Bond Rating Agencies: An In-Depth Look at Their Role, Advantages, and Controversies
Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in the financial market by providing investors with information about the creditworthiness of bond issuers. These agencies assess the credit risk associated with a particular bond or issuer and assign a rating that reflects the likelihood of default. This rating helps investors make informed decisions about which bonds to invest in and at what price.
One of the main advantages of using bond rating agencies is that they provide independent and objective analysis. They have access to a wide range of financial data and use sophisticated models to evaluate the creditworthiness of issuers. This helps to ensure that investors have access to reliable information when making investment decisions.
Another advantage of bond rating agencies is that their ratings serve as a benchmark for the market. Investors often rely on these ratings to compare the credit quality of different bonds and issuers. This standardization helps to facilitate the trading of bonds and promotes liquidity in the market.
However, bond rating agencies have also faced controversies. One of the main criticisms is that their ratings can be influenced by conflicts of interest. In some cases, the agencies are paid by the issuers themselves to provide ratings, which can create a potential bias. This conflict of interest was evident during the financial crisis of 2008, when many highly-rated mortgage-backed securities defaulted, leading to a loss of confidence in the agencies’ ratings.
Another controversy surrounding bond rating agencies is the lack of transparency in their rating methodologies. The models and criteria used by these agencies are often complex and not fully disclosed to the public. This lack of transparency can make it difficult for investors to fully understand the basis of the ratings and assess their accuracy.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. Investors should consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in the financial market by providing investors with an assessment of the creditworthiness of bond issuers. These agencies evaluate the risk associated with a particular bond and assign it a rating based on various factors.
The primary function of bond rating agencies is to provide independent and objective opinions on the creditworthiness of bond issuers. They analyze the financial health of the issuer, including its ability to meet its debt obligations and generate sufficient cash flow. This analysis helps investors make informed decisions about whether to invest in a particular bond.
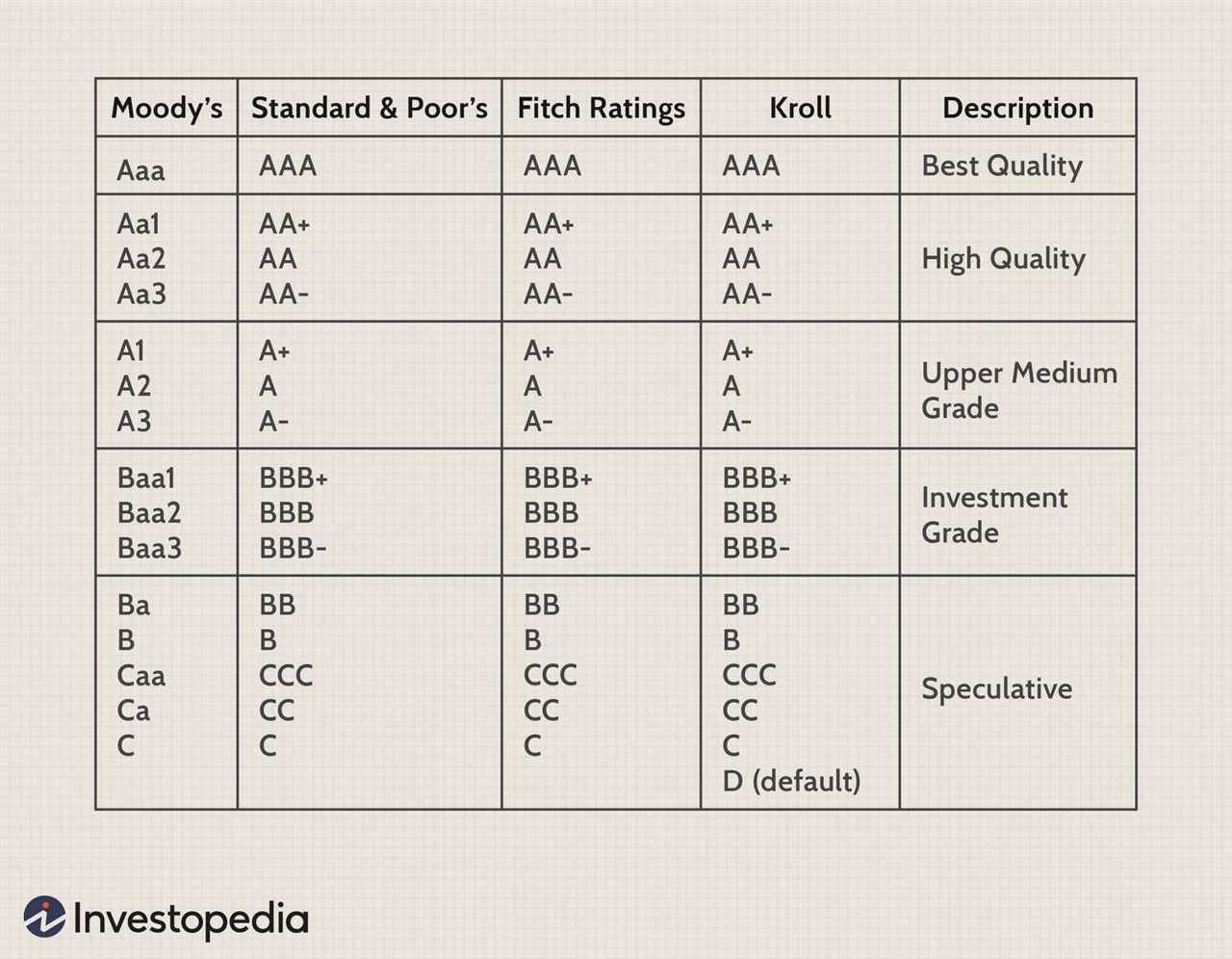
Bond rating agencies use a rating scale to classify bonds into different categories based on their level of risk. The most commonly used rating scale is the one developed by Standard & Poor’s, which ranges from AAA (highest rating) to D (default). Other rating agencies, such as Moody’s and Fitch, have their own rating scales.
