Distributed Ledgers: A Comprehensive Guide to Definition, Uses, and Potential
A distributed ledger is a type of database that is shared and synchronized across multiple nodes or computers in a network. It is designed to provide a decentralized and transparent system for recording and verifying transactions or any other form of data.
One of the key features of distributed ledgers is their ability to maintain a consistent and tamper-proof record of all transactions. This is achieved through the use of cryptographic algorithms and consensus mechanisms, which ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of each transaction.
Definition and Key Concepts
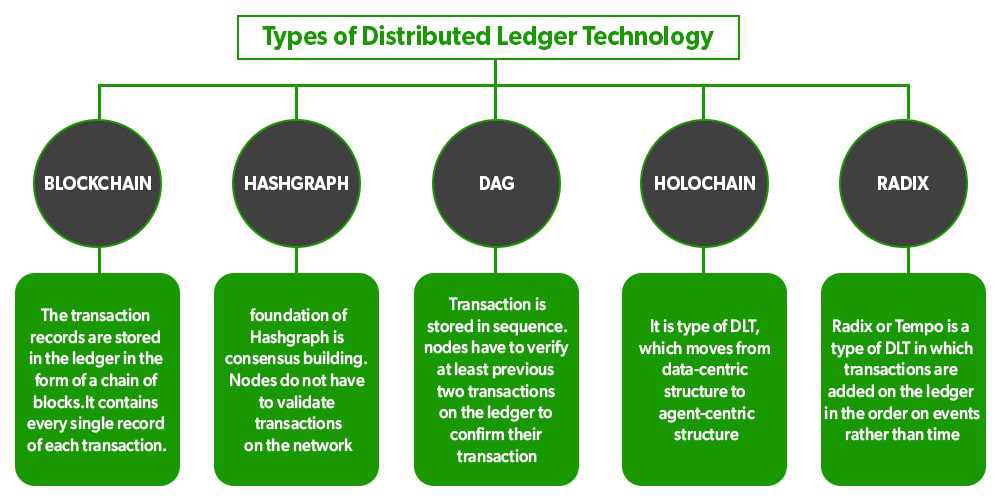
In a distributed ledger, data is stored in a series of blocks, with each block containing a list of transactions or data entries. These blocks are linked together in a chain-like structure, hence the term “blockchain”. Each block contains a unique identifier called a hash, which is generated based on the data it contains and the hash of the previous block.
One of the key concepts in distributed ledgers is the concept of consensus. Consensus mechanisms are used to ensure that all participants in the network agree on the validity of each transaction. There are different consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS), each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Exploring the Uses of Distributed Ledgers in Various Industries
Distributed ledgers have the potential to revolutionize various industries by providing a more efficient, secure, and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions. Some of the key industries that can benefit from distributed ledgers include:
- Finance and Banking: Distributed ledgers can streamline the process of cross-border payments, reduce fraud, and improve transparency in financial transactions.
- Supply Chain Management: Distributed ledgers can provide a transparent and traceable record of the movement of goods, which can help reduce fraud and improve efficiency in supply chain operations.
- Healthcare: Distributed ledgers can securely store and share patient records, ensuring privacy and improving the efficiency of healthcare systems.
- Real Estate: Distributed ledgers can streamline the process of property transactions, reduce fraud, and improve transparency in real estate transactions.
Unlocking the Potential of Distributed Ledgers: Future Developments and Challenges
While distributed ledgers have shown great promise, there are still challenges that need to be addressed for their widespread adoption. Some of the key challenges include scalability, interoperability, and regulatory concerns.
However, there are ongoing developments and research efforts to address these challenges and unlock the full potential of distributed ledgers. These include the development of new consensus mechanisms, the integration of distributed ledgers with other emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and Internet of Things, and the establishment of regulatory frameworks to ensure the legal and ethical use of distributed ledgers.
