What is Market Capitalization?
Market capitalization is an important measure for investors as it provides insights into the company’s overall worth and its position in the market. It helps investors assess the company’s size, growth potential, and risk factors.
Market capitalization is a key factor that investors consider when making investment decisions. It helps them gauge the company’s size and compare it with other companies in the same industry or sector.
Investors often use market capitalization to categorize companies into different groups, such as large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap. Large-cap companies are typically well-established and have a market capitalization of over $10 billion. Mid-cap companies have a market capitalization between $2 billion and $10 billion, while small-cap companies have a market capitalization below $2 billion.
Market capitalization also provides insights into the company’s growth potential and risk factors. Generally, larger companies with higher market capitalization are considered less risky and more stable, while smaller companies with lower market capitalization may have higher growth potential but also higher risk.
Calculating Market Capitalization

To calculate market capitalization, you need to know the total number of outstanding shares and the current market price per share. The formula for market capitalization is:
Market Capitalization = Total Number of Outstanding Shares * Current Market Price per Share
For example, if a company has 10 million outstanding shares and the current market price per share is $50, the market capitalization would be $500 million.
Factors That Influence Market Capitalization
Several factors can influence a company’s market capitalization. These include the company’s financial performance, industry trends, investor sentiment, and overall market conditions.
A company’s financial performance, such as revenue growth, profitability, and debt levels, can impact its market capitalization. Positive financial results often lead to an increase in market capitalization, while negative results can cause a decrease.
Industry trends and investor sentiment can also play a role in market capitalization. If a company operates in a growing industry or has a positive outlook, investors may be more willing to invest in its stock, leading to an increase in market capitalization.
Overall market conditions, such as economic factors and market volatility, can affect the market capitalization of all companies. During periods of economic uncertainty or market downturns, market capitalization may decrease across the board.
Significance of Market Capitalization for Investors
Investors often use market capitalization as a basis for constructing their investment portfolios. They may choose to invest in large-cap companies for stability and dividends, mid-cap companies for growth potential, or small-cap companies for higher risk and potential high returns.
Market capitalization also provides insights into the liquidity of a company’s stock. Generally, larger companies with higher market capitalization have more liquid stocks, meaning they are easier to buy and sell without significantly impacting the stock price.
How Market Capitalization Can Indicate Investment Opportunities
Market capitalization can indicate investment opportunities for investors. By analyzing companies with different market capitalizations, investors can identify potential undervalued or overvalued stocks.
Investors can also use market capitalization to identify trends and patterns in the market. For example, if there is a shift in investor preference towards small-cap stocks, it may indicate a bullish sentiment and potential investment opportunities in that segment.
Market capitalization is a key concept in the world of investing. It refers to the total value of a company’s outstanding shares of stock. It is calculated by multiplying the current market price of a single share by the total number of outstanding shares.
Market capitalization is important for investors as it provides a snapshot of a company’s size and value in the market. It helps investors gauge the overall worth of a company and compare it to other companies in the same industry or sector. This information can be used to make informed investment decisions.
Importance of Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is an important metric for investors because it can indicate the level of risk associated with investing in a particular company. Generally, larger companies with higher market capitalizations are considered to be more stable and less risky compared to smaller companies with lower market capitalizations.
Investors often use market capitalization as a way to categorize and classify companies. The three main categories based on market capitalization are:
- Large-cap companies: These are companies with a market capitalization of over $10 billion. They are typically well-established, stable, and have a proven track record of success.
- Mid-cap companies: These are companies with a market capitalization between $2 billion and $10 billion. They are often in a growth phase and have the potential for future expansion.
- Small-cap companies: These are companies with a market capitalization of less than $2 billion. They are usually younger companies or startups that may have higher growth potential but also higher risk.
Considerations for Investors
While market capitalization is a useful metric, it should not be the sole factor considered when making investment decisions. Other factors, such as a company’s financial health, industry trends, competitive landscape, and management team, should also be taken into account.
Additionally, market capitalization can change over time as a company’s stock price fluctuates and the number of outstanding shares changes. Therefore, it is important for investors to regularly monitor and reassess the market capitalization of companies in their investment portfolio.
