Distribution in Finance: Types and Examples
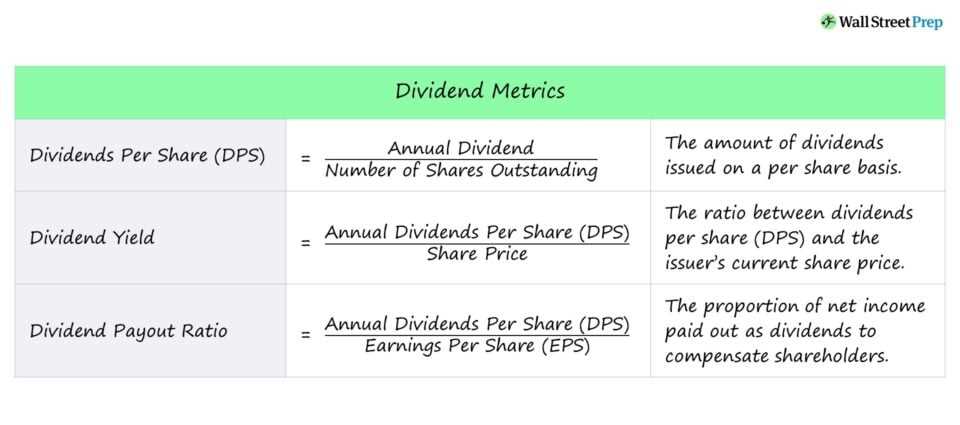
Distribution in finance refers to the process of getting financial products or services to customers. It involves the movement of money, securities, or other financial instruments from the provider to the end user. There are various types of distribution in finance, and each type has its own characteristics and examples.
Direct Distribution
Direct distribution in finance occurs when financial products or services are sold directly from the provider to the end user without the involvement of intermediaries. This can include selling products or services through a company’s website, physical branches, or sales representatives. Direct distribution allows for direct communication between the provider and the customer, which can result in a more personalized experience.
For example, a bank may offer online banking services where customers can access their accounts, transfer funds, and pay bills directly through the bank’s website. This eliminates the need for customers to visit a physical branch or interact with a bank representative.
Indirect Distribution
Indirect distribution in finance involves the use of intermediaries to sell financial products or services to customers. These intermediaries can include brokers, financial advisors, or other financial institutions. Indirect distribution allows for wider reach and access to a larger customer base.
For example, a mutual fund company may distribute its funds through various financial advisors or brokers. These intermediaries help match the investment needs of customers with suitable mutual funds and provide guidance on investment decisions.
Distribution Channels in Finance
Distribution channels in finance refer to the different paths or methods through which financial products or services reach customers. These channels can include online platforms, physical branches, call centers, or mobile applications.
For example, a credit card company may have multiple distribution channels such as online applications, phone applications, and physical branches. This allows customers to choose the most convenient method of applying for a credit card based on their preferences.
Direct Distribution
There are several advantages to direct distribution in finance. Firstly, it allows for better control over the sales process and customer experience. The financial institution can tailor its offerings and services to meet the specific needs of individual customers, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Secondly, direct distribution can be more cost-effective for the financial institution. By cutting out intermediaries, such as brokers or agents, the institution can reduce distribution costs and potentially offer lower prices to customers.
Direct distribution also allows for faster and more efficient communication between the financial institution and its customers. With direct channels, such as online platforms or mobile apps, customers can access information and make transactions in real-time, without the need for physical visits or lengthy paperwork.
Examples of direct distribution in finance include online banking, where customers can access their accounts and perform transactions through internet banking platforms, and robo-advisors, which provide automated investment advice and portfolio management services directly to customers.
Indirect Distribution in Finance: Types and Examples
Indirect distribution is a common method used in finance to distribute financial products and services to consumers. It involves the use of intermediaries or third-party entities to reach the end customers. These intermediaries can be banks, brokers, financial advisors, or other financial institutions.
There are several types of indirect distribution in finance:
1. Brokerage Networks: Brokerage networks act as intermediaries between financial institutions and customers. They provide a platform for customers to access a wide range of financial products and services offered by different institutions. Examples of brokerage networks include online trading platforms and investment platforms.
