All You Need to Know About Federal Income Tax
There are several key things to know about federal income tax:
- Taxable Income: Federal income tax is based on your taxable income, which is calculated by subtracting any deductions and exemptions from your total income. Deductions can include things like mortgage interest, student loan interest, and medical expenses, while exemptions can include dependents and certain other situations.
- Tax Brackets: Federal income tax is divided into different tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. The tax brackets are based on your filing status (such as single, married filing jointly, or head of household) and your taxable income. The tax rates range from 10% to 37%.
- Withholding: Most employees have federal income tax withheld from their paychecks by their employer. This is done based on the information you provide on your Form W-4, which determines how much tax should be withheld based on your filing status and the number of allowances you claim.
- Filing Requirements: Whether or not you need to file a federal income tax return depends on your filing status, age, and income level. Generally, if you are a single individual under the age of 65 and your income is below a certain threshold, you may not be required to file a return. However, it is always a good idea to check the IRS guidelines to determine your specific filing requirements.
- Filing Deadlines: The deadline for filing your federal income tax return is typically April 15th of each year. However, if April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline may be extended. It is important to file your return on time to avoid penalties and interest.
1. Taxable Income: Taxable income is the amount of income that is subject to federal income tax. It includes wages, salaries, tips, interest, dividends, capital gains, and other sources of income. However, certain types of income, such as gifts, inheritances, and life insurance proceeds, are generally not taxable.
2. Tax Brackets: Federal income tax rates are divided into tax brackets, which determine the percentage of income that is taxed. The tax brackets are progressive, meaning that the more income you earn, the higher your tax rate will be. It is important to note that you are only taxed at the highest tax rate for the income that falls within that bracket.
4. Withholding and Estimated Taxes: Most taxpayers have federal income tax withheld from their paychecks by their employers. This withholding is based on the information provided on the employee’s Form W-4. However, if you have additional sources of income or are self-employed, you may need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to avoid underpayment penalties.
5. Tax Filing Status: Your tax filing status determines the tax rates and deductions you are eligible for. The most common filing statuses are single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, and qualifying widow(er) with dependent child. It is important to choose the correct filing status to ensure you are paying the correct amount of tax.
Calculating Federal Income Tax
Taxable Income
The first step in calculating federal income tax is determining your taxable income. This is the amount of income that is subject to taxation after deductions and exemptions. To calculate your taxable income, you need to subtract any deductions and exemptions from your total income.
Tax Brackets

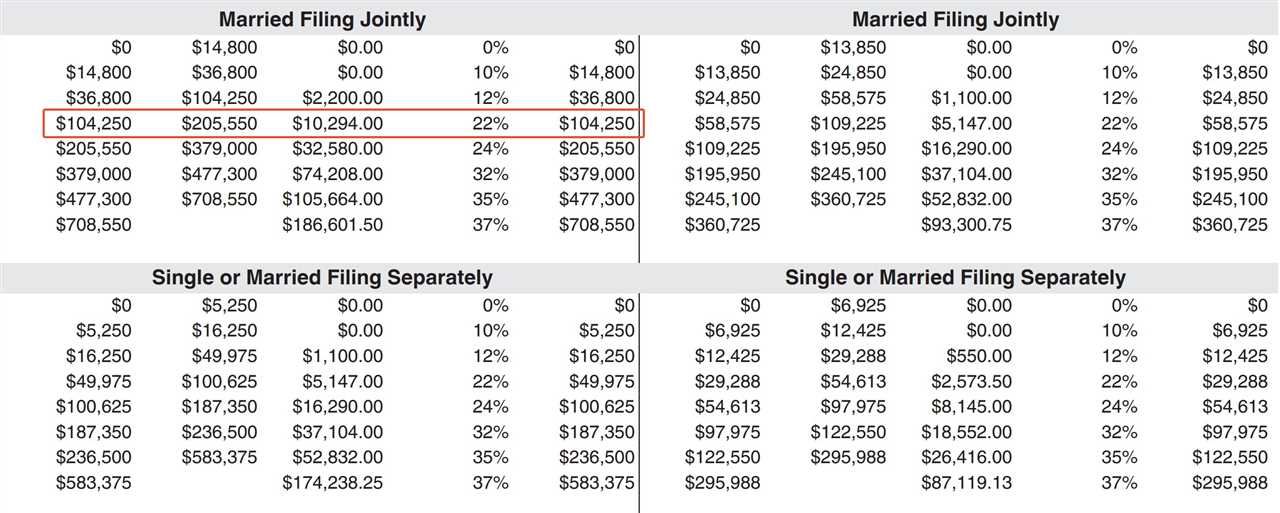
Once you have determined your taxable income, you need to determine which tax bracket you fall into. The federal income tax system has several tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. The tax rates increase as your income increases, so the higher your income, the higher your tax rate.
| Taxable Income | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 10% | |
| 12% | |
| 22% | |
| 24% | |
| 32% | |
| 35% | |
| $518,401+ | 37% |
For example, if your taxable income is $50,000 and you fall into the 22% tax bracket, you would pay 10% on the first $9,875, 12% on the portion between $9,876 and $40,125, and 22% on the portion between $40,126 and $50,000.
It’s also worth mentioning that there are various tax credits and deductions available that can reduce your federal income tax liability. These include credits for child and dependent care expenses, education expenses, and retirement contributions, as well as deductions for mortgage interest, state and local taxes, and charitable contributions.
Filing Federal Income Tax

