Margin of Safety: Examples, Meaning and FAQ
The margin of safety is a financial concept that is widely used in investing and risk management. It refers to the difference between the intrinsic value of an investment and its market price. In other words, it is the amount by which the market price of an investment can fall before it reaches its intrinsic value.
The margin of safety is an important concept for investors because it provides a cushion against potential losses. By investing in assets with a large margin of safety, investors can protect themselves from the inherent uncertainties and risks in the market.
By investing in a stock with a significant margin of safety, you are essentially buying a stock at a discount. This provides a buffer against any potential declines in the market price and increases the likelihood of generating a positive return on investment.
Examples of Margin of Safety
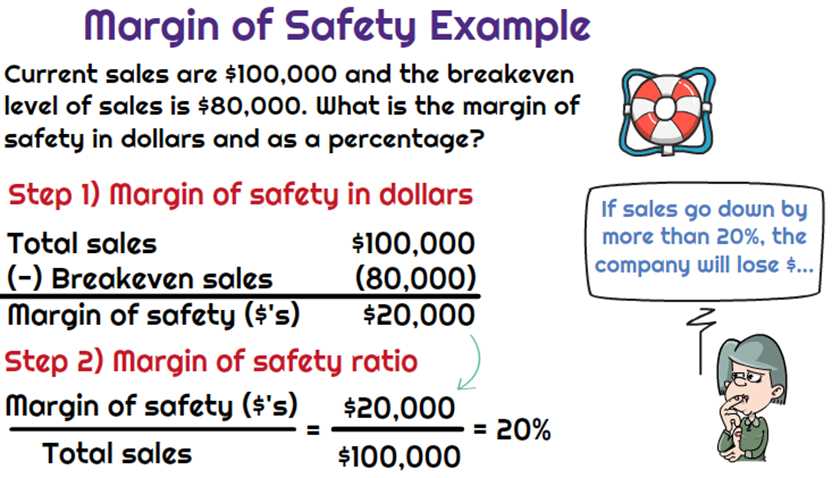
The margin of safety can be applied to various types of investments, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and businesses. Here are a few examples:
Stocks: When investing in stocks, the margin of safety can be calculated by comparing the market price to the intrinsic value of the stock. If the market price is significantly lower than the intrinsic value, it indicates a larger margin of safety.
Bonds: In the case of bonds, the margin of safety can be determined by analyzing the creditworthiness of the issuer. If the issuer has a strong credit rating, it indicates a lower risk of default and a larger margin of safety for bondholders.
Frequently Asked Questions about Margin of Safety
Q: Why is the margin of safety important?
A: The margin of safety is important because it helps investors protect themselves from potential losses and reduces the overall risk of their investments.
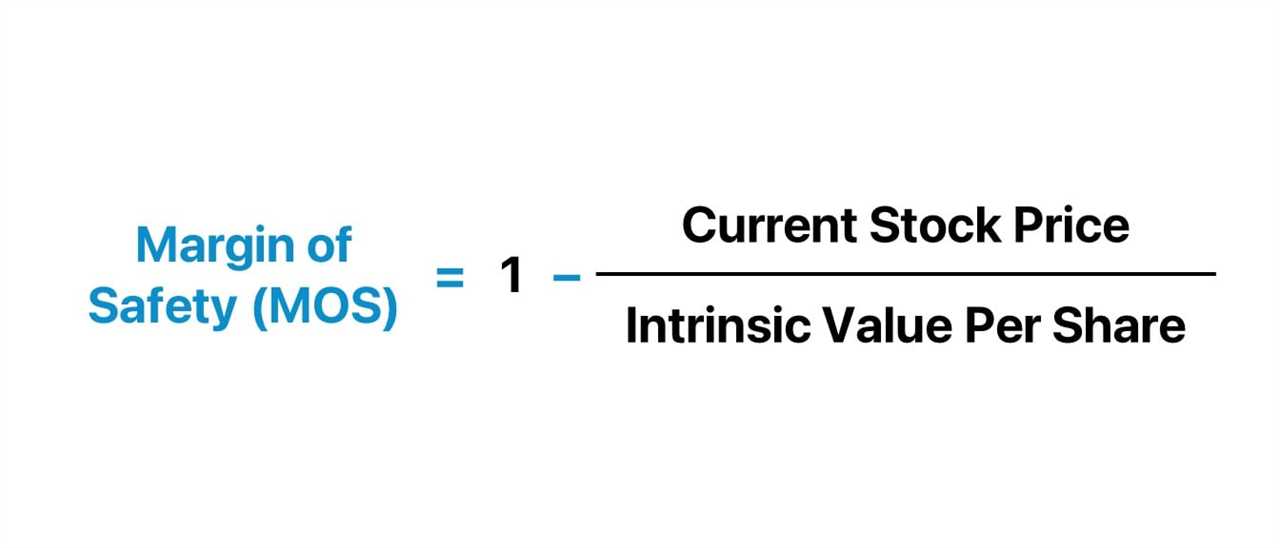
Q: How is the margin of safety calculated?
