Exploring the Concept of Equity
Equity is a fundamental concept in economics that refers to the fairness and justice in the distribution of resources and opportunities within a society. It is concerned with ensuring that everyone has an equal chance to succeed and that no one is disadvantaged due to their background or circumstances.
There are different dimensions of equity that economists consider when analyzing the distribution of resources. One dimension is equality of outcome, which focuses on ensuring that everyone receives the same level of resources, regardless of their individual contributions or abilities. Another dimension is equality of opportunity, which aims to provide everyone with an equal chance to succeed, regardless of their starting point.
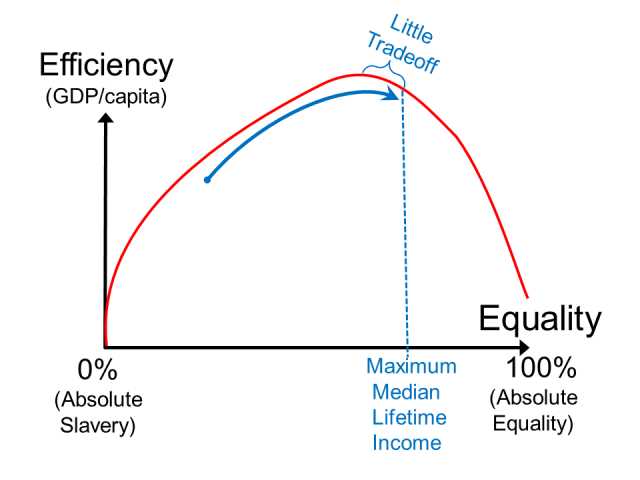
Equity is often contrasted with the concept of efficiency. While equity focuses on fairness, efficiency is concerned with maximizing productivity and output. There is often a tradeoff between equity and efficiency, as policies that promote greater equity may reduce incentives for individuals to work hard or innovate, potentially leading to lower overall productivity.
However, it is important to note that equity and efficiency are not necessarily mutually exclusive. In fact, some economists argue that greater equity can actually lead to greater efficiency in the long run. When everyone has access to education, healthcare, and other essential resources, they are more likely to be productive members of society, which can ultimately benefit the economy as a whole.
Types of Equity

There are several types of equity that economists consider when analyzing the distribution of resources:
- Income Equity: This refers to the fairness in the distribution of income among individuals or households. It aims to ensure that everyone has a sufficient level of income to meet their basic needs and participate in society.
- Gender Equity: This focuses on ensuring equal opportunities and treatment for individuals of different genders. It aims to eliminate gender-based discrimination and promote gender equality in all aspects of life.
- Racial Equity: This is concerned with eliminating racial discrimination and ensuring equal opportunities for individuals of different races or ethnicities. It aims to address historical injustices and promote racial equality.
These are just a few examples of the different types of equity that economists consider. Each type of equity has its own unique challenges and requires specific policies and interventions to address them.
Examining the Importance of Efficiency
Efficiency plays a crucial role in the functioning of any economic system. It refers to the ability to maximize output with the given resources and minimize waste. In the context of the equity-efficiency tradeoff, efficiency is often pitted against fairness, as prioritizing one aspect may come at the expense of the other.
Efficiency is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it leads to increased productivity. When resources are utilized efficiently, more goods and services can be produced, leading to economic growth and higher living standards. Efficient allocation of resources ensures that they are used in the most productive manner, resulting in optimal outcomes for businesses and consumers.
Efficiency also promotes innovation and technological advancement. When firms strive to be more efficient, they are incentivized to develop new technologies, processes, and techniques that can streamline production and reduce costs. This drive for efficiency fosters progress and drives economic development.
Furthermore, efficiency contributes to the overall competitiveness of an economy. In a globalized world, countries that can produce goods and services efficiently have a competitive advantage. Efficient economies can offer products at lower prices, attracting consumers and boosting exports. This competitiveness leads to increased trade and economic prosperity.
However, it is important to note that pursuing efficiency alone can have negative consequences. It can lead to income inequality, as those who are more productive and efficient may accumulate more wealth, while others may struggle to keep up. This is where the equity-efficiency tradeoff comes into play, as societies must strike a balance between efficiency and fairness.
Finding the Balance: The Tradeoff between Equity and Efficiency
The Importance of Equity
Equity plays a vital role in ensuring a just and equitable society. It focuses on the fair distribution of resources, opportunities, and benefits among individuals and groups. In an equitable system, everyone has equal access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, regardless of their background or socioeconomic status.
By promoting equity, societies can reduce income inequality and social disparities. This not only improves the quality of life for individuals but also fosters social cohesion and stability. When people feel that they are being treated fairly and have equal opportunities, they are more likely to trust and support the economic system.
The Significance of Efficiency
Efficiency, on the other hand, is essential for maximizing productivity and output within an economy. It focuses on utilizing resources in the most effective and optimal way, minimizing waste and inefficiencies. In an efficient system, goods and services are produced at the lowest cost possible, allowing for higher levels of economic growth and development.
Efficiency is crucial for maintaining competitiveness in a globalized world. It enables countries to produce goods and services at competitive prices, making them attractive to both domestic and international markets. Additionally, efficiency allows for the allocation of resources to their most productive uses, leading to innovation, technological advancements, and overall economic prosperity.
However, pursuing efficiency without considering equity can lead to negative consequences. If resources are allocated solely based on productivity and profitability, certain individuals or groups may be left behind, resulting in income inequality and social unrest. This can undermine the stability and sustainability of the economic system in the long run.
Finding the Balance
Striking the right balance between equity and efficiency is a complex task that requires careful consideration and policy-making. It involves designing economic systems and institutions that promote both fairness and productivity.
One approach is to implement progressive taxation systems that redistribute wealth from the rich to the poor. This helps to reduce income inequality and provide resources for social welfare programs, ensuring that everyone has access to basic necessities. Additionally, investing in education and skill development programs can help bridge the gap between different socioeconomic groups, promoting equal opportunities for all.
At the same time, it is important to foster an environment that encourages innovation, entrepreneurship, and productivity. This can be achieved by implementing policies that promote competition, remove barriers to entry, and provide incentives for research and development. By doing so, societies can ensure that resources are allocated efficiently and that economic growth is sustained.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