1. Determine your filing status

Before you start the filing process, you need to determine your filing status. This will depend on your marital status and other factors such as whether you have dependents. The most common filing statuses are single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, and qualifying widow(er) with dependent child. Make sure to choose the correct filing status as it can affect your tax liability and eligibility for certain deductions and credits.
2. Gather all necessary documents
Before you begin filling out your tax return, gather all the necessary documents and information. This includes your W-2 forms from your employer, 1099 forms for any additional income, receipts for deductible expenses, and any other relevant financial records. Having all the required documents on hand will make the filing process smoother and help ensure accuracy.
Tip: Consider using tax preparation software or hiring a professional tax preparer to help you gather and organize your documents and ensure that you claim all eligible deductions and credits.
3. Choose the appropriate tax form
There are several different tax forms available, depending on your income level and the complexity of your tax situation. The most common form is the 1040 form, but there are also simplified versions like the 1040A and 1040EZ. Make sure to choose the form that best suits your needs and accurately reflects your financial situation.
4. Fill out your tax return accurately
When filling out your tax return, pay close attention to detail and ensure that all information is accurate. Double-check your calculations and review all entries before submitting your return. Mistakes or omissions can result in delays in processing your return or even trigger an audit by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Tip: Consider e-filing your tax return instead of mailing a paper copy. E-filing is faster, more secure, and can help you receive any refund owed to you more quickly.
5. Pay any taxes owed or claim a refund
After completing your tax return, you will either owe taxes or be eligible for a refund. If you owe taxes, make sure to pay them by the filing deadline to avoid penalties and interest charges. If you are due a refund, you can choose to have it directly deposited into your bank account or receive a paper check in the mail.
Tip: Consider setting up a payment plan with the IRS if you are unable to pay your tax bill in full. This can help you avoid hefty penalties and interest charges.
By following these steps and taking the time to understand the filing process, you can ensure that you accurately file your federal income tax and remain in compliance with the law. Remember to keep copies of all your tax documents and retain them for at least three years in case of an audit or review by the IRS.
Important Considerations for Federal Income Tax
First and foremost, it is crucial to understand the tax laws and regulations that apply to your specific situation. The federal income tax code is complex and can be difficult to navigate without the proper knowledge. Consider consulting with a tax professional or utilizing tax software to ensure that you are following the correct procedures and maximizing your tax benefits.
Another important consideration is keeping accurate records of your income and expenses throughout the year. This includes maintaining receipts, bank statements, and any other relevant documentation. Having organized records will make the filing process much smoother and can help protect you in the event of an audit.
Additionally, it is important to be aware of any changes to the tax code that may affect your filing. The tax laws can change from year to year, so staying informed about any updates or revisions is crucial. This can include changes to tax rates, deductions, or credits that may impact your overall tax liability.
One consideration that many taxpayers overlook is the option to file jointly or separately. Married couples have the choice to file their federal income tax return together or separately. It is important to evaluate which option will result in the lowest tax liability for your specific situation. This decision can have a significant impact on the amount of taxes owed or the size of your refund.
Lastly, it is important to file your federal income tax return on time. The deadline for filing is typically April 15th, but it can vary depending on the year and any extensions that may be granted. Failing to file on time can result in penalties and interest charges, so it is important to mark the deadline on your calendar and plan accordingly.
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Tax laws and regulations | Understand the applicable tax laws and regulations to ensure accurate filing. |
| Record keeping | Maintain organized records of income and expenses for easy filing and potential audits. |
| Tax code changes | Stay informed about any changes to the tax code that may impact your filing. |
| Filing jointly or separately | Evaluate the benefits of filing jointly or separately for married couples. |
| Timely filing | File your federal income tax return on time to avoid penalties and interest charges. |
By considering these important factors, you can ensure that your federal income tax return is accurate and in compliance with the law. Taking the time to understand the process and staying informed about any changes can help you minimize your tax liability and maximize your potential refund.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
