Corporate Governance: Definition and Principles
Corporate governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. It encompasses the relationships between various stakeholders, such as shareholders, management, employees, customers, and the community. The primary objective of corporate governance is to ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in the decision-making process and to protect the interests of all stakeholders.
Definition of Corporate Governance
Principles of Corporate Governance
There are several key principles that underpin effective corporate governance:
- Accountability: Companies should be accountable to their shareholders and other stakeholders for their actions and decisions.
- Transparency: Companies should provide accurate, timely, and relevant information to shareholders and other stakeholders.
- Responsibility: Companies should act responsibly and ethically, taking into consideration the interests of all stakeholders.
- Independence: Companies should have independent directors who can provide objective and impartial advice.
- Fairness: Companies should treat all shareholders and stakeholders fairly and equitably.
These principles help to establish a framework for good corporate governance practices, which in turn can contribute to the long-term success and sustainability of a company.
What is Corporate Governance?
Corporate governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. It encompasses the relationships between the various stakeholders involved in the company, such as shareholders, management, employees, customers, suppliers, and the community.
The main objective of corporate governance is to ensure transparency, accountability, and fairness in the company’s operations. It provides a framework for decision-making and establishes the mechanisms through which the interests of different stakeholders are protected.
Importance of Corporate Governance

Effective corporate governance is crucial for the long-term success and sustainability of a company. It helps to build trust and confidence among investors, as well as other stakeholders, by ensuring that the company is being managed in a responsible and ethical manner.
Good corporate governance practices can also contribute to the company’s financial performance. By promoting transparency and accountability, it reduces the risk of fraud, corruption, and mismanagement, which can have a negative impact on the company’s reputation and profitability.
Principles of Corporate Governance
There are several key principles that underpin good corporate governance:
- Accountability: Companies should be accountable to their shareholders and other stakeholders for their actions and decisions.
- Transparency: Companies should provide accurate and timely information to shareholders and other stakeholders, ensuring transparency in their operations.
- Responsibility: Companies should act in a responsible and ethical manner, taking into consideration the interests of all stakeholders.
- Independence: The board of directors should be independent and free from conflicts of interest, ensuring objective decision-making.
- Fairness: Companies should treat all shareholders and stakeholders fairly and equally, without favoritism or discrimination.
By adhering to these principles, companies can enhance their corporate governance practices and create a culture of trust, integrity, and accountability.
Principles of Corporate Governance

Corporate governance refers to the system of rules, practices, and processes by which a company is directed and controlled. It involves balancing the interests of various stakeholders such as shareholders, management, customers, suppliers, financiers, government, and the community.
1. Transparency
Transparency is a fundamental principle of corporate governance. It involves providing accurate and timely information to shareholders and stakeholders about the company’s financial performance, operations, and decision-making processes. This includes disclosing relevant information in annual reports, financial statements, and other public disclosures.
2. Accountability
Accountability is another key principle of corporate governance. It involves holding the board of directors and management accountable for their actions and decisions. This includes establishing clear lines of responsibility and ensuring that individuals are held responsible for their performance. Accountability also extends to external auditors, who are responsible for providing an independent assessment of the company’s financial statements.
3. Fairness
Fairness is an important principle in corporate governance. It involves treating all shareholders and stakeholders fairly and equitably. This includes ensuring that minority shareholders are protected and that their rights are respected. Fairness also extends to the company’s dealings with employees, customers, suppliers, and the community.
4. Independence
Independence is a crucial principle in corporate governance. It involves having an independent board of directors that is free from conflicts of interest and can make decisions in the best interests of the company and its shareholders. Independence also extends to external auditors, who should be independent and objective in their assessment of the company’s financial statements.
5. Responsibility
Responsibility is a core principle of corporate governance. It involves taking responsibility for the company’s actions and their impact on society and the environment. This includes implementing sustainable and ethical business practices, managing risks effectively, and complying with applicable laws and regulations. Responsibility also extends to engaging with stakeholders and addressing their concerns.
6. Effectiveness
Effectiveness is a key principle in corporate governance. It involves ensuring that the board of directors and management are effective in their roles and responsibilities. This includes having a diverse and independent board that provides strategic guidance and oversight. Effectiveness also involves having a strong corporate culture and ethical standards that promote integrity and accountability.
Corporate Governance Models and Examples
1. The Shareholder Model
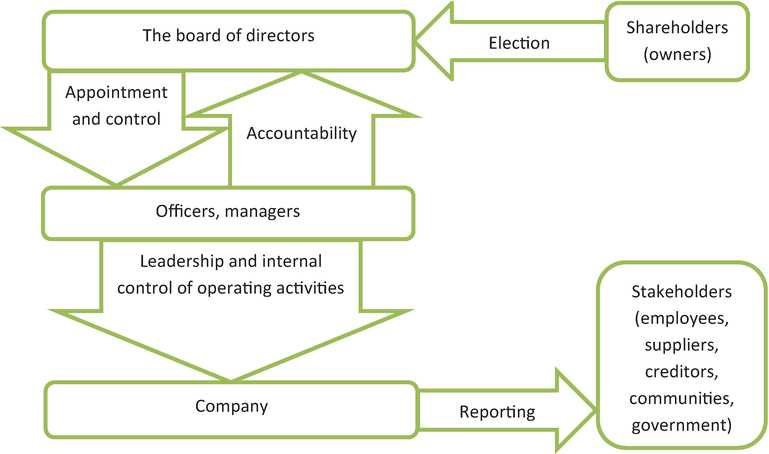
The shareholder model is one of the most widely recognized corporate governance models. It emphasizes the interests of shareholders and their rights to influence decision-making processes. Under this model, the board of directors is responsible for representing the shareholders’ interests and ensuring that the company operates in their best interest. Examples of companies that follow the shareholder model include Apple Inc., Microsoft Corporation, and Berkshire Hathaway.
2. The Stakeholder Model
3. The Board-Centric Model

In the board-centric model, the board of directors plays a central role in corporate governance. It is responsible for making key decisions, overseeing management, and ensuring compliance with regulations. This model is commonly found in non-profit organizations and government agencies. Examples include the World Health Organization (WHO), the United Nations (UN), and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
4. The Family-Owned Model
5. The Hybrid Model
The hybrid model combines elements from different corporate governance models to create a customized approach that suits the specific needs of a company. It takes into account the unique characteristics and challenges faced by the organization. Many companies adopt a hybrid model by incorporating elements from the shareholder and stakeholder models. Examples of companies following the hybrid model include Google (Alphabet Inc.), General Electric, and Procter & Gamble.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