A: The margin of safety is calculated by subtracting the market price of an investment from its intrinsic value.
Q: Can the margin of safety change over time?
A: Yes, the margin of safety can change over time as market conditions and the intrinsic value of an investment fluctuate.
Q: Should I always invest in assets with a large margin of safety?
What is Margin of Safety?
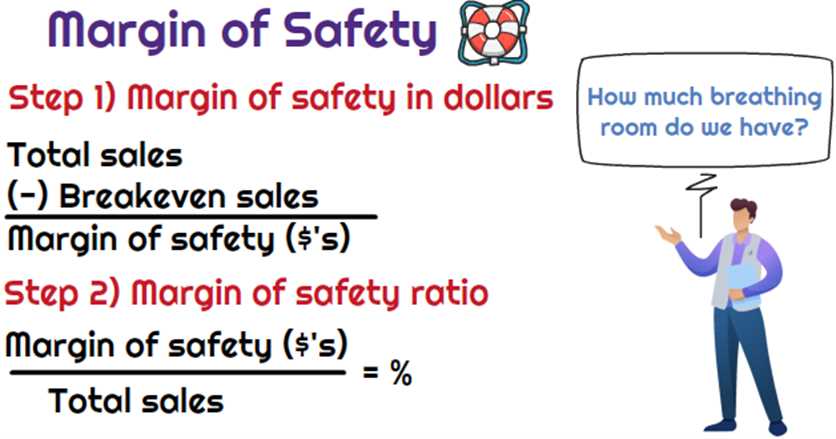
The margin of safety is a financial concept that measures the difference between the actual or estimated value of an asset and its intrinsic value. It is a measure of the cushion or buffer that exists between the purchase price of an asset and its true value.
The margin of safety is an important concept in investing and risk management. It provides a margin of protection against unforeseen events or changes in market conditions that could negatively impact the value of an asset. By investing with a margin of safety, investors can reduce their risk and increase their potential for long-term gains.
Calculating the Margin of Safety
To calculate the margin of safety, you need to determine the intrinsic value of an asset and compare it to its market price. The intrinsic value is the estimated or actual value of an asset based on its underlying fundamentals, such as its earnings, cash flow, and growth prospects.
For example, if a stock is trading at $50 per share and its intrinsic value is estimated to be $70 per share, the margin of safety would be $20 per share. This means that the stock has a cushion of $20 per share before it reaches its intrinsic value.
Benefits of Margin of Safety
There are several benefits to investing with a margin of safety:
1. Risk Reduction: By investing with a margin of safety, investors can reduce their risk of loss. The cushion provided by the margin of safety helps protect against unforeseen events or changes in market conditions that could negatively impact the value of an asset.
2. Potential for Higher Returns: Investing with a margin of safety can increase the potential for higher returns. By purchasing assets below their intrinsic value, investors have the opportunity to profit when the market eventually recognizes the true value of the asset.
3. Long-Term Perspective: Investing with a margin of safety encourages a long-term perspective. By focusing on the intrinsic value of an asset rather than short-term market fluctuations, investors can make more informed and rational investment decisions.
Conclusion
The margin of safety is a crucial concept in investing and risk management. It provides a cushion or buffer between the purchase price of an asset and its intrinsic value, reducing the risk of loss and increasing the potential for long-term gains. By calculating and investing with a margin of safety, investors can make more informed and rational investment decisions.
Examples of Margin of Safety
The concept of margin of safety is widely used in various industries and scenarios. Here are some examples that illustrate its application:
- Investing: In the world of finance, margin of safety is often used in investing. It refers to the difference between the intrinsic value of a stock and its market price. By investing in stocks with a significant margin of safety, investors aim to protect themselves against potential losses and increase their chances of making a profit.