Calculating Market Capitalization
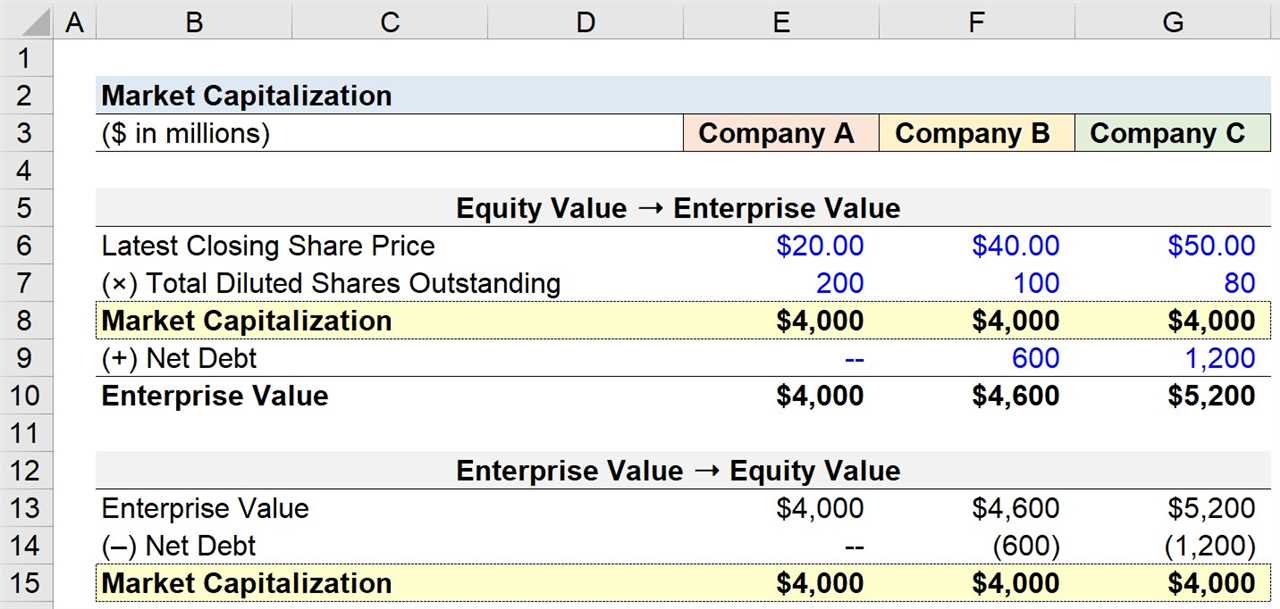
Market capitalization is a crucial metric that investors use to evaluate the size and value of a company. It is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares. This calculation provides a snapshot of the market’s perception of a company’s worth.
Step 1: Determine the Stock Price

The first step in calculating market capitalization is to determine the current stock price. This information is readily available on financial news websites, stock exchanges, and brokerage platforms. The stock price represents the value that investors are willing to pay for a single share of the company’s stock.
Step 2: Find the Total Number of Outstanding Shares
The second step is to find the total number of outstanding shares. Outstanding shares refer to the total number of shares issued by the company that are currently held by investors. This information can be found in the company’s financial statements or through financial data providers.
Step 3: Multiply the Stock Price by the Total Number of Outstanding Shares
Once you have the stock price and the total number of outstanding shares, you can calculate market capitalization by multiplying these two numbers. The formula is simple:
Market Capitalization = Stock Price x Total Number of Outstanding Shares
For example, if a company’s stock price is $50 and it has 10 million outstanding shares, the market capitalization would be:
Market Capitalization = $50 x 10,000,000 = $500,000,000
Step 4: Interpret the Market Capitalization
After calculating the market capitalization, it is essential to interpret the result in the context of the company’s industry and market. Market capitalization can vary significantly between companies and sectors, and it is crucial to compare it to peers to gain meaningful insights.
Generally, companies are categorized into three main groups based on their market capitalization:
- Large-cap: Companies with a market capitalization of $10 billion or more.
- Mid-cap: Companies with a market capitalization between $2 billion and $10 billion.
- Small-cap: Companies with a market capitalization below $2 billion.
