Oversubscribed Definition: What Does It Mean?
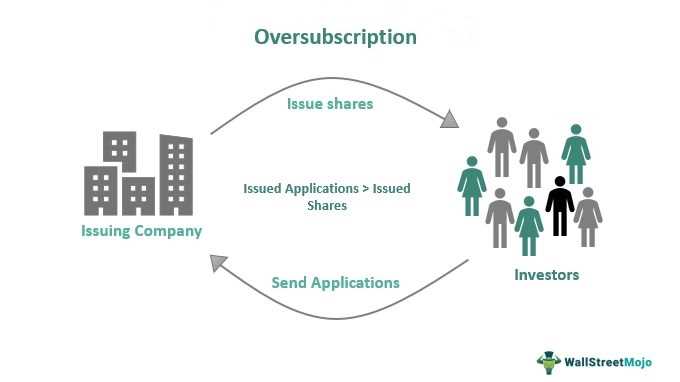
Oversubscription is a term used in the financial world to describe a situation where the demand for a particular investment or offering exceeds the available supply. It occurs when the number of investors or buyers seeking to participate in an initial public offering (IPO), for example, is greater than the number of shares or securities being offered.
When an investment or offering is oversubscribed, it indicates a high level of interest and demand from investors. This can be seen as a positive sign for the company or organization issuing the investment, as it suggests that there is strong market interest and potential for success.
Oversubscription is a significant concept in the financial world because it can have both positive and negative implications. On one hand, it can indicate strong market demand and investor confidence in the investment or offering. This can lead to increased share prices and a successful IPO or fundraising campaign.
On the other hand, oversubscription can also create challenges for companies and organizations. It can lead to allocation issues, where not all investors are able to receive their desired allocation of shares or securities. This can result in disappointment and potentially negative sentiment among investors.
Overall, oversubscription is an important concept to understand in the financial world, as it can have significant implications for both investors and companies. It is a reflection of market demand and can impact the success and perception of an investment or offering.
Oversubscription is a term used in finance to describe a situation where the demand for a particular investment exceeds the supply available. This phenomenon typically occurs during initial public offerings (IPOs), where investors are eager to buy shares in a newly listed company.
When a company decides to go public and offer its shares to the public for the first time, it sets a certain number of shares to be sold. However, if the demand for these shares exceeds the number available, the IPO becomes oversubscribed. This means that there are more investors willing to buy shares than there are shares available.
The significance of oversubscription lies in the fact that it indicates a high level of investor interest and confidence in the company. It suggests that investors believe the company has strong growth potential and that its shares are likely to increase in value. This can be seen as a positive signal for the company and may attract more investors in the future.
Oversubscription can also have implications for the pricing of the shares. When a company is oversubscribed, it may choose to increase the price of the shares to meet the high demand. This can result in higher profits for the company and its existing shareholders.
Factors Contributing to Oversubscription
There are several factors that can contribute to oversubscription in an IPO:
- Strong market sentiment: If the overall market is performing well and investor sentiment is positive, it can create a favorable environment for oversubscription.
- Perceived growth potential: Investors are more likely to oversubscribe to an IPO if they believe the company has strong growth potential and can deliver attractive returns.
- Limited supply: When the number of shares available for sale is limited, it can create a sense of scarcity and drive up demand.
- Investor confidence: If investors have confidence in the management team and the company’s business model, they may be more willing to oversubscribe to the IPO.
Implications and Risks of Oversubscription
While oversubscription can be seen as a positive sign for a company, it also carries certain implications and risks:
Price volatility: If the demand for shares exceeds the supply by a significant margin, it can lead to price volatility in the secondary market. This can create risks for both the company and the investors.
Regulatory scrutiny: Oversubscription can attract regulatory scrutiny, as it may raise concerns about market manipulation or unfair practices. Companies need to ensure that their IPO process is transparent and compliant with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
Example of Oversubscription in Practice
Oversubscription is a phenomenon that often occurs in the financial markets, particularly during initial public offerings (IPOs). To understand how oversubscription works, let’s look at a real-world example.
Company XYZ’s IPO
Imagine that Company XYZ, a technology startup, plans to go public and offers its shares to the public for the first time. The company sets a price range for its shares, say $10 to $12 per share, and intends to sell 10 million shares.
Investors who are interested in buying shares of Company XYZ can submit their orders to their brokers or through online trading platforms. However, the demand for Company XYZ’s shares far exceeds the number of shares available.
Allotment and Allocation
In an oversubscribed IPO, the company and its underwriters need to decide how to allocate the limited number of shares among the interested investors. Typically, they use a pro-rata allotment method to distribute the shares.
Using the example of Company XYZ, if an investor requested 1,000 shares and the oversubscription factor is 3, they would receive 333 shares (1,000 divided by 3). This ensures that each investor receives a proportionate share of the available shares.
Implications for Investors
Oversubscription can have both positive and negative implications for investors. On one hand, it indicates high demand for the company’s shares, which can be seen as a positive signal for the company’s prospects. It also creates a sense of exclusivity, as not all investors who wanted to buy shares were able to do so.
Conclusion
| Benefits of Oversubscription | Costs of Oversubscription |
|---|---|
| – Indicates high demand for company’s shares | – Disappointment for investors who are not allocated desired shares |
| – Creates a sense of exclusivity | – Share price volatility in the aftermarket |
| – Positive signal for company’s prospects |
Real-world Case Study Highlighting the Phenomenon
One real-world case study that highlights the phenomenon of oversubscription is the initial public offering (IPO) of a popular tech company. Let’s take the example of Company X, a highly anticipated tech startup that plans to go public.
Company X has gained significant attention and has a strong reputation in the industry. As a result, there is a high demand from investors who want to participate in the IPO and become shareholders of the company.
