Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) Definition Formula
Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) is a financial metric used to evaluate the value of a company’s stock. It is calculated by dividing the net current assets of a company by the number of outstanding shares.
Definition
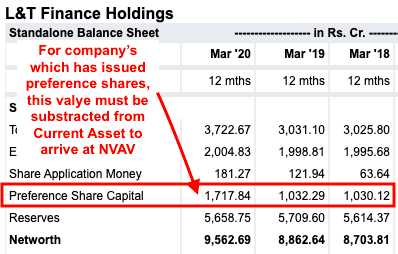
Net Current Assets refer to the current assets of a company minus its total liabilities. Current assets include cash, accounts receivable, and inventory, while total liabilities include both short-term and long-term debts.
The formula for calculating NCAVPS is:
NCAVPS is a conservative measure of a company’s value. It focuses on the liquidation value of a company, assuming that all assets are sold and all liabilities are paid off. It provides investors with an estimate of the minimum value of a company’s stock.
Investors often use NCAVPS as a value investing strategy. If the market price of a stock is significantly lower than its NCAVPS, it may indicate that the stock is undervalued and potentially a good investment opportunity.
Calculating NCAVPS
To calculate NCAVPS, you need to gather the financial statements of a company and determine its current assets, total liabilities, and number of outstanding shares. Once you have these values, you can plug them into the formula mentioned above to calculate the NCAVPS.
Importance of NCAVPS
NCAVPS provides investors with a conservative estimate of a company’s value. It helps identify potential undervalued stocks that may offer good investment opportunities. By comparing the market price of a stock to its NCAVPS, investors can make informed decisions about buying or selling stocks.
Additionally, NCAVPS can be used as a benchmark to evaluate a company’s financial health. If a company’s NCAVPS is consistently decreasing over time, it may indicate financial distress and potential risks for investors.
Limitations of NCAVPS
Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) is a financial metric used by investors to assess the value of a company’s shares based on its net current assets. It is derived by dividing the net current assets of a company by the number of outstanding shares.
Net current assets refer to the current assets of a company minus its total liabilities. Current assets are assets that can be easily converted into cash within a year, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. Liabilities, on the other hand, are the company’s obligations or debts that need to be paid within a year.
NCAVPS is considered a conservative measure of a company’s value because it focuses on the liquidation value of its assets. It assumes that a company’s assets can be sold off to pay its liabilities, and any remaining value would be distributed to shareholders.
Calculating NCAVPS
The formula to calculate NCAVPS is:
By using this formula, investors can determine the value of each share based on the company’s net current assets. A higher NCAVPS indicates that the company’s shares are undervalued, while a lower NCAVPS suggests that the shares may be overvalued.
Importance of NCAVPS
NCAVPS is important because it provides investors with a conservative estimate of a company’s value. It focuses on the company’s liquidation value, which can be useful in situations where a company is facing financial distress or bankruptcy. By comparing the NCAVPS to the current market price of a share, investors can identify potential investment opportunities.
Investors who follow the NCAVPS strategy look for companies whose shares are trading below their calculated NCAVPS. They believe that these companies are undervalued and have the potential for significant returns in the long run.
Limitations of NCAVPS
Additionally, NCAVPS does not consider intangible assets such as patents, brand value, or intellectual property, which can also contribute to a company’s overall value. Therefore, it is important for investors to consider other financial metrics and qualitative factors when making investment decisions.
Calculating Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS)
Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) is a financial metric used by investors to assess the value of a company’s shares. It is calculated by dividing the net current assets of a company by the number of outstanding shares.
The formula for calculating NCAVPS is as follows:
| Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) | = | / | Number of Outstanding Shares |
|---|
To calculate NCAVPS, you need to gather the necessary financial information from a company’s balance sheet. The current assets include cash, accounts receivable, and inventory, while the total liabilities include debts and other obligations.
Once you have the current assets and total liabilities, subtract the total liabilities from the current assets to get the net current assets. Then, divide the net current assets by the number of outstanding shares to obtain the NCAVPS.
For example, let’s say a company has $1,000,000 in current assets and $500,000 in total liabilities. The company also has 100,000 outstanding shares. To calculate the NCAVPS, you would subtract $500,000 from $1,000,000 to get $500,000 in net current assets. Then, divide $500,000 by 100,000 to get an NCAVPS of $5.
Calculating NCAVPS can help investors determine if a company’s shares are undervalued or overvalued. If the NCAVPS is higher than the current market price per share, it suggests that the shares may be undervalued and could be a good investment opportunity. On the other hand, if the NCAVPS is lower than the market price per share, it indicates that the shares may be overvalued.
Importance of Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS)
Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) is an important financial metric that investors use to assess the value of a company’s shares. It provides a conservative estimate of the company’s liquidation value and can be used as a tool for identifying potential investment opportunities.
1. Identifying Undervalued Stocks
One of the main reasons why NCAVPS is important is that it can help investors identify undervalued stocks. If a company’s NCAVPS is higher than its market price per share, it suggests that the stock may be undervalued. This means that the company’s assets, after deducting all liabilities, are worth more than the market is currently valuing the company.
2. Margin of Safety
NCAVPS also provides investors with a margin of safety. By investing in stocks with a higher NCAVPS, investors can potentially reduce their risk of loss. The higher the NCAVPS, the greater the margin of safety, as it indicates that the company has a larger cushion to cover its liabilities.
3. Potential for Capital Appreciation
Investing in stocks with a higher NCAVPS can also provide the potential for capital appreciation. If the market eventually recognizes the true value of the company’s assets, the stock price may increase, resulting in capital gains for investors.
4. Contrarian Investing
NCAVPS is often used by contrarian investors who seek out opportunities in companies that are overlooked or out of favor with the market. By identifying companies with a low market price per share relative to their NCAVPS, contrarian investors can potentially profit from the market’s mispricing.
5. Long-Term Investment Strategy
Limitations of Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS)
While Net Current Asset Value Per Share (NCAVPS) is a useful metric for value investors, it is important to understand its limitations. Here are some of the key limitations to consider:
1. Lack of Consideration for Future Earnings

NCAVPS only takes into account the current assets and liabilities of a company, without considering its future earnings potential. This means that it may not accurately reflect the true value of a company if it has strong growth prospects or if its current assets are not indicative of its future earnings.
2. Exclusion of Intangible Assets
NCAVPS does not include intangible assets such as patents, trademarks, and brand value. These intangible assets can often be valuable and contribute significantly to a company’s overall worth. Excluding them from the calculation can lead to an undervaluation of the company.
3. Industry-Specific Considerations
Net Current Asset Value Per Share may not be applicable or meaningful for certain industries. For example, technology companies often have high research and development costs, which are not reflected in the calculation of NCAVPS. Additionally, companies in rapidly growing industries may have higher levels of debt or negative working capital, which can distort the NCAVPS calculation.
4. Market Efficiency
The market is not always efficient in pricing stocks based on their net current asset value. This means that even if a stock is trading below its NCAVPS, it does not guarantee that it is undervalued. Other factors such as market sentiment, investor perception, and macroeconomic conditions can influence stock prices.
5. Limited Information
NCAVPS is based on publicly available financial statements, which may not provide a complete picture of a company’s financial health. Companies can manipulate their financial statements or engage in off-balance sheet transactions, which may not be captured in the calculation of NCAVPS.
Despite these limitations, NCAVPS can still be a useful tool for value investors when used in conjunction with other financial analysis methods. It provides a conservative estimate of a company’s intrinsic value and can help identify potential investment opportunities. However, it is important to consider these limitations and conduct thorough research before making investment decisions based solely on NCAVPS.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