Investors often use market capitalization as a tool to assess the risk and growth potential of a company. Large-cap companies are typically more stable and less volatile, while small-cap companies may offer higher growth opportunities but come with higher risks.
Exploring the Formula and Factors That Influence Market Capitalization
The formula for calculating market capitalization is:
| Market Capitalization | = | Current Stock Price | × | Total Number of Outstanding Shares |
|---|
The current stock price refers to the price at which the company’s shares are currently trading in the market. This price is determined by various factors such as supply and demand, company performance, market conditions, and investor sentiment.
The total number of outstanding shares represents the total number of shares issued by the company that are held by investors. It includes shares held by institutional investors, individual investors, and company insiders. The number of outstanding shares can change over time due to factors such as stock splits, share buybacks, and new share issuances.
Several factors can influence market capitalization:
- Company Performance: A company’s financial performance, including revenue growth, profitability, and market share, can have a significant impact on its market capitalization. Positive performance indicators often lead to an increase in stock price and market capitalization.
- Industry Trends: Market trends and conditions within a specific industry can affect the market capitalization of companies operating in that industry. For example, emerging technologies or changes in consumer preferences can drive up the market capitalization of companies in the tech sector.
- Investor Sentiment: Investor sentiment, which is influenced by factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, and market news, can impact market capitalization. Positive sentiment can lead to increased buying activity and higher stock prices.
- Competition: The competitive landscape within an industry can affect market capitalization. Companies facing intense competition may experience lower market capitalization compared to dominant players in the market.
- Market Manipulation: Illegal activities such as market manipulation can artificially inflate or deflate a company’s market capitalization. It is essential for investors to be aware of such activities and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions.
Investors use market capitalization as a tool to compare companies within the same industry or across different sectors. It helps them assess the relative size and value of companies and make informed investment decisions. Companies with larger market capitalization are often considered more stable and less volatile, while those with smaller market capitalization may have higher growth potential but also higher risk.
Significance of Market Capitalization for Investors
One of the main reasons why market capitalization is significant for investors is that it reflects the overall value of a company in the stock market. It is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares. A higher market capitalization indicates that a company is larger and more established, while a lower market capitalization suggests a smaller and potentially riskier company.
Investors often use market capitalization as a criterion for categorizing stocks into different groups. These groups include large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks. Large-cap stocks typically have a market capitalization of over $10 billion, mid-cap stocks have a market capitalization between $2 billion and $10 billion, and small-cap stocks have a market capitalization below $2 billion.
Each category has its own characteristics and investment considerations. Large-cap stocks are generally considered more stable and less volatile, making them suitable for conservative investors. Mid-cap stocks offer a balance between stability and growth potential, making them attractive to investors seeking moderate risk. Small-cap stocks, on the other hand, are often more volatile but can offer significant growth opportunities for investors willing to take on higher risk.
Furthermore, market capitalization can provide insights into the liquidity of a stock. Stocks with higher market capitalization tend to have higher trading volumes, making it easier for investors to buy or sell shares without significantly impacting the stock price. On the other hand, stocks with lower market capitalization may have lower trading volumes, which can result in wider bid-ask spreads and potentially higher transaction costs.
How Market Capitalization Can Indicate Investment Opportunities

Size Matters
One of the key aspects that market capitalization reveals is the size of a company. Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the current stock price by the total number of outstanding shares. This calculation provides a measure of the company’s total value as perceived by the market.
Large-cap companies, with a market capitalization of over $10 billion, are typically well-established and have a proven track record. These companies are often considered more stable and less volatile compared to smaller companies. They tend to have a strong market presence, substantial resources, and a higher level of investor confidence.
On the other hand, small-cap companies, with a market capitalization of under $2 billion, are generally younger and have higher growth potential. These companies are often in the early stages of development and may offer innovative products or services. While small-cap stocks can be more volatile, they also present an opportunity for higher returns.
Stability and Growth Potential
Market capitalization can also indicate the stability and growth potential of a company. Large-cap companies are typically more stable due to their size, diversification, and established market position. They are often able to weather economic downturns better and may offer more consistent dividends.
Investment Opportunities

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
