What is an Instrument in Finance?
Types of Financial Instruments
There are various types of financial instruments, each serving different purposes and catering to different investment needs. Some common types include:
- Equities: These are shares or stocks that represent ownership in a company.
- Bonds: These are debt instruments issued by governments or corporations to raise capital.
- Derivatives: These are financial contracts whose value is derived from an underlying asset, such as options or futures.
- Commodities: These are physical goods, such as gold or oil, that can be traded.
- Currencies: These are foreign exchange instruments used for trading different currencies.
Functions of Financial Instruments
Financial instruments serve several functions in the world of finance. They provide a means for investors to diversify their portfolios, hedge against risks, and speculate on price movements. They also facilitate the flow of capital between borrowers and lenders, enabling businesses and governments to raise funds for various purposes.
Furthermore, financial instruments play a crucial role in determining interest rates, asset valuations, and overall market stability. They provide a framework for pricing and trading assets, allowing for efficient allocation of resources in the economy.
In finance, the term “instrument” refers to a financial asset or contract that has value and can be traded. These instruments play a crucial role in the functioning of financial markets and are used by individuals, businesses, and governments to manage risk, raise capital, and invest.
Types of Financial Instruments
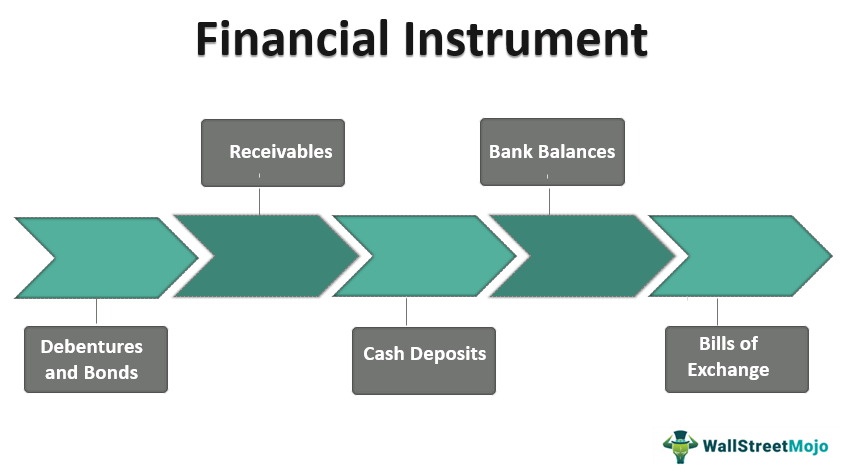
There are various types of financial instruments available in the market, each serving a specific purpose. Some common types of financial instruments include:
- Equity Instruments: These instruments represent ownership in a company and include stocks and shares. Investors who hold equity instruments are entitled to a share of the company’s profits and have voting rights.
- Debt Instruments: Debt instruments are contracts that represent a loan made by an investor to a borrower. Examples of debt instruments include bonds, loans, and mortgages. Investors who hold debt instruments receive regular interest payments and the return of their principal amount at maturity.
- Derivative Instruments: Derivative instruments derive their value from an underlying asset, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities. Examples of derivative instruments include options, futures, and swaps. These instruments are often used for hedging purposes or speculative trading.
- Commodity Instruments: Commodity instruments are used for trading commodities such as gold, oil, or agricultural products. These instruments include futures contracts, options, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Commodity instruments allow investors to gain exposure to the price movements of commodities without owning the physical assets.
Importance of Instruments in Finance
Financial instruments play a crucial role in the functioning of financial markets and the overall economy. They provide individuals, businesses, and governments with the means to manage risk, raise capital, and invest. Without these instruments, it would be challenging for market participants to transfer and allocate funds efficiently.
Financial instruments also contribute to market liquidity by providing a mechanism for buying and selling assets. They enable investors to diversify their portfolios and access a wide range of investment opportunities. Additionally, these instruments facilitate price discovery and help determine the fair value of assets.
Furthermore, financial instruments allow individuals and businesses to hedge against various risks, such as interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, and commodity price risk. By using derivative instruments, market participants can protect themselves from adverse market movements and stabilize their cash flows.
Instrument Definition in Economics
In economics, an instrument refers to a tool or mechanism that is used to achieve a specific economic objective. It can be a policy, a regulation, or a financial instrument that is designed to influence economic behavior or outcomes.
One of the key aspects of instruments in economics is their ability to shape incentives and behavior. For example, a government may use fiscal policy instruments such as taxes and subsidies to encourage or discourage certain economic activities. By adjusting tax rates or providing subsidies, the government can influence consumer spending, investment, and overall economic growth.
Financial instruments also play a crucial role in the economy. These instruments include stocks, bonds, derivatives, and other securities that facilitate the flow of capital and investment. Financial instruments allow individuals and organizations to allocate their resources efficiently, manage risk, and participate in economic activities.
Moreover, instruments in economics can be used to address market failures and promote economic stability. For instance, central banks use monetary policy instruments such as interest rates and open market operations to regulate the money supply and stabilize inflation. By adjusting these instruments, central banks can influence borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic activity.
Overall, instruments in economics are powerful tools that shape economic behavior, promote economic growth, and address market failures. They are essential for policymakers, economists, and market participants to understand and utilize in order to achieve desired economic outcomes.
Exploring the Role of Instruments in Economic Systems
Definition of Instruments
In the context of economics, instruments refer to the various mechanisms and tools that are used to facilitate economic activities. These instruments can take different forms, such as money, contracts, securities, and derivatives. Each instrument serves a specific purpose and function within the economic system.
