Factors Influencing the Federal Funds Rate
Economic Conditions

One of the primary factors influencing the Federal Funds Rate is the state of the economy. The Federal Reserve closely monitors various economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, employment levels, and consumer spending, to assess the overall health of the economy. If the economy is growing at a rapid pace and inflationary pressures are building up, the Federal Reserve may decide to raise the Federal Funds Rate to cool down the economy and prevent excessive inflation.
On the other hand, if the economy is experiencing a downturn or is facing deflationary pressures, the Federal Reserve may lower the Federal Funds Rate to stimulate economic activity and encourage borrowing and investment. By adjusting the Federal Funds Rate, the Federal Reserve aims to achieve its dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices.
Monetary Policy Decisions
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions play a crucial role in determining the Federal Funds Rate. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is responsible for setting monetary policy, meets regularly to assess the state of the economy and make decisions regarding interest rates.
When the FOMC decides to raise the Federal Funds Rate, it does so by increasing the target range for the rate. This signals to financial institutions that borrowing costs will be higher, which can lead to higher interest rates on loans and credit cards for consumers and businesses. Conversely, when the FOMC decides to lower the Federal Funds Rate, it decreases the target range, signaling lower borrowing costs and potentially lower interest rates for consumers and businesses.
Market Forces
Market forces also play a role in determining the Federal Funds Rate. The rate is influenced by the supply and demand dynamics of the banking system. When there is excess liquidity in the banking system, banks have more funds available to lend to each other, leading to a decrease in the Federal Funds Rate. Conversely, when there is a shortage of liquidity, banks may compete for funds, driving up the Federal Funds Rate.
Additionally, market expectations and investor sentiment can impact the Federal Funds Rate. If investors anticipate future changes in monetary policy, they may adjust their borrowing and lending behavior accordingly, which can influence the Federal Funds Rate.
Role of the Federal Reserve in Setting the Federal Funds Rate
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in determining and setting the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks and other depository institutions lend funds to each other overnight. This rate has a significant impact on the overall economy, as it influences borrowing costs for businesses and consumers.
Open Market Operations
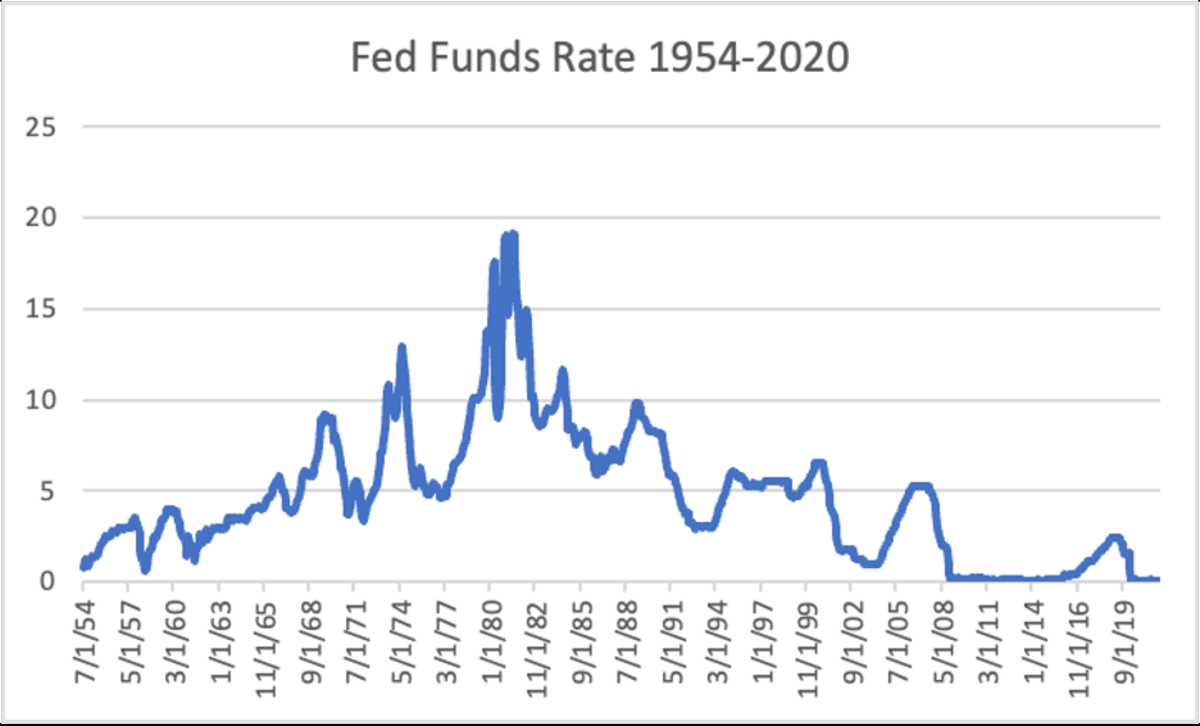
One of the primary tools used by the Federal Reserve to influence the federal funds rate is open market operations. Through these operations, the Federal Reserve buys or sells government securities, such as Treasury bonds, in the open market. When the Federal Reserve buys these securities, it injects money into the banking system, thereby increasing the supply of funds available for lending. This increase in the supply of funds tends to lower the federal funds rate. Conversely, when the Federal Reserve sells securities, it reduces the money supply, leading to a higher federal funds rate.
