions in the tax code that allow individuals and businesses to reduce their taxable income or tax liability. These benefits are designed to incentivize certain behaviors or activities that are considered beneficial to the economy or society as a whole.
There are several types of tax benefits available, including deductions, credits, exemptions, and exclusions. Each type has its own set of rules and requirements that must be met in order to qualify for the benefit.
Types of Tax Benefits
1. Deductions: Deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of income that is subject to tax. Common deductions include mortgage interest, medical expenses, and business expenses.
2. Credits: Tax credits are dollar-for-dollar reductions in your tax liability. Unlike deductions, which reduce your taxable income, credits directly reduce the amount of tax you owe. Examples of tax credits include the Child Tax Credit, the Earned Income Tax Credit, and the American Opportunity Credit.
3. Exemptions: Exemptions are a specific amount of income that is not subject to tax. In the past, individuals could claim personal exemptions for themselves and their dependents. However, with recent changes to the tax code, personal exemptions have been eliminated for tax years 2018 through 2025.
4. Exclusions: Exclusions are types of income that are not included in your taxable income. Common examples of exclusions include gifts and inheritances, certain types of insurance proceeds, and income from qualified retirement accounts.
IRS Rules on Tax Benefits
The IRS has specific rules and guidelines that determine whether an individual or business is eligible for a particular tax benefit. These rules can vary depending on the type of benefit and the taxpayer’s specific circumstances.
It is important to carefully review the IRS guidelines and consult with a tax professional to ensure that you are eligible for any tax benefits you plan to claim. Failing to comply with the IRS rules can result in penalties, fines, or even an audit.
Maximizing Tax Benefits

In order to maximize your tax benefits, it is important to stay informed about changes to the tax code and take advantage of any new provisions or incentives that may be available. Keeping detailed records of your income, expenses, and deductions can also help ensure that you are claiming all eligible tax benefits.
Additionally, working with a qualified tax professional can help you navigate the complexities of the tax code and identify opportunities for tax savings. They can help you determine which tax benefits you qualify for and develop a tax strategy that minimizes your tax liability.
Types of Tax Benefits
There are several types of tax benefits that individuals and businesses can take advantage of. Some common types include:
- Deductions: Deductions allow taxpayers to subtract certain expenses from their taxable income. This can include expenses such as mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions.
- Credits: Credits are a dollar-for-dollar reduction of the tax liability. They can be refundable or non-refundable. Refundable credits can result in a tax refund if the credit exceeds the tax liability, while non-refundable credits can only reduce the tax liability to zero.
- Exemptions: Exemptions are a specific amount of income that is not subject to tax. For example, individuals may be able to claim exemptions for themselves, their spouse, and their dependents.
- Deferrals: Deferrals allow taxpayers to postpone the payment of taxes on certain income or gains. This can be beneficial for individuals and businesses who expect their tax rate to be lower in the future.
IRS Rules on Tax Benefits
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is responsible for administering and enforcing the tax laws in the United States. They have established rules and regulations regarding tax benefits to ensure compliance and prevent abuse. It is important for taxpayers to understand these rules in order to properly claim and maximize their tax benefits.
Some common IRS rules on tax benefits include:
- Documentation: Taxpayers must keep accurate records and documentation to support their claims for tax benefits. This can include receipts, invoices, and other relevant documents.
- Timeliness: Taxpayers must file their tax returns and claim their tax benefits within the specified deadlines. Failing to do so can result in penalties and interest.
- Eligibility: Taxpayers must meet certain eligibility requirements to qualify for specific tax benefits. These requirements can vary depending on the type of benefit and the taxpayer’s individual circumstances.
Types of Tax Benefits
There are several types of tax benefits that individuals and businesses can take advantage of. These benefits can help reduce the amount of tax owed or provide incentives for certain actions. Here are some common types of tax benefits:
- Tax deductions: Deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from your taxable income, reducing the amount of tax you owe. Common deductions include mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions.