Functions of Instruments

One of the primary functions of instruments in economic systems is to serve as a medium of exchange. Money, for example, is a widely recognized instrument that enables individuals and businesses to trade goods and services. It acts as a common unit of value, making transactions more efficient and convenient.
In addition to being a medium of exchange, instruments also serve as a store of value. They allow individuals and businesses to save and accumulate wealth over time. For instance, individuals can invest in financial instruments like stocks and bonds to preserve and grow their wealth.
Furthermore, instruments provide a means of transferring and allocating risk. Derivatives, such as options and futures contracts, allow individuals and businesses to hedge against price fluctuations and manage their exposure to various risks. This helps to stabilize the economy and reduce uncertainty.
Importance of Instruments in Economic Systems
Instruments also contribute to the overall efficiency of economic systems. They enable the division of labor and specialization, allowing individuals and businesses to focus on their core competencies. This leads to increased productivity and economic growth.
Moreover, instruments facilitate the flow of capital within the economy. Financial instruments, such as stocks and bonds, provide individuals and businesses with access to capital for investment and expansion. This promotes innovation and entrepreneurship, driving economic development.
Conclusion
The Importance of Instruments in Law
Instruments play a crucial role in the field of law, serving as legal documents that establish rights, obligations, and agreements between parties. These legal instruments provide a framework for conducting transactions, resolving disputes, and ensuring compliance with laws and regulations.
Defining Legal Instruments
Legal instruments serve as evidence of the parties’ intentions and provide a record of their rights and obligations. They outline the terms and conditions of an agreement, specify the rights and responsibilities of each party, and establish the consequences of non-compliance or breach of contract.
Importance in Legal Proceedings
Legal instruments also play a vital role in litigation. They serve as evidence in court, supporting the claims and defenses of the parties involved. Judges rely on these documents to make informed decisions and determine the outcome of a case.
Creating Legal Certainty
One of the primary purposes of legal instruments is to create legal certainty. By clearly defining the rights and obligations of the parties involved, these documents minimize ambiguity and provide a solid foundation for legal relationships.
Enforcing Compliance

Legal instruments also play a crucial role in enforcing compliance with laws and regulations. They outline the consequences of non-compliance or breach of contract, providing a basis for legal action and remedies.
When parties fail to fulfill their obligations as outlined in a legal instrument, the affected party can seek legal redress. They can file a lawsuit, seek damages, or request specific performance to enforce the terms of the agreement. Legal instruments provide a clear framework for resolving disputes and holding parties accountable for their actions.
Examining the Legal Significance of Instruments
Legal Instruments:
Legal instruments can take various forms, such as contracts, deeds, promissory notes, wills, and patents. Each of these instruments serves a specific purpose and has its own set of legal requirements and implications.
Contracts:
Contracts are perhaps the most common type of legal instrument. They are written agreements between two or more parties that outline the terms and conditions of a particular transaction or relationship. Contracts can cover a wide range of areas, including business transactions, employment agreements, real estate deals, and more. These instruments ensure that all parties involved understand their rights and obligations and provide a legal framework for resolving disputes.
Deeds:
A deed is a legal instrument used to transfer ownership of real estate or property from one party to another. It is a written document that includes a detailed description of the property, the names of the parties involved, and the terms of the transfer. Deeds are essential for establishing legal ownership and protecting property rights.
Promissory Notes:
Promissory notes are instruments used in financial transactions, particularly in lending and borrowing. They are written promises to repay a specific amount of money within a specified timeframe. These instruments outline the terms of the loan, including the interest rate, repayment schedule, and any collateral involved. Promissory notes provide legal protection to both the lender and the borrower and ensure that the loan agreement is enforceable.
Wills:
Wills are legal instruments that dictate how a person’s assets and property should be distributed after their death. They outline the wishes of the deceased and provide instructions for the executor of the will. Wills are crucial for ensuring that a person’s assets are distributed according to their wishes and can help prevent disputes among family members.
Patents:
Patents are legal instruments that grant exclusive rights to inventors for their inventions. They provide legal protection and prevent others from using, selling, or manufacturing the patented invention without permission. Patents encourage innovation and provide inventors with the opportunity to profit from their creations.
Enforceability and Legal Protection:
One of the key aspects of legal instruments is their enforceability. These documents are legally binding and can be used as evidence in a court of law. If one party fails to fulfill their obligations as outlined in the instrument, the other party can seek legal remedies and enforce the terms of the agreement.
Conclusion:
Types of Instruments in Finance, Economics, and Law
1. Financial Instruments
Financial instruments are assets that can be traded in financial markets. They represent a contractual agreement between two parties and have a monetary value. Examples of financial instruments include stocks, bonds, derivatives, options, futures, and currencies. These instruments allow individuals and organizations to invest, hedge risks, and manage their financial portfolios.
2. Economic Instruments
Economic instruments are policy tools used by governments and organizations to achieve specific economic objectives. These instruments are designed to influence economic behavior and promote sustainable development. Examples of economic instruments include taxes, subsidies, tariffs, quotas, and regulations. They are used to address market failures, encourage resource conservation, and promote social welfare.
3. Legal Instruments
Legal instruments are documents or agreements that have legal significance and create rights and obligations for the parties involved. These instruments are used in various legal transactions, such as contracts, deeds, wills, and patents. They provide a formal framework for conducting business, resolving disputes, and protecting intellectual property rights. Legal instruments ensure legal certainty and enforceability of rights in the legal system.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
