Jobless Claims and the Market: Why They Matter, FAQs

What are Jobless Claims?
Jobless claims are reported on a weekly basis by the U.S. Department of Labor. The data includes both initial claims, which represent the number of individuals filing for unemployment benefits for the first time, and continuing claims, which represent the number of individuals who are still receiving benefits after their initial claim.
Why Do Jobless Claims Matter?
Jobless claims are closely watched by economists, investors, and policymakers because they provide valuable insights into the health of the labor market and the overall economy. Here are a few reasons why jobless claims matter:
1. Unemployment Rate: Jobless claims can be used as a leading indicator of the unemployment rate. When jobless claims are high, it suggests that more individuals are losing their jobs, which can lead to an increase in the unemployment rate. Conversely, a decrease in jobless claims indicates a stronger labor market and can contribute to a decline in the unemployment rate.
2. Economic Growth: Jobless claims can also provide insight into the overall health of the economy. When jobless claims are low, it suggests that businesses are hiring and the economy is growing. On the other hand, an increase in jobless claims can indicate a slowdown in economic growth or a recession.
3. Consumer Spending: The labor market plays a crucial role in consumer spending, as employed individuals have more disposable income to spend. When jobless claims are high, it can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, which can have a negative impact on businesses and the overall economy.
FAQs about Jobless Claims
Q: How are jobless claims calculated?
A: Jobless claims are calculated based on the number of individuals who file for unemployment benefits within a given week. The data is collected by state unemployment agencies and reported to the U.S. Department of Labor.
Q: How long do individuals typically receive unemployment benefits?
A: The duration of unemployment benefits varies by state. In most states, individuals can receive benefits for up to 26 weeks. However, during times of economic downturn, extended benefits may be available.
Q: Do jobless claims include all unemployed individuals?
A: No, jobless claims only include individuals who have filed for unemployment benefits. It does not capture individuals who are unemployed but have not filed for benefits, such as those who have exhausted their benefits or are not eligible.
Q: Can jobless claims be influenced by seasonal factors?
A: Yes, jobless claims can be influenced by seasonal factors, such as temporary layoffs during holidays or industries that experience fluctuations in demand throughout the year. Economists adjust the data to account for these seasonal variations.
Overall, jobless claims are an important economic indicator that can provide valuable insights into the labor market and the overall economy. Monitoring jobless claims can help investors and traders make more informed decisions and navigate market trends.
The data on jobless claims is collected and reported by the U.S. Department of Labor on a weekly basis. It is considered a leading indicator, as it provides an early indication of the overall state of the economy. When jobless claims are high, it suggests that there is a significant number of individuals losing their jobs, which can be a sign of economic weakness. Conversely, when jobless claims are low, it indicates a strong labor market and a healthy economy.
The jobless claims data is used by economists, policymakers, and investors to assess the current economic conditions and make informed decisions. It helps them understand the trends in unemployment and gauge the impact of economic policies and market conditions on the labor market.
Jobless claims can be influenced by various factors, including changes in business cycles, economic policies, and external shocks. For example, during periods of economic recession or downturn, jobless claims tend to increase as companies lay off workers to cut costs. On the other hand, during periods of economic expansion, jobless claims typically decrease as companies hire more workers to meet the growing demand.
| Key Points |
|---|
| – Jobless claims refer to the number of individuals who have filed for unemployment benefits for the first time during a given week. |
| – They are a leading indicator that provides insights into the health of the labor market and the overall state of the economy. |
| – Jobless claims data is used by economists, policymakers, and investors to assess economic conditions and make informed decisions. |
| – Jobless claims can be influenced by various factors, including business cycles, economic policies, and external shocks. |
| – The data is often analyzed in conjunction with other economic indicators to get a comprehensive view of the economy. |
The Impact of Jobless Claims on the Market
Why do jobless claims matter?
Jobless claims provide valuable insights into the health of the labor market and can serve as an early indicator of economic trends. When jobless claims are high, it suggests that more people are losing their jobs, which can lead to reduced consumer spending and slower economic growth. On the other hand, a decline in jobless claims indicates a strengthening job market and can be a positive sign for the economy.