- Tax credits: Credits are direct reductions of the tax you owe. They are typically more valuable than deductions because they directly reduce your tax liability. Examples of tax credits include the child tax credit, earned income tax credit, and education credits.
- Tax exemptions: Exemptions are a set amount of income that is not subject to tax. For example, individuals can claim a personal exemption for themselves and each dependent they have. Some organizations, such as churches and nonprofit organizations, may also be exempt from certain taxes.
- Tax deferrals: Deferrals allow taxpayers to postpone paying taxes on certain income or gains until a later date. This can help individuals and businesses manage their cash flow and potentially reduce their overall tax liability.
- Tax-free investments: Certain investments, such as municipal bonds, may provide tax-free income. This means that the income generated from these investments is not subject to federal income tax.
- Tax incentives: Tax incentives are designed to encourage certain behaviors or investments. For example, the government may offer tax incentives for investing in renewable energy or starting a small business in an economically disadvantaged area.
IRS Rules on Tax Benefits
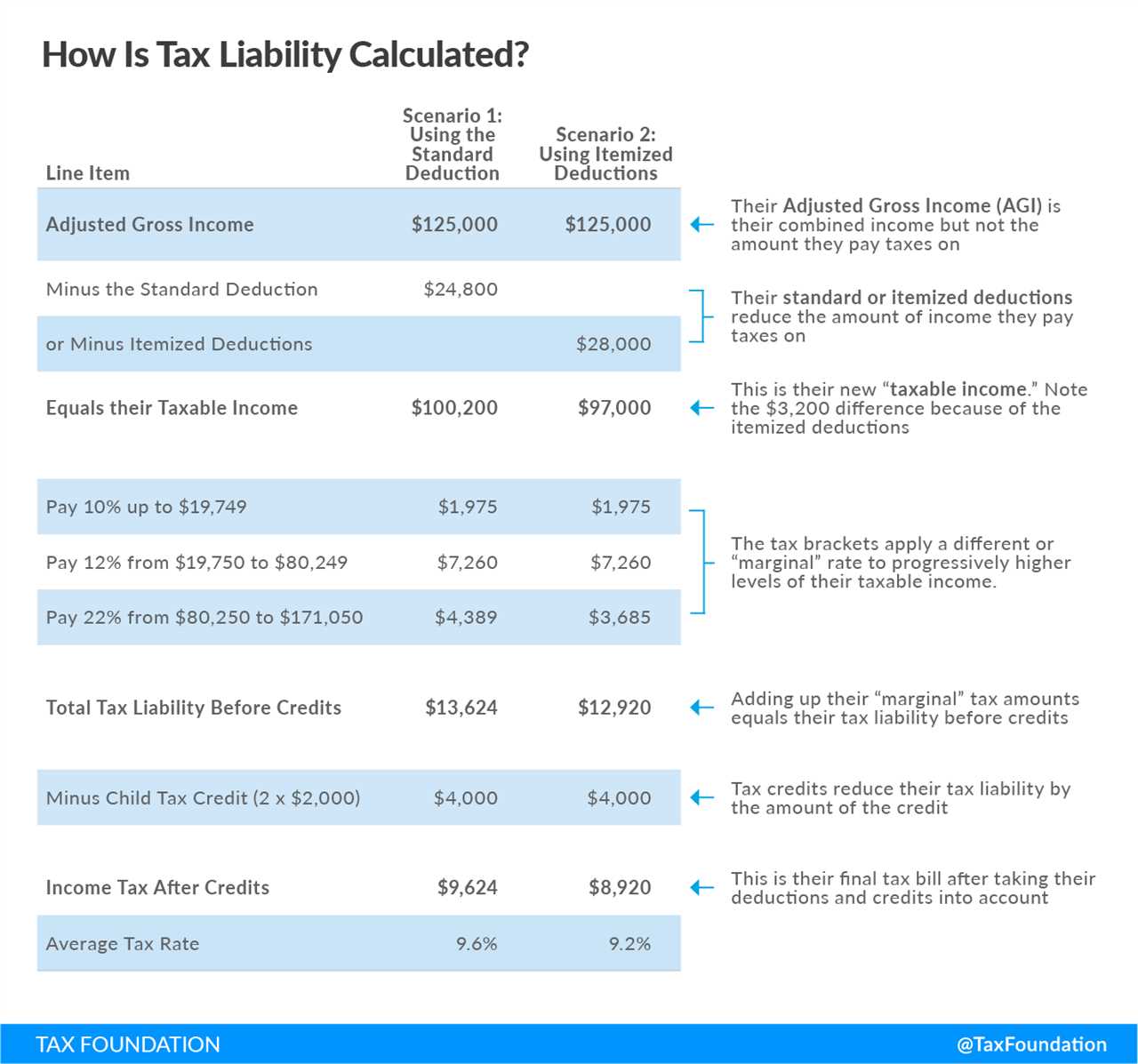
Here are some key IRS rules on tax benefits:
1. Documentation:
The IRS requires taxpayers to keep proper documentation to support their claims for tax benefits. This includes keeping records of expenses, receipts, invoices, and any other relevant documents. Without proper documentation, the IRS may disallow the claimed tax benefits.
2. Eligibility:
Not all taxpayers are eligible for every tax benefit. The IRS has specific criteria that determine who can qualify for certain tax benefits. For example, certain tax credits may only be available to low-income individuals or families, while others may be limited to specific industries or activities.
3. Time Limits:
There are time limits for claiming certain tax benefits. For example, individuals must file their tax return within a specific timeframe to claim deductions, credits, or exemptions. Additionally, some tax benefits may only be available for a limited number of years or have expiration dates.
4. Reporting Requirements:
5. Anti-Abuse Rules:
The IRS has implemented anti-abuse rules to prevent taxpayers from taking advantage of tax benefits in an abusive or fraudulent manner. These rules aim to ensure that tax benefits are used for their intended purpose and not for tax avoidance or evasion.