A distributed ledger is a type of database that is shared and synchronized across multiple locations or participants in a network. Unlike traditional centralized databases, distributed ledgers do not rely on a central authority or intermediary to validate and record transactions. Instead, they use consensus algorithms and cryptographic techniques to ensure the integrity and security of the data.
Key concepts of distributed ledgers include:
1. Decentralization:
Distributed ledgers are decentralized, meaning that there is no single point of control or failure. The data is stored and replicated across multiple nodes or computers in the network, making it more resilient to attacks and failures. This decentralized nature also allows for greater transparency and trust among participants.
2. Consensus:
In order to reach an agreement on the validity of transactions and the order in which they are recorded, distributed ledgers use consensus algorithms. These algorithms ensure that all participants in the network come to a mutual agreement, preventing double-spending and other fraudulent activities.
3. Immutability:
Once a transaction is recorded on a distributed ledger, it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability is achieved through cryptographic hashing, which creates a unique digital fingerprint for each transaction. Any attempt to tamper with the data would result in a mismatched hash, alerting the network to the fraudulent activity.
4. Smart Contracts:
Distributed ledgers can also support the execution of smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with the terms of the contract directly written into code. These contracts are automatically enforced and executed by the network, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud or error.
Overall, distributed ledgers offer a more secure, transparent, and efficient way of recording and verifying transactions. They have the potential to revolutionize various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, and more. By eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing a tamper-proof record of transactions, distributed ledgers can streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance trust among participants.
Exploring the Uses of Distributed Ledgers in Various Industries
1. Financial Services
The financial services industry is one of the primary sectors that can greatly benefit from distributed ledgers. Blockchain technology can streamline and automate processes such as cross-border payments, trade settlements, and identity verification. By eliminating intermediaries, distributed ledgers can reduce costs, increase transaction speed, and enhance security.
2. Supply Chain Management
Distributed ledgers can revolutionize supply chain management by providing transparency and traceability. With blockchain technology, every step of the supply chain can be recorded and verified, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of products. This can help prevent counterfeiting, improve inventory management, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
3. Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, distributed ledgers can improve data security and interoperability. By storing medical records on a blockchain, patients can have full control over their data and grant access to healthcare providers as needed. This can streamline the sharing of medical information, reduce errors, and improve patient care.
4. Real Estate
The real estate industry can benefit from distributed ledgers by simplifying property transactions and reducing fraud. With blockchain technology, property ownership records can be securely stored and verified, eliminating the need for intermediaries such as title companies. This can speed up the process of buying and selling properties and increase transparency in the market.
5. Energy
Distributed ledgers can play a significant role in the energy sector by enabling peer-to-peer energy trading and improving grid management. With blockchain technology, individuals and businesses can trade excess energy directly, reducing reliance on centralized energy providers. This can promote renewable energy adoption and increase energy efficiency.
These are just a few examples of how distributed ledgers can be applied in various industries. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative use cases and transformative impacts on different sectors.
Unlocking the Potential of Distributed Ledgers: Future Developments and Challenges

The potential of distributed ledgers, such as blockchain technology, is vast and continues to evolve. As industries and organizations explore the uses of distributed ledgers, there are several future developments and challenges that need to be addressed.
1. Scalability: One of the main challenges facing distributed ledgers is scalability. As more transactions are added to the ledger, the network can become slower and less efficient. Future developments will focus on improving scalability through various techniques, such as sharding and off-chain transactions.
2. Interoperability: Another challenge is interoperability between different distributed ledger systems. Currently, there are multiple blockchain platforms and protocols, making it difficult for them to communicate and share data. Future developments will aim to create standards and protocols that allow for seamless interoperability between different distributed ledgers.
5. Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating distributed ledgers with existing systems can be complex and challenging. Many organizations have legacy systems in place, and transitioning to distributed ledgers requires careful planning and coordination. Future developments will focus on creating tools and frameworks that facilitate seamless integration and migration, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of distributed ledgers without disrupting their existing operations.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
