What is Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR)?

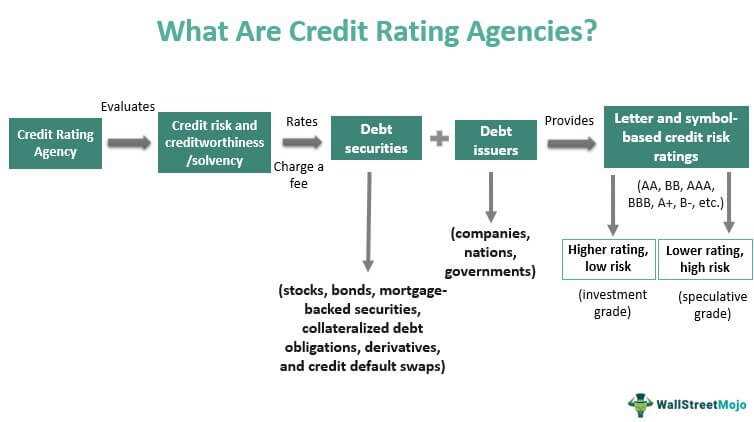
Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) is a credit rating agency based in Japan. It is one of the leading credit rating agencies in the country and provides independent credit ratings for various financial instruments, including bonds.
Credit rating agencies play a crucial role in the financial markets by assessing the creditworthiness of issuers and their financial instruments. JCR evaluates the credit risk associated with bonds and assigns them a rating based on their assessment.
Importance of Credit Ratings
Credit ratings are important for both investors and issuers in the bond market. For investors, credit ratings provide an indication of the risk associated with a particular bond. Higher-rated bonds are considered to have lower credit risk and are generally perceived as safer investments. On the other hand, lower-rated bonds carry higher credit risk and may offer higher yields to compensate for the increased risk.
Responsibilities of Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR)

JCR is responsible for conducting thorough credit analysis and assigning credit ratings to bonds issued by various entities in Japan. The agency follows a rigorous and transparent methodology to evaluate the creditworthiness of issuers and their bonds.
JCR’s responsibilities include:
- Assessing the financial strength and stability of issuers
- Evaluating the credit risk associated with bonds
- Assigning credit ratings based on their assessment
- Monitoring and updating credit ratings as necessary
- Providing timely and accurate credit rating reports to investors and market participants
JCR aims to provide reliable and independent credit ratings to facilitate informed investment decisions in the bond market.
Overall, Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) plays a crucial role in the bond market by providing credit ratings that help investors assess the creditworthiness of bonds and issuers. Its independent and transparent evaluation process contributes to the efficiency and transparency of the financial markets in Japan.
Importance of Credit Ratings
Credit ratings play a crucial role in the financial world, providing investors with valuable information about the creditworthiness of companies and governments. These ratings help investors make informed decisions about where to invest their money and assess the risk associated with different investment options.
One of the main reasons why credit ratings are important is that they provide an objective assessment of the likelihood that a borrower will default on their financial obligations. This information is particularly important for bond investors who rely on the income generated by these investments. A higher credit rating indicates a lower risk of default, which translates into lower interest rates and higher demand for the bonds.
Credit ratings also serve as a benchmark for comparing the creditworthiness of different entities. Investors can use these ratings to evaluate the relative risk of investing in different companies or governments. For example, a company with a higher credit rating may be considered a safer investment compared to a company with a lower credit rating.
In addition, credit ratings are used by regulatory bodies and financial institutions to determine capital requirements and set risk management policies. These ratings help regulators assess the financial stability of banks and other financial institutions, ensuring the overall health of the financial system.
Furthermore, credit ratings can have a significant impact on the cost of borrowing for companies and governments. A higher credit rating allows borrowers to access capital at lower interest rates, reducing their borrowing costs and potentially increasing their profitability.
Overall, credit ratings provide a standardized and objective measure of creditworthiness, helping investors, regulators, and borrowers make informed decisions in the financial markets. They play a vital role in promoting transparency, stability, and efficiency in the global economy.
Responsibilities of Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR)
Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) is responsible for providing credit ratings for various financial instruments, including bonds, loans, and other debt securities. The agency plays a crucial role in the financial market by assessing the creditworthiness of issuers and providing investors with valuable information to make informed investment decisions.
Some of the key responsibilities of Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) include:
| 1. Credit Rating Assignments | |
| 2. Credit Rating Monitoring | JCR continuously monitors the credit ratings of issuers and their financial instruments to ensure that they remain accurate and up-to-date. The agency reviews relevant financial and economic information regularly and makes necessary adjustments to the credit ratings if there are any changes in the issuer’s creditworthiness. |
| 3. Credit Rating Reports | JCR prepares detailed credit rating reports that provide in-depth analysis and insights into the creditworthiness of issuers and their financial instruments. These reports are made available to investors, financial institutions, and other market participants to help them assess the risks associated with their investments. |
| 4. Investor Education | |
| 5. Regulatory Compliance | JCR complies with the regulatory requirements and guidelines set by the relevant authorities. The agency ensures that its credit rating methodologies and processes are in line with the industry standards and best practices to maintain the integrity and credibility of its ratings. |
Role of Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) in the Bond Market
The Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) plays a crucial role in the bond market by providing independent credit ratings for various types of bonds. These ratings are essential for investors, issuers, and regulators to assess the creditworthiness and risk associated with different bond offerings.
Importance of Credit Ratings
Credit ratings serve as an important tool for investors to make informed decisions about investing in bonds. They provide an assessment of the creditworthiness of bond issuers and their ability to repay their debt obligations. Higher credit ratings indicate lower risk, making bonds more attractive to investors. On the other hand, lower credit ratings imply higher risk, which may result in higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk.
Responsibilities of Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR)
The Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) has several key responsibilities in the bond market:
- Assigning Credit Ratings: JCR assigns credit ratings to various types of bonds based on their assessment of the issuer’s creditworthiness and the risk associated with the bonds.
- Conducting Credit Analysis: JCR conducts thorough credit analysis, including evaluating the issuer’s financial health, industry conditions, and economic factors that may impact the issuer’s ability to meet its debt obligations.
- Monitoring Credit Ratings: JCR continuously monitors the credit ratings of bonds and issuers to ensure they remain accurate and up-to-date. They may revise ratings if there are significant changes in the issuer’s financial position or market conditions.
- Providing Research and Insights: JCR provides research reports and insights on the bond market, helping investors and market participants make informed decisions.
- Enhancing Transparency: JCR aims to enhance transparency in the bond market by providing clear and objective credit ratings, promoting fair and efficient market practices.
Overall, the role of Japan Credit Rating Agency (JCR) in the bond market is to provide independent and reliable credit ratings, contributing to the efficient functioning of the market and facilitating informed investment decisions.
| Benefits of JCR’s Role | Challenges |
|---|---|
|
|

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