- Construction: Margin of safety is also important in the construction industry. When designing structures, engineers incorporate a margin of safety to ensure that the building can withstand loads and stresses beyond what it is expected to encounter. This helps to prevent structural failures and ensure the safety of occupants.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers use margin of safety to determine the maximum load or stress that a product can handle without failing. This allows them to set appropriate safety factors and design products that meet quality and safety standards. For example, a car manufacturer may design a vehicle with a certain margin of safety to ensure it can withstand crashes and protect passengers.
- Inventory management: Margin of safety is also relevant in inventory management. Businesses often maintain a buffer stock or safety stock to account for uncertainties in demand or supply. This ensures that they have enough inventory to meet customer demands even in unexpected situations, such as delays in shipments or sudden spikes in demand.
- Project management: In project management, margin of safety is used to account for uncertainties and risks. Project managers allocate extra time and resources to tasks to accommodate potential delays or setbacks. This helps to ensure that projects are completed on time and within budget.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and importance of margin of safety in various fields. By incorporating a margin of safety, individuals and businesses can mitigate risks, protect themselves against potential losses, and ensure the safety and success of their endeavors.
The margin of safety is a financial concept that measures the difference between the intrinsic value of an investment and its market price. It is a tool used by investors to assess the potential risk of an investment and determine whether it is a good opportunity.
When the market price of an investment is lower than its intrinsic value, there is a margin of safety. This means that even if the market price were to decline, the investor would still have a cushion of safety because the investment is undervalued. On the other hand, if the market price is higher than the intrinsic value, there is no margin of safety, and the investment may be considered risky.
Investors use the margin of safety to protect themselves against potential losses. By investing in assets that have a margin of safety, they can minimize the risk of losing money if the market price were to decline. This is because even if the market price were to drop, the investment would still have room to recover and potentially generate a profit.
It is important to note that the margin of safety is not a guarantee of profitability. It is simply a measure of the potential risk associated with an investment. Investors should conduct thorough research and analysis to determine the intrinsic value of an investment and assess its potential for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions about Margin of Safety
Margin of Safety is a concept used in finance and investing to assess the level of risk associated with an investment. It is the difference between the intrinsic value of an asset and its market price. Here are some frequently asked questions about Margin of Safety:
1. Why is Margin of Safety important?
Margin of Safety is important because it provides a cushion against potential losses. By investing in assets that have a significant margin of safety, investors can protect themselves from the downside risk and increase their chances of earning a profit.
2. How is Margin of Safety calculated?
3. What is the significance of a high Margin of Safety?
A high Margin of Safety indicates that an asset is undervalued and offers a greater potential for profit. It suggests that the market price is significantly lower than the asset’s intrinsic value, providing investors with a larger margin for error and a higher probability of achieving a positive return.
4. Can Margin of Safety be negative?
5. How does Margin of Safety help in risk management?
Margin of Safety helps in risk management by providing a buffer against unexpected events or changes in market conditions. It allows investors to have a margin for error and protects them from the potential downside of an investment. By investing in assets with a high margin of safety, investors can mitigate the risk and increase the likelihood of achieving their investment goals.
6. Is Margin of Safety applicable to all types of investments?
Yes, Margin of Safety is applicable to all types of investments, including stocks, bonds, real estate, and other financial instruments. The concept of Margin of Safety can be used to assess the risk and potential return of any investment. However, the calculation and interpretation of Margin of Safety may vary depending on the specific asset class.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. Why is Margin of Safety important? | Margin of Safety is important because it provides a cushion against potential losses. |
| 2. How is Margin of Safety calculated? | Margin of Safety is calculated by subtracting the market price of an asset from its intrinsic value. |
| 3. What is the significance of a high Margin of Safety? | A high Margin of Safety indicates that an asset is undervalued and offers a greater potential for profit. |
| 4. Can Margin of Safety be negative? | No, Margin of Safety cannot be negative. |
| 5. How does Margin of Safety help in risk management? | Margin of Safety helps in risk management by providing a buffer against unexpected events or changes in market conditions. |
| 6. Is Margin of Safety applicable to all types of investments? | Yes, Margin of Safety is applicable to all types of investments. |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
