Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) Definition
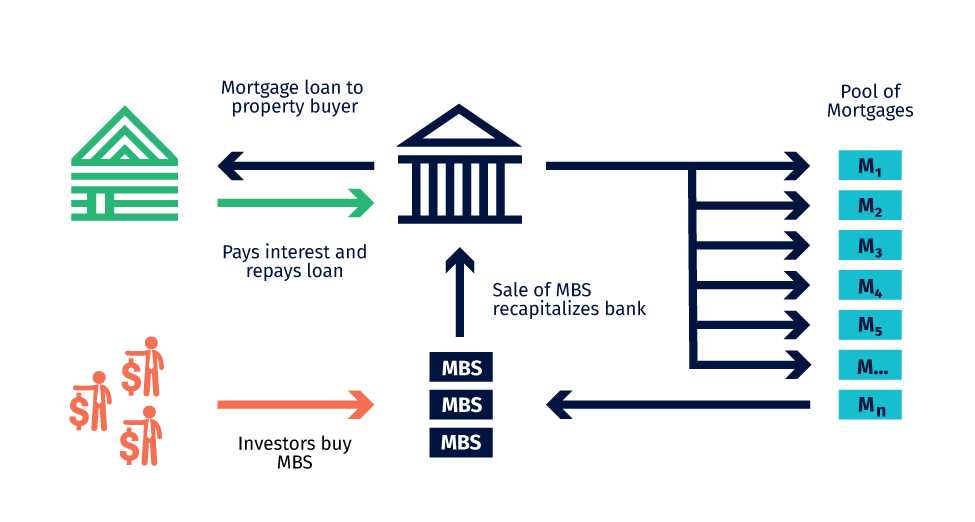
Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) are financial instruments that represent an ownership interest in a pool of mortgage loans. These loans are typically issued by banks, mortgage lenders, or other financial institutions and are backed by real estate properties. MBS are created by packaging individual mortgage loans together and selling them to investors as a single security.
How MBS Work
When a borrower takes out a mortgage loan, they make monthly payments that consist of both principal and interest. These payments are then collected by the mortgage lender. In order to generate liquidity and manage risk, mortgage lenders sell these loans to investment banks or government-sponsored enterprises, such as Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac.
Types of MBS
There are several types of MBS, including:
- Pass-Through Securities: These are the most common type of MBS. Investors receive a pro-rata share of the principal and interest payments made by the borrowers.
- Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs): These are structured MBS that divide the cash flows into different tranches, each with its own risk and return characteristics.
- Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities: These are MBS that separate the principal and interest payments into separate securities, allowing investors to choose the type of cash flow they prefer.
These different types of MBS provide investors with various options to match their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Overall, Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) provide investors with an opportunity to invest in the real estate market without directly owning properties. They offer a predictable income stream and can be a valuable addition to a diversified investment portfolio.
How MBS Work
When a borrower takes out a mortgage loan, they make regular payments to the lender, which typically includes both interest and principal. These payments are then collected by a mortgage servicer, who acts as an intermediary between the borrower and the investor.
The mortgage servicer is responsible for collecting the payments from the borrowers and distributing them to the investors. In the case of MBS, the servicer collects the payments from the homeowners and then distributes them to the investors based on their ownership share in the pool of mortgage loans.
Investors in MBS can choose between different types of securities, such as pass-through securities or collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs). Pass-through securities provide investors with a pro-rata share of the cash flows from the underlying mortgage loans, while CMOs offer different classes of securities with varying levels of risk and return.
Benefits of Investing in MBS
Investing in MBS offers several benefits:
- Income Generation: MBS provide a steady stream of income through the interest and principal payments made by the homeowners.
- Diversification: MBS allow investors to diversify their investment portfolio by adding exposure to the real estate market.
- Relative Safety: MBS are backed by the cash flows from the underlying mortgage loans, providing a level of safety compared to other types of investments.
- Liquidity: MBS are traded on the secondary market, providing investors with the ability to buy and sell their investments as needed.
Overall, investing in MBS can be a profitable and relatively safe investment strategy, offering a combination of income generation, diversification, and liquidity.
Types of Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) are financial instruments that are created by pooling together a group of mortgage loans. These securities are then sold to investors, who receive regular payments based on the interest and principal payments made by the borrowers of the underlying mortgage loans.
There are several types of MBS, each with its own unique characteristics:
1. Pass-Through Securities
2. Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs)
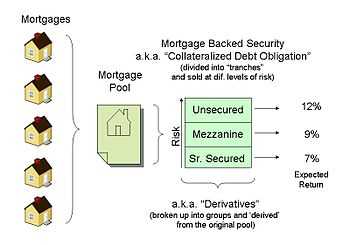
Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs) are structured MBS that offer different classes, or tranches, of securities to investors. Each tranche has a different priority of receiving cash flows and bears a different level of risk. The cash flows from the underlying mortgage loans are divided among the tranches based on a predetermined set of rules. CMOs allow investors to choose the level of risk and return that best suits their investment objectives.