Discount Rate
Another tool utilized by the Federal Reserve is the discount rate. This is the interest rate at which depository institutions can borrow funds directly from the Federal Reserve. By adjusting the discount rate, the Federal Reserve can influence the cost of borrowing for banks. If the discount rate is lowered, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow from the Federal Reserve, which can encourage them to lend more funds to other institutions and individuals. Conversely, if the discount rate is raised, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can discourage lending and lead to higher interest rates.
By using these tools, the Federal Reserve can effectively control the federal funds rate and influence the overall level of interest rates in the economy. This ability to set interest rates is crucial for the Federal Reserve in fulfilling its mandate of promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
Importance of the Federal Funds Rate for the Economy
The Federal Funds Rate plays a crucial role in the overall health and stability of the economy. This interest rate, which is set by the Federal Reserve, affects various aspects of the financial system and has a direct impact on businesses, consumers, and the overall economic growth.
One of the primary ways in which the Federal Funds Rate influences the economy is through its effect on borrowing costs. When the Federal Reserve lowers the Federal Funds Rate, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow money from each other. This, in turn, leads to lower interest rates on loans for businesses and consumers. Lower borrowing costs encourage businesses to invest in new projects, expand operations, and hire more employees. It also makes it easier for consumers to obtain loans for major purchases, such as homes and cars, stimulating consumer spending.
Conversely, when the Federal Reserve raises the Federal Funds Rate, borrowing costs increase. Higher interest rates make it more expensive for businesses to borrow money for investment, which can lead to a decrease in business activity and potential job losses. Additionally, higher interest rates make it more difficult for consumers to obtain loans, reducing their purchasing power and potentially slowing down economic growth.
Another important aspect of the Federal Funds Rate is its impact on inflation. The Federal Reserve uses the Federal Funds Rate as a tool to control inflation. By raising interest rates, the Federal Reserve can slow down economic activity and reduce inflationary pressures. On the other hand, lowering interest rates can stimulate economic growth and increase inflation. Maintaining a balance between economic growth and inflation is crucial for a healthy and stable economy.
The Federal Funds Rate also has implications for the financial markets. Changes in the Federal Funds Rate can influence the yield on government bonds, which in turn affects the interest rates on other types of debt, such as mortgages and corporate bonds. These changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on the performance of the stock market and other financial assets.
Implications of Changes in the Federal Funds Rate
The Federal Funds Rate is a key interest rate that influences the cost of borrowing money for banks and other financial institutions. Changes in the Federal Funds Rate have significant implications for the economy as a whole. Here are some of the major implications of changes in the Federal Funds Rate:
| Implication | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Monetary Policy | Changes in the Federal Funds Rate are a key tool used by the Federal Reserve to implement monetary policy. By adjusting the Federal Funds Rate, the Federal Reserve can influence the availability of credit and the overall level of economic activity. |
| 2. Interest Rates | Changes in the Federal Funds Rate can have a ripple effect on other interest rates in the economy. When the Federal Funds Rate is lowered, it becomes cheaper for banks to borrow money, which can lead to lower interest rates for consumers and businesses. Conversely, when the Federal Funds Rate is raised, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money, which can lead to higher interest rates. |
| 3. Investment and Consumption | Changes in interest rates resulting from changes in the Federal Funds Rate can impact investment and consumption decisions. Lower interest rates can incentivize businesses to invest in new projects and consumers to borrow money for big-ticket purchases, such as homes and cars. Conversely, higher interest rates can discourage investment and consumption, as borrowing becomes more expensive. |
| 4. Inflation | The Federal Funds Rate can also influence inflationary pressures in the economy. When the Federal Funds Rate is lowered, it stimulates economic activity, which can lead to increased demand for goods and services. This increased demand can potentially lead to higher prices and inflation. Conversely, when the Federal Funds Rate is raised, it can help to cool down an overheating economy and mitigate inflationary pressures. |
| 5. Exchange Rates | Changes in the Federal Funds Rate can impact exchange rates. When the Federal Funds Rate is higher than rates in other countries, it can attract foreign investors seeking higher returns. This increased demand for the currency can lead to an appreciation in its value relative to other currencies. Conversely, when the Federal Funds Rate is lower than rates in other countries, it can lead to a depreciation in the currency. |
Overall, changes in the Federal Funds Rate have far-reaching implications for the economy, influencing monetary policy, interest rates, investment and consumption decisions, inflation, and exchange rates. It is important for policymakers, businesses, and consumers to closely monitor and understand these implications in order to make informed decisions and navigate the economic landscape effectively.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
