Big Data: Definition and Importance
Definition of Big Data
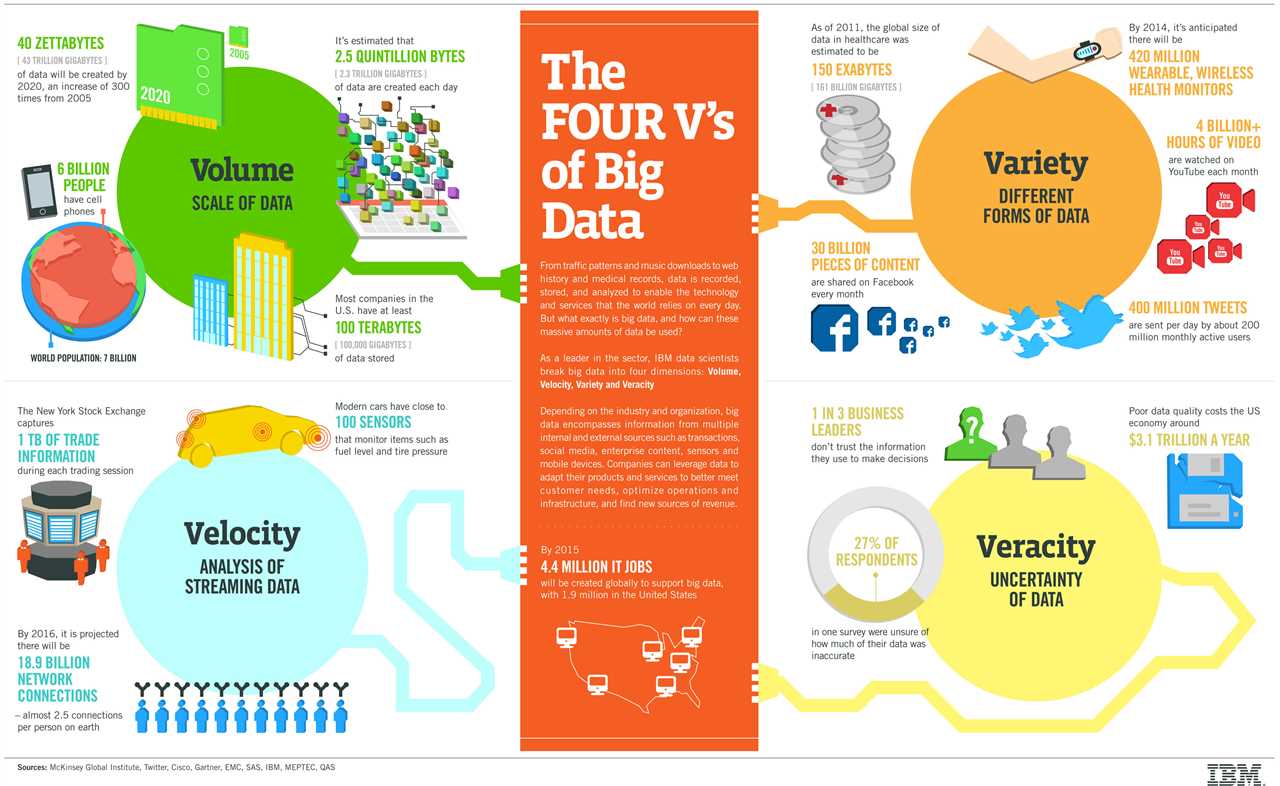
Big Data is characterized by the three Vs: volume, variety, and velocity. Volume refers to the vast amount of data generated from various sources, such as social media platforms, sensors, and online transactions. Variety refers to the diverse types of data, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Velocity refers to the speed at which data is generated and needs to be processed in real-time or near real-time.