Investors rely on the ratings provided by these agencies to assess the risk associated with a bond investment. Higher-rated bonds are considered less risky and generally offer lower yields, while lower-rated bonds carry higher risk and offer higher yields to compensate investors for taking on that risk.
One advantage of using bond rating agencies is that they provide a standardized and widely recognized measure of credit risk. This allows investors to compare the creditworthiness of different bonds and make informed investment decisions. Additionally, bond ratings serve as a benchmark for regulatory purposes, as some institutional investors are required to hold only investment-grade bonds.
The Role of Bond Rating Agencies in the Financial Market
Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in the financial market by providing independent assessments of the creditworthiness of bond issuers. These agencies evaluate the risk associated with investing in bonds and assign ratings that reflect the likelihood of default.
One of the main functions of bond rating agencies is to provide investors with reliable information about the credit quality of bonds. This information helps investors make informed decisions about whether to invest in a particular bond or not. By assigning ratings to bonds, these agencies provide a standardized measure of credit risk, which allows investors to compare different bonds and assess their relative safety.
Bond rating agencies use a variety of factors to determine the creditworthiness of issuers. These factors include the issuer’s financial strength, its ability to generate cash flow, its debt levels, and its overall business and economic environment. The agencies also consider the specific terms and conditions of the bond, such as its maturity date and interest rate.
The ratings assigned by bond rating agencies have a significant impact on the cost of borrowing for bond issuers. A higher rating indicates lower credit risk and allows issuers to borrow at lower interest rates. On the other hand, a lower rating indicates higher credit risk and leads to higher borrowing costs. Therefore, bond issuers often strive to maintain or improve their ratings to access cheaper funding.
Furthermore, bond rating agencies play a critical role in the regulation of the financial market. Many regulatory frameworks require certain investors, such as pension funds and insurance companies, to only invest in bonds with a minimum rating. This requirement helps protect investors by ensuring that they only invest in bonds that meet certain creditworthiness standards.
However, bond rating agencies have faced criticism for their role in the financial market. One of the main controversies is the potential conflict of interest that arises from the fact that bond issuers pay for the rating services. Critics argue that this payment structure may create incentives for rating agencies to provide favorable ratings to issuers, compromising the independence and objectivity of their assessments.
Advantages of Using Bond Rating Agencies
Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in the financial market by providing investors with important information about the creditworthiness of bond issuers. These agencies assess the risk associated with a particular bond and assign a rating based on their evaluation. Here are some of the key advantages of using bond rating agencies:
1. Objective Evaluation
Bond rating agencies provide an independent and objective evaluation of the creditworthiness of bond issuers. They use a standardized rating system to assess the risk associated with different bonds, which helps investors make informed decisions. The ratings provided by these agencies are based on a thorough analysis of various factors, including the issuer’s financial health, industry trends, and economic conditions.
2. Risk Assessment
By using bond rating agencies, investors can effectively assess the risk associated with different bonds. The ratings provided by these agencies give investors an indication of the likelihood of default or non-payment of interest by the bond issuer. This helps investors make informed decisions and manage their investment portfolios effectively.
3. Market Transparency
Bond rating agencies contribute to market transparency by providing information about the creditworthiness of bond issuers. The ratings provided by these agencies are widely available to investors, allowing them to compare different bonds and make informed investment decisions. This transparency helps promote efficient capital allocation and enhances market efficiency.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in regulatory compliance. Many regulatory frameworks require institutional investors to consider the ratings provided by these agencies when making investment decisions. By using bond rating agencies, investors can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and avoid potential legal and regulatory risks.