Furthermore, jobless claims data can impact financial markets, including stocks, bonds, and currencies. Investors analyze this data to assess the overall health of the economy and make investment decisions accordingly. Higher jobless claims can lead to increased market volatility as investors become more cautious and risk-averse. Conversely, lower jobless claims can boost investor confidence and drive market optimism.
How do jobless claims affect different sectors?
Additionally, jobless claims can affect consumer sentiment and spending patterns. When jobless claims are high, individuals may become more cautious with their spending, leading to a decrease in consumer demand. This can have a ripple effect on various sectors of the economy, including housing, transportation, and leisure activities.
How can policymakers use jobless claims data?
Jobless claims data is an essential tool for policymakers in formulating economic policies and making informed decisions. By analyzing jobless claims trends, policymakers can assess the effectiveness of existing policies and implement necessary changes to support job creation and economic growth.
For example, if jobless claims are rising, policymakers may consider implementing measures such as providing additional unemployment benefits, offering job training programs, or creating incentives for businesses to hire more workers. Conversely, if jobless claims are declining, policymakers may focus on maintaining a favorable business environment and promoting sustainable economic growth.
Key Factors Influencing Jobless Claims
Economic Conditions
One of the key factors influencing jobless claims is the overall state of the economy. During periods of economic recession or downturn, jobless claims tend to increase as businesses reduce their workforce or shut down. Conversely, during periods of economic growth, jobless claims tend to decrease as businesses expand and create more job opportunities.
Industry-Specific Factors
Jobless claims can also be influenced by industry-specific factors. Certain industries may experience higher levels of unemployment due to technological advancements, changes in consumer demand, or global economic trends. For example, the manufacturing sector may see an increase in jobless claims as automation replaces manual labor, while the technology sector may see a decrease in jobless claims as demand for skilled workers grows.
Government Policies
Government policies and regulations can have a significant impact on jobless claims. Policies that promote job creation, such as tax incentives for businesses or investment in infrastructure projects, can help reduce jobless claims. On the other hand, policies that restrict business growth or increase labor costs may lead to higher jobless claims.
Seasonal Factors
Seasonal fluctuations can also influence jobless claims. Certain industries, such as tourism or agriculture, may experience higher levels of unemployment during specific seasons. For example, jobless claims in the tourism industry may increase during the off-peak season when there is less demand for travel and hospitality services.
Demographic Factors
Demographic factors, such as age, education level, and geographic location, can also impact jobless claims. Certain demographic groups may face higher unemployment rates due to structural factors or discrimination in the labor market. Additionally, jobless claims may vary across different regions or states depending on the availability of job opportunities and the overall economic conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Jobless Claims

What are jobless claims?
Jobless claims refer to the number of individuals who have filed for unemployment benefits with the government. These claims are typically filed by individuals who have lost their jobs and are seeking financial assistance.
Why do jobless claims matter?
Jobless claims are an important economic indicator because they provide information about the number of people who are unemployed and actively seeking work. High jobless claims can indicate a weak job market, while low jobless claims can suggest a strong job market.
How are jobless claims measured?
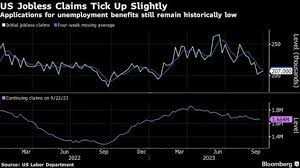
Jobless claims are measured on a weekly basis and reported by the Department of Labor. The data is collected through state unemployment offices, where individuals file their claims. The number of jobless claims is then compiled and reported as a national figure.
What is the impact of jobless claims on the market?
Jobless claims can have a significant impact on the financial markets. When jobless claims are higher than expected, it can lead to concerns about the overall health of the economy and potentially result in a decline in stock prices. Conversely, lower-than-expected jobless claims can boost investor confidence and lead to an increase in stock prices.
What are the key factors influencing jobless claims?
How can jobless claims be used by investors?
Investors can use jobless claims data to gain insights into the overall health of the economy and make informed investment decisions. High jobless claims may suggest a weak job market and potential economic challenges, which could influence investment strategies. Conversely, low jobless claims may indicate a strong job market and potential investment opportunities.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