Importance of Big Data
Big Data plays a crucial role in various industries and sectors, including business, healthcare, finance, and government. Here are some key reasons why Big Data is important:
| 1. Data-driven decision making: | Big Data provides valuable insights and patterns that can help businesses make informed decisions. By analyzing large datasets, organizations can identify trends, customer preferences, and market opportunities. |
| 2. Improved operational efficiency: | Big Data analytics can optimize business processes, improve resource allocation, and enhance overall operational efficiency. By analyzing data in real-time, organizations can identify bottlenecks, streamline operations, and reduce costs. |
| 3. Personalized customer experiences: | Big Data enables businesses to understand their customers better and provide personalized experiences. By analyzing customer data, organizations can tailor their products, services, and marketing campaigns to individual preferences and needs. |
| 4. Fraud detection and prevention: | Big Data analytics can help identify patterns and anomalies that indicate fraudulent activities. By analyzing large volumes of data in real-time, organizations can detect and prevent fraud, protecting their assets and customers. |
| 5. Scientific research and innovation: |
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to the vast amount of structured and unstructured data that is generated from various sources such as social media, sensors, mobile devices, and other digital platforms. This data is characterized by its volume, velocity, and variety, which makes it difficult to manage and analyze using traditional data processing methods.
Big Data can be categorized into three types:
Structured Data:
This type of data is highly organized and can be easily stored, accessed, and analyzed using traditional databases. It includes data from spreadsheets, relational databases, and other structured sources.
Unstructured Data:
This type of data does not have a predefined structure and is often in the form of text, images, videos, and social media posts. It requires advanced analytics techniques to extract meaningful insights from it.
Big Data is also characterized by its velocity, which refers to the speed at which data is generated and processed. With the advent of technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT), data is being generated at an unprecedented rate, requiring real-time processing and analysis.
The variety of data in Big Data refers to the different formats and types of data that are being generated. It includes structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, as well as data from various sources such as social media, sensors, and mobile devices.
Overall, Big Data is a term used to describe the massive amount of data that is being generated and collected from various sources. It poses challenges in terms of storage, processing, and analysis, but also offers immense opportunities for businesses and organizations to gain valuable insights and make data-driven decisions.
Why is Big Data Important?
Big Data has become a crucial aspect of modern businesses and organizations. Its importance lies in its ability to provide valuable insights and drive informed decision-making. Here are some reasons why Big Data is important:
1. Enhanced Decision Making
Big Data allows businesses to make data-driven decisions by analyzing large volumes of structured and unstructured data. It provides insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency, enabling organizations to identify opportunities and make informed decisions.
2. Improved Customer Experience
3. Cost Optimization
Big Data analytics can help businesses optimize their operations and reduce costs. By analyzing data related to supply chain management, production processes, and resource allocation, organizations can identify inefficiencies and make improvements that lead to cost savings.
4. Competitive Advantage
5. Risk Management
Big Data analytics can help organizations identify and mitigate risks. By analyzing data from various sources, such as financial transactions, social media, and customer feedback, businesses can detect potential risks and take proactive measures to prevent or minimize their impact.
6. Innovation and Research
Big Data plays a crucial role in driving innovation and research. By analyzing large datasets, researchers can uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that can lead to new discoveries and advancements in various fields, such as healthcare, finance, and technology.
Working Mechanism of Big Data
Big Data refers to the vast amount of structured and unstructured data that is generated from various sources such as social media, sensors, and other digital platforms. The working mechanism of Big Data involves several steps to process and analyze this massive amount of data efficiently.
Data Collection
The first step in the working mechanism of Big Data is data collection. This involves gathering data from various sources such as websites, social media platforms, mobile devices, and sensors. The collected data can be in different formats, including text, images, videos, and audio.
Data Storage
Once the data is collected, it needs to be stored in a suitable format for further processing and analysis. Big Data storage systems are designed to handle large volumes of data and provide high-speed access. These systems can be distributed across multiple servers or cloud-based platforms to ensure scalability and reliability.
Data Processing
After the data is stored, it needs to be processed to extract meaningful insights. This involves various techniques such as data cleaning, transformation, and integration. Data cleaning removes any inconsistencies or errors in the data, while transformation and integration help in combining different datasets for analysis.
Data Analysis
Once the data is processed, it can be analyzed using various techniques such as statistical analysis, data mining, and machine learning. These techniques help in identifying patterns, trends, and correlations within the data, which can be used for making informed decisions and predictions.
Data Visualization

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