6. Limitations and Phaseouts:
Some tax benefits have limitations or phaseouts based on income levels or other factors. This means that as a taxpayer’s income increases, the amount of the tax benefit may be reduced or completely phased out. It is important to understand these limitations to accurately calculate the tax benefit.
Maximizing Tax Benefits
1. Keep Accurate Records
One of the most important steps in maximizing tax benefits is to keep accurate and detailed records of all income, expenses, and transactions. This includes receipts, invoices, bank statements, and any other relevant documents. By maintaining organized records, taxpayers can ensure that they claim all eligible deductions and credits.
2. Understand Tax Laws and Regulations
It is crucial to stay informed about current tax laws and regulations in order to take full advantage of available tax benefits. Tax laws are subject to change, and staying up-to-date can help taxpayers identify new deductions or credits that they may be eligible for. Consulting with a tax professional or utilizing online resources can provide valuable insights into the latest tax laws.
3. Contribute to Retirement Accounts
Contributing to retirement accounts, such as a 401(k) or an IRA, can provide significant tax benefits. These contributions are often tax-deductible, meaning that they reduce taxable income. Additionally, any earnings within the account are tax-deferred until they are withdrawn, allowing for potential tax savings in the long term.
4. Take Advantage of Tax Credits
5. Consider Charitable Contributions
Donating to qualified charitable organizations can provide both financial and tax benefits. Taxpayers who itemize deductions can deduct the value of their charitable contributions from their taxable income, reducing their overall tax liability. It is important to keep proper documentation, such as receipts or acknowledgment letters, to substantiate these deductions.
6. Consult with a Tax Professional
When in doubt, it is always beneficial to consult with a tax professional. They can provide personalized advice and guidance based on an individual’s specific financial situation. A tax professional can help identify additional tax benefits, ensure compliance with IRS rules, and maximize potential tax savings.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
