What is Earnings Before Interest After Taxes (EBIAT)?
Earnings Before Interest After Taxes (EBIAT) is a financial metric used to measure a company’s profitability. It represents the earnings generated by a company before taking into account interest expenses and taxes. EBIAT is considered a more accurate measure of a company’s profitability than other metrics such as net income, as it focuses on the core operations of the business.
EBIAT is calculated by subtracting interest expenses and taxes from a company’s earnings before taxes (EBT). This metric provides a clearer picture of a company’s profitability by excluding the impact of interest expenses and taxes, which can vary significantly between companies.
Calculating EBIAT
To calculate EBIAT, you need to have the following information:
- Earnings Before Taxes (EBT)
- Interest Expenses
- Taxes
Once you have these figures, you can use the following formula to calculate EBIAT:
Interpreting EBIAT
EBIAT provides insights into a company’s profitability by focusing on its core operations. A higher EBIAT indicates that a company is generating more earnings from its core business activities, which is generally seen as a positive sign.
Comparing EBIAT across different companies or industries can help investors and analysts assess the relative profitability of these entities. It allows for a more accurate comparison by excluding the impact of interest expenses and taxes, which can vary based on factors such as debt levels and tax rates.
Additionally, EBIAT can be used to evaluate a company’s financial health and sustainability. A consistent and positive EBIAT over time indicates that a company is able to generate sustainable profits, which is important for long-term success.
Overall, EBIAT is a valuable financial metric that provides a clearer picture of a company’s profitability by excluding the impact of interest expenses and taxes. It allows for a more accurate assessment of a company’s core operations and can be used for comparative analysis and evaluating financial health.
Calculating EBIAT
Calculating Earnings Before Interest After Taxes (EBIAT) is an essential step in financial analysis. It helps businesses and investors understand the true profitability of a company by excluding the effects of interest and taxes.
To calculate EBIAT, you need to follow a simple formula:
EBIAT = Net Income + Interest Expense + Tax Expense
Net Income refers to the company’s total earnings after deducting all expenses, including operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization. It is typically found on the income statement.
Interest Expense represents the amount of money a company pays in interest on its debt obligations. It can be found on the income statement or the notes to the financial statements.
Tax Expense refers to the amount of taxes a company pays to the government. It is usually listed on the income statement.
By adding Net Income, Interest Expense, and Tax Expense together, you can calculate the EBIAT figure. This metric provides a clearer picture of a company’s profitability as it removes the impact of interest and taxes.
Once you have calculated the EBIAT, you can use it to compare the financial performance of different companies or assess the financial health of a single company over time. It can also be used to evaluate the efficiency of a company’s operations and make informed investment decisions.
Interpreting EBIAT
When analyzing a company’s financial performance, it is essential to understand and interpret the Earnings Before Interest After Taxes (EBIAT) ratio. This ratio provides valuable insights into a company’s ability to generate profits from its operations.
Positive EBIAT
A positive EBIAT indicates that a company’s operations are generating profits after accounting for all expenses, including interest and taxes. This is a favorable sign and suggests that the company is financially healthy and capable of meeting its obligations.
Investors and stakeholders often view a positive EBIAT as a sign of a well-managed company with strong operational efficiency. It demonstrates that the company is generating sufficient earnings to cover its interest expenses and taxes while still having profits left over.
Negative EBIAT
A negative EBIAT indicates that a company’s operations are not generating enough profits to cover its interest expenses and taxes. This is a concerning sign and suggests that the company may be facing financial difficulties.
When a company has a negative EBIAT, it may indicate that its operations are not efficient enough to generate profits or that it has high interest expenses and tax obligations. This can be a warning sign for investors and stakeholders, as it may indicate potential financial instability or the need for restructuring.
Comparing EBIAT
Comparing a company’s EBIAT ratio to its competitors or industry benchmarks can provide valuable insights into its financial performance. If a company has a higher EBIAT ratio compared to its peers, it may indicate that it is more efficient in generating profits from its operations.
On the other hand, if a company has a lower EBIAT ratio compared to its competitors, it may suggest that it is facing challenges in generating profits or that it has higher interest expenses and tax obligations.
Importance of EBIAT in Financial Analysis
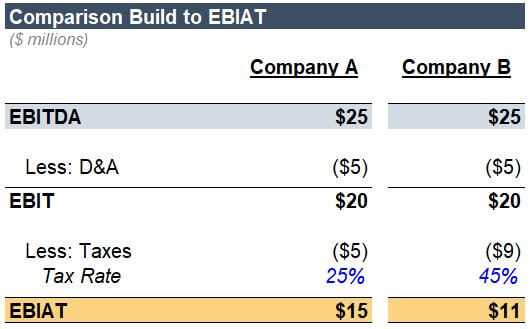
Earnings Before Interest After Taxes (EBIAT) is a crucial financial ratio that provides valuable insights into a company’s profitability. It is a measure of a company’s ability to generate profits from its core operations, excluding the impact of interest expenses and taxes.
1. Assessing Operational Efficiency
EBIAT helps analysts and investors evaluate a company’s operational efficiency by focusing solely on its core earnings. By excluding interest expenses and taxes, EBIAT provides a clearer picture of a company’s ability to generate profits from its day-to-day operations. This allows for a more accurate assessment of a company’s operational efficiency and helps identify areas for improvement.
2. Comparing Performance Across Industries
EBIAT is a useful metric for comparing the financial performance of companies operating in different industries. Since EBIAT focuses on core earnings, it eliminates the impact of variations in interest expenses and tax rates across industries. This allows for a more meaningful comparison of profitability across companies in different sectors.
3. Evaluating Financial Health
EBIAT is an important indicator of a company’s financial health. By excluding interest expenses and taxes, EBIAT provides a more accurate measure of a company’s ability to generate profits that can be used to cover debt obligations and taxes. A higher EBIAT indicates a stronger financial position and a greater ability to meet financial obligations.
4. Making Informed Investment Decisions
EBIAT is a valuable tool for investors looking to make informed investment decisions. By analyzing a company’s EBIAT, investors can assess its profitability and financial health. This information can help investors identify companies with strong earnings potential and make more informed investment decisions.
| Benefits of EBIAT in Financial Analysis |
|---|
| Assesses operational efficiency |
| Allows for comparison across industries |
| Evaluates financial health |
| Facilitates informed investment decisions |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