When the IPO is announced, the company sets a certain number of shares to be offered to the public. However, due to the overwhelming interest and demand, the number of shares requested by investors exceeds the number of shares available.
As a result, the IPO becomes oversubscribed. This means that there are more investors willing to buy shares than there are shares available. In such a scenario, the company and its underwriters need to determine how to allocate the limited number of shares.
In the case of Company X, the oversubscription of its IPO indicates the high level of confidence and interest from investors. It also reflects the market’s belief in the company’s potential for growth and profitability.
This case study highlights the significance of oversubscription in the context of IPOs and how it can be a positive indicator for a company’s future prospects. It demonstrates the strong demand for the company’s shares and the potential for a successful public offering.
Overall, this real-world example showcases the impact of oversubscription on a company’s IPO and the importance of managing the allocation process effectively to ensure fairness and maximize the benefits for both the company and its investors.
Costs Associated with Oversubscription

Oversubscription can come with various costs that businesses need to consider. These costs can include:
1. Increased production costs:
When a product or service is oversubscribed, the demand exceeds the supply. This can lead to increased production costs as businesses may need to ramp up their production capacity to meet the high demand. This can involve investing in additional equipment, hiring more staff, or outsourcing production, all of which can incur additional expenses.
2. Supply chain challenges:
Oversubscription can put a strain on the supply chain, especially if the demand surge is unexpected. Businesses may face challenges in sourcing raw materials, managing inventory, and coordinating logistics to meet the increased demand. These challenges can result in additional costs, such as expedited shipping fees or higher procurement costs.
3. Customer service and support:
With oversubscription, businesses may experience a higher volume of customer inquiries, complaints, and support requests. Meeting the increased customer service demands can require additional resources, such as hiring more customer support staff or investing in customer relationship management systems. These additional resources can add to the overall costs associated with oversubscription.
4. Marketing and advertising expenses:
When a product or service is oversubscribed, businesses may need to invest more in marketing and advertising to manage the high demand and maintain customer satisfaction. This can involve running additional campaigns, creating targeted promotions, or increasing advertising budgets. These marketing and advertising expenses can contribute to the overall costs of oversubscription.
5. Potential reputational risks:
Oversubscription can create reputational risks for businesses if they are unable to meet the high demand or deliver on customer expectations. This can result in negative reviews, customer dissatisfaction, and damage to the brand’s reputation. Rebuilding trust and repairing a damaged reputation can be costly and time-consuming.
Overall, while oversubscription can bring potential benefits, businesses need to carefully consider and manage the associated costs to ensure a successful and profitable outcome.
Exploring the Financial Implications of Oversubscription
Oversubscription, despite its potential benefits, can also have significant financial implications for both the company issuing the securities and the investors participating in the offering. It is important to understand these implications before deciding to invest in an oversubscribed offering.
1. Increased Demand and Higher Prices: When a securities offering is oversubscribed, it indicates a high demand for the company’s shares or bonds. This increased demand often leads to higher prices for the securities, as investors are willing to pay more to secure their allocation. As a result, investors may need to pay a premium to participate in the oversubscribed offering.
2. Allocation and Scaling Back: In an oversubscribed offering, the company may not be able to fulfill the entire demand for its securities. This means that the allocation of securities to investors may be scaled back, resulting in a smaller allocation than anticipated. Investors should be prepared for the possibility of receiving a reduced allocation or not being able to participate at all.
3. Market Volatility: Oversubscribed offerings can create market volatility, especially if the demand significantly exceeds the supply of securities. This volatility can affect the price of the securities both during and after the offering. Investors should be aware of the potential for price fluctuations and be prepared for the associated risks.
4. Liquidity Challenges: Investing in an oversubscribed offering may pose liquidity challenges for investors. If the securities are not easily tradable or if there is limited market liquidity, investors may face difficulties in selling their holdings or accessing their investment capital. It is important to consider the liquidity of the securities before investing in an oversubscribed offering.
5. Dilution of Ownership: In some cases, oversubscribed offerings may result in dilution of ownership for existing shareholders. If the company issues additional shares to meet the oversubscribed demand, the ownership percentage of existing shareholders may decrease. This dilution can impact the value of existing shares and should be taken into consideration when evaluating the financial implications of oversubscription.
6. Investor Suitability: Oversubscribed offerings may not be suitable for all types of investors. The financial implications, risks, and potential rewards associated with oversubscription should be carefully evaluated based on individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation. Investors should consult with their financial advisors to determine if participating in an oversubscribed offering aligns with their investment strategy.
Overall, while oversubscription can offer potential benefits such as increased demand and higher prices for securities, it is important to carefully consider the financial implications and associated risks before deciding to invest in an oversubscribed offering.
Benefits of Oversubscription
Oversubscription can bring several benefits to companies and investors alike. Here are some of the key advantages:
1. Increased Demand and Market Perception
When a company’s initial public offering (IPO) is oversubscribed, it creates a perception of high demand for the company’s shares. This can generate positive market sentiment and increase the company’s perceived value. Investors may view an oversubscribed IPO as a sign of potential growth and profitability, leading to increased interest in the company’s stock.
2. Higher Stock Price
Oversubscription can drive up the price of a company’s stock. As more investors compete for a limited number of shares, the demand exceeds the supply, resulting in an increase in the stock price. This can benefit both the company and its existing shareholders by increasing their wealth and market capitalization.
3. Access to Capital
An oversubscribed IPO can provide a company with significant capital to fund its growth and expansion plans. The additional funds raised through the oversubscription can be used for research and development, marketing, acquisitions, or other strategic initiatives. This influx of capital can help accelerate the company’s growth and enhance its competitive position in the market.
4. Enhanced Company Profile
5. Increased Liquidity

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
