What Is a Brokerage Account: Definition, How to Choose, and Types
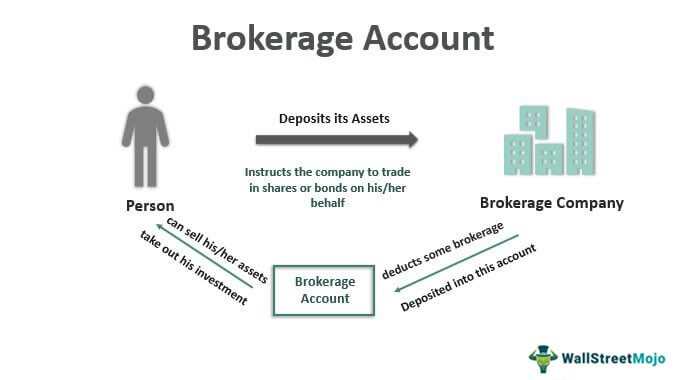
A brokerage account is a type of financial account that allows individuals to buy and sell various types of securities, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It serves as a platform for investors to access the stock market and other investment opportunities.
When choosing a brokerage account, there are several factors to consider. First, you’ll want to assess the fees and commissions associated with the account. Some brokers charge a flat fee per trade, while others have a tiered pricing structure based on the size of the trade. You should also consider the account minimums and any additional account maintenance fees.
Another important factor to consider is the types of investments available through the brokerage account. Different brokers may specialize in certain types of securities or offer a wider range of investment options. Consider your investment goals and preferences to determine which brokerage account offers the most suitable investment opportunities for you.
Additionally, it’s essential to evaluate the trading platform and tools provided by the brokerage. A user-friendly interface, real-time market data, and research tools can greatly enhance your trading experience. Look for a brokerage that offers a robust trading platform with the features and tools you need to make informed investment decisions.
Lastly, consider the level of customer support and educational resources offered by the brokerage. A reputable brokerage should provide responsive customer service and educational materials to help you navigate the world of investing. Look for resources such as tutorials, webinars, and market analysis to support your investment journey.
A brokerage account is a type of financial account that allows individuals to buy and sell various types of securities, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). It serves as a platform for investors to access the financial markets and participate in trading activities.
When opening a brokerage account, individuals typically work with a brokerage firm or a stockbroker, who acts as an intermediary between the investor and the financial markets. The brokerage firm provides the necessary infrastructure and tools for investors to execute trades, manage their portfolios, and access market research and analysis.
Brokerage accounts offer several key features and benefits. Firstly, they provide liquidity, allowing investors to easily buy and sell securities. This flexibility enables investors to take advantage of market opportunities and respond to changing market conditions. Additionally, brokerage accounts offer diversification, as investors can choose from a wide range of investment options, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
Brokerage accounts also provide access to valuable research and analysis tools. Many brokerage firms offer their clients access to market research reports, financial news, and investment analysis from their team of experts. This information can help investors make informed decisions and stay updated on market trends.
It’s worth noting that brokerage accounts come in different types, including individual brokerage accounts, joint brokerage accounts, custodial accounts for minors, and retirement accounts such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and 401(k) accounts. Each type of account has its own set of rules and regulations, as well as tax implications.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Brokerage Account
- Investment Options: Consider the range of investment options offered by the brokerage account. Some brokerage accounts may specialize in certain types of investments, such as stocks, bonds, or mutual funds, while others may offer a wider range of investment choices. Make sure the brokerage account provides the investment options that align with your financial goals.
- Account Minimums: Some brokerage accounts require a minimum deposit to open an account. Consider whether you can meet the minimum deposit requirements and if it aligns with your investment budget.
- Customer Service: Look for a brokerage account that offers excellent customer service. This includes responsive support, easy access to account information, and helpful educational resources. Good customer service can make a significant difference, especially for beginners who may need guidance and support.
- Trading Tools and Platform: Consider the trading tools and platform offered by the brokerage account. A user-friendly and intuitive trading platform can make it easier to execute trades and monitor your investments. Look for features such as real-time market data, research tools, and customizable charts.
- Security: Ensure that the brokerage account has robust security measures in place to protect your personal and financial information. Look for features such as two-factor authentication and encryption to safeguard your account.
- Additional Services: Some brokerage accounts offer additional services such as retirement planning, tax advice, and access to initial public offerings (IPOs). Consider whether these additional services align with your needs and goals.
By carefully considering these key factors, you can choose a brokerage account that best suits your investment needs and preferences. Remember to research and compare different brokerage firms to make an informed decision.
Types of Brokerage Accounts: Exploring Your Options
1. Individual Brokerage Account: This is the most common type of brokerage account and is designed for individual investors. It allows you to buy and sell securities in your own name and gives you full control over your investment decisions.
2. Joint Brokerage Account: A joint brokerage account is opened by two or more individuals, such as spouses or business partners. It allows multiple individuals to contribute funds and make investment decisions together.
3. Margin Account: A margin account is a type of brokerage account that allows you to borrow money from the broker to purchase securities. This can increase your buying power and potentially enhance your investment returns, but it also comes with additional risks.
4. Retirement Account: Retirement accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) and 401(k)s, can also be opened as brokerage accounts. These accounts offer tax advantages and are designed to help individuals save for retirement.
5. Cash Account: A cash account is a basic type of brokerage account where you can only trade with the cash available in your account. This account does not allow you to borrow money from the broker, which can help you avoid excessive debt and interest charges.
6. Managed Account: A managed account is a type of brokerage account where a professional money manager makes investment decisions on your behalf. This can be a good option for individuals who prefer a hands-off approach to investing.
Comparing Different Stock Brokers: Finding the Right Fit
- Investment Options: Different brokers may offer different investment options, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, and more. Consider the types of investments you are interested in and choose a broker that offers those options.
- Research and Tools: Look for brokers that offer robust research and analysis tools to help you make informed investment decisions. These tools can include stock screeners, market analysis, and educational resources.
- Customer Service: Consider the level of customer service offered by different brokers. Look for brokers that provide responsive and helpful customer support, whether it’s through phone, email, or online chat.
- Mobile App: If you prefer to manage your investments on the go, consider brokers that offer a user-friendly mobile app. A mobile app can make it easier to monitor your investments and execute trades from anywhere.
- Security: Ensure that the broker you choose has strong security measures in place to protect your personal and financial information. Look for brokers that are regulated by reputable financial authorities.
- Account Types: Consider the different types of brokerage accounts offered by different brokers. These can include individual brokerage accounts, joint accounts, retirement accounts, and more. Choose a broker that offers the account types that align with your investment goals.
- Additional Services: Some brokers may offer additional services, such as financial planning, tax advice, or access to initial public offerings (IPOs). Consider whether these additional services are important to you and choose a broker accordingly.
By carefully comparing these factors, you can find the stock broker that best meets your investment needs and preferences. Remember to consider your own investment goals, risk tolerance, and trading style when making your decision. Happy investing!

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