CMOs are often divided into two main types:
a. Sequential-Pay CMOs:
b. Planned Amortization Class (PAC) CMOs:
PAC CMOs provide investors with a more stable cash flow stream by protecting the tranches from prepayment risk. Prepayment risk is the risk that borrowers will pay off their mortgage loans earlier than expected, which can disrupt the cash flow distribution to the tranches. PAC CMOs achieve this by creating a support tranche that absorbs the excess prepayments, allowing the other tranches to receive a more stable cash flow.
3. Stripped Mortgage-Backed Securities

Overall, the different types of MBS offer investors a range of options to invest in the mortgage market, with varying levels of risk and return. It is important for investors to carefully consider their investment objectives and risk tolerance before investing in MBS.
Investment in Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
Investing in Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) can be a lucrative opportunity for investors looking to diversify their portfolios and generate steady income. MBS are investment products that are backed by a pool of mortgage loans, which are typically issued by financial institutions such as banks or mortgage lenders.
When you invest in MBS, you essentially become a shareholder in the underlying mortgage loans. As homeowners make their monthly mortgage payments, you receive a portion of the interest and principal payments as income. This makes MBS an attractive investment option for those seeking regular cash flow.
One of the key advantages of investing in MBS is the potential for higher yields compared to other fixed-income investments. Since MBS are backed by a pool of mortgage loans, they offer higher interest rates than traditional bonds or Treasury securities. This can be especially beneficial in a low-interest-rate environment, as it allows investors to earn a higher return on their investment.
Additionally, investing in MBS provides investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios. By adding MBS to your investment mix, you can reduce the overall risk of your portfolio by spreading it across different asset classes. This can help protect your investments from the volatility of the stock market and provide a more stable return.
Another risk is the potential for default on the underlying mortgage loans. If a large number of homeowners default on their mortgages, it can lead to a decrease in the value of the MBS and a loss of income for investors.
Benefits of Investing in MBS
Investing in Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) can offer several benefits for investors:
1. Diversification
MBS provide an opportunity for diversification within an investment portfolio. By investing in MBS, investors can spread their risk across a pool of mortgages, rather than investing in individual mortgages. This diversification can help reduce the impact of any single mortgage default on the overall investment.
2. Regular Income
MBS typically pay regular income to investors in the form of interest payments. These payments are generated from the mortgage payments made by homeowners. This regular income can be attractive to investors seeking a consistent cash flow.
3. Potential for Higher Yields
MBS often offer higher yields compared to other fixed-income investments, such as government bonds. This higher yield is due to the additional risk associated with mortgage-backed securities. Investors who are willing to take on this additional risk may be rewarded with higher returns.
4. Liquidity
MBS are traded on the secondary market, which provides investors with the ability to buy and sell their investments relatively easily. This liquidity can be advantageous for investors who may need to access their funds quickly.
5. Government Support
MBS are backed by government-sponsored entities, such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, which provide a level of guarantee on the underlying mortgages. This government support can help mitigate some of the risks associated with investing in MBS.
Overall, investing in Mortgage-Backed Securities can offer diversification, regular income, potential for higher yields, liquidity, and government support. However, it is important for investors to carefully evaluate the risks and conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
Risks of Investing in MBS
Investing in Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS) can offer attractive returns, but it is important to be aware of the risks involved. Here are some of the key risks to consider:
| 1. Interest Rate Risk | MBS prices are sensitive to changes in interest rates. When interest rates rise, the value of MBS tends to decline, and vice versa. This can result in potential losses for investors. |
| 2. Prepayment Risk | MBS are backed by a pool of mortgage loans, and borrowers have the option to prepay their mortgages. When interest rates fall, borrowers may choose to refinance their mortgages, resulting in early repayment of the underlying loans. This can lead to a decrease in the expected cash flows for MBS investors. |
| 3. Credit Risk | MBS are subject to credit risk, which is the risk that borrowers may default on their mortgage payments. If a significant number of borrowers default, it can lead to losses for MBS investors. |
| 4. Liquidity Risk | MBS can be less liquid compared to other investments. This means that it may be more difficult to buy or sell MBS at desired prices, especially during times of market stress. Illiquidity can limit an investor’s ability to exit a position or take advantage of investment opportunities. |
| 5. Market Risk | MBS are subject to market risk, which is the risk of overall market fluctuations. Factors such as economic conditions, investor sentiment, and geopolitical events can impact the performance of MBS. |
It is important to carefully assess these risks and consider your risk tolerance before investing in MBS. Diversification and thorough research can help mitigate some of these risks, but it is important to consult with a financial advisor or investment professional to make informed investment decisions.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