5. Time-saving
By relying on the expertise of bond rating agencies, investors can save time and effort in conducting their own credit analysis. These agencies have access to extensive data and resources, allowing them to conduct thorough evaluations of bond issuers. Investors can leverage this expertise to make more efficient investment decisions and focus on other aspects of their investment strategy.
| Advantages | Description |
|---|---|
| Objective Evaluation | Bond rating agencies provide an independent and objective evaluation of the creditworthiness of bond issuers. |
| Risk Assessment | By using bond rating agencies, investors can effectively assess the risk associated with different bonds. |
| Market Transparency | Bond rating agencies contribute to market transparency by providing information about the creditworthiness of bond issuers. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in regulatory compliance. |
| Time-saving | By relying on the expertise of bond rating agencies, investors can save time and effort in conducting their own credit analysis. |
Controversies Surrounding Bond Rating Agencies
Bond rating agencies play a crucial role in the financial market by providing investors with an assessment of the creditworthiness of bond issuers. However, these agencies have faced significant controversies over the years, raising questions about their credibility and independence.
One of the main controversies surrounding bond rating agencies is the issue of conflicts of interest. These agencies are often paid by the issuers themselves to rate their bonds, creating a potential conflict of interest. Critics argue that this arrangement may lead to biased ratings, as agencies may feel pressured to provide favorable ratings to maintain their business relationships.
Another controversy is the accuracy of the ratings provided by these agencies. In the lead-up to the 2008 financial crisis, bond rating agencies were heavily criticized for their failure to accurately assess the risks associated with complex financial products, such as mortgage-backed securities. Many argue that the agencies’ ratings were overly optimistic and did not reflect the true level of risk involved.
Furthermore, there have been concerns about the transparency and accountability of bond rating agencies. Critics argue that the methodologies used by these agencies to assign ratings are often opaque and not easily understood by investors. This lack of transparency makes it difficult for investors to assess the reliability of the ratings and make informed investment decisions.
Additionally, there have been allegations of conflicts of interest within the agencies themselves. It has been suggested that some employees of these agencies may have personal financial interests in the bonds they are rating, creating a potential bias in the rating process.
These controversies have led to calls for increased regulation and oversight of bond rating agencies. Some argue that the current system, where agencies are paid by the issuers, should be reformed to ensure greater independence and objectivity. Others suggest that alternative models, such as a publicly funded rating agency, should be explored to reduce conflicts of interest.
| Controversies | Impact |
|---|---|
| Conflicts of interest | Potential biased ratings |
| Inaccurate ratings | Misleading investors |
| Lack of transparency | Difficulty in assessing reliability |
| Internal conflicts of interest | Potential bias in rating process |
The Future of Bond Rating Agencies
Bond rating agencies have played a crucial role in the financial market for many years. They provide investors with valuable information about the creditworthiness of bond issuers, helping them make informed investment decisions. However, these agencies have also faced criticism and controversy, raising questions about their future role and relevance.
Challenges and Changes
In response to these challenges, bond rating agencies have made efforts to improve their methodologies and increase transparency. They have implemented stricter criteria for rating complex financial products and have enhanced their disclosure practices. Additionally, regulatory reforms have been introduced to enhance oversight of these agencies and reduce conflicts of interest.
The Role of Technology
Technology is also expected to play a significant role in shaping the future of bond rating agencies. With the advent of big data and artificial intelligence, these agencies can leverage advanced analytics to improve their rating models and identify potential risks more effectively. This can help them provide more accurate and timely ratings, enhancing investor confidence.
Collaboration and Competition
Another aspect of the future of bond rating agencies is the increasing competition and collaboration among different players in the market. Traditional rating agencies are facing competition from new entrants, such as fintech companies and alternative data providers. These new players are leveraging innovative technologies and alternative data sources to offer different perspectives on creditworthiness.
At the same time, there is also a trend towards collaboration between bond rating agencies and other stakeholders in the financial ecosystem. This includes partnerships with regulators, financial institutions, and investors to enhance the quality and relevance of ratings. By working together, these stakeholders can address the limitations of traditional rating models and develop more comprehensive and robust assessment frameworks.
Conclusion
The future of bond rating agencies is likely to be shaped by a combination of technological advancements, regulatory reforms, and industry collaboration. While these agencies have faced criticism and controversy in the past, they continue to play a crucial role in the financial market. By embracing change and adapting to new challenges, bond rating agencies can enhance their credibility and relevance, providing investors with valuable insights and contributing to the stability and efficiency of the financial system.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