2. Financial Advisors: Financial advisors play a crucial role in indirect distribution. They provide personalized advice and guidance to customers based on their financial goals and risk tolerance. Financial advisors work closely with customers to understand their needs and recommend suitable financial products and services.
3. Banks and Credit Unions: Banks and credit unions also play a significant role in indirect distribution. They offer a variety of financial products and services, such as loans, mortgages, and investment options. Customers can access these products and services through their local bank branches or online banking platforms.
4. Insurance Agents: Insurance agents are another example of intermediaries in indirect distribution. They help customers choose the right insurance policies based on their needs and provide assistance throughout the claims process. Insurance agents work for insurance companies and earn commissions based on the policies they sell.
Indirect distribution in finance offers several benefits. It allows financial institutions to reach a larger customer base and expand their market presence. It also provides customers with a wide range of options and personalized advice, helping them make informed financial decisions.
Distribution Channels in Finance
In the world of finance, distribution channels play a crucial role in the successful delivery of financial products and services to customers. These channels act as intermediaries between financial institutions and consumers, facilitating the flow of funds and information.
There are various types of distribution channels in finance, each serving a specific purpose and catering to different customer needs. Some common distribution channels include:
1. Banks: Banks are one of the most traditional and widely used distribution channels in finance. They offer a wide range of financial products and services, including savings accounts, loans, credit cards, and investment opportunities. Banks act as a one-stop-shop for customers, providing them with easy access to various financial solutions.
2. Insurance Agents: Insurance agents are another important distribution channel in the finance industry. They specialize in selling insurance policies and helping customers choose the right coverage for their needs. Insurance agents provide personalized advice and assistance, ensuring that customers understand the terms and conditions of their policies.
3. Brokers: Brokers are intermediaries who facilitate the buying and selling of financial securities, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds. They act as a bridge between investors and financial markets, executing trades on behalf of their clients. Brokers provide market insights, research reports, and investment recommendations to help customers make informed decisions.
4. Online Platforms: With the advancement of technology, online platforms have emerged as a popular distribution channel in finance. These platforms allow customers to access and manage their financial accounts, make transactions, and invest in various financial products. Online platforms provide convenience, speed, and accessibility, making it easier for customers to engage in financial activities.
5. Financial Advisors: Financial advisors are professionals who offer personalized financial advice and guidance to individuals and businesses. They help customers develop financial plans, set goals, and make informed investment decisions. Financial advisors provide a holistic approach to financial management, considering factors such as risk tolerance, time horizon, and financial objectives.
These distribution channels work together to ensure that financial products and services reach the right customers at the right time. They provide convenience, accessibility, and expertise, enhancing the overall customer experience in the finance industry.
Examples of Distribution in Finance
Distribution plays a crucial role in the world of finance, as it determines how financial products and services reach the end consumers. Here are some examples of distribution in finance:
1. Banks
Banks are one of the most common examples of distribution channels in finance. They act as intermediaries between individuals or businesses who have excess funds and those who need to borrow money. Banks offer a wide range of financial products and services, such as loans, mortgages, credit cards, and investment opportunities. Through their physical branches, online platforms, and mobile applications, banks distribute these products and services to their customers.
2. Insurance Companies
Insurance companies also rely on distribution channels to reach their customers. They offer various types of insurance policies, including life insurance, health insurance, auto insurance, and property insurance. Insurance companies use agents, brokers, and online platforms to distribute their policies to individuals and businesses. These distribution channels help insurance companies reach a wider audience and provide customers with convenient access to their services.
3. Mutual Funds
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. They rely on distribution channels to attract investors and distribute their funds. Mutual funds can be distributed through various channels, such as financial advisors, banks, online platforms, and direct marketing. These channels help mutual funds reach potential investors and provide them with information about the fund’s performance, fees, and investment strategies.
4. Online Trading Platforms
With the rise of technology, online trading platforms have become popular distribution channels in finance. These platforms allow individuals to buy and sell financial securities, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities, directly. Online trading platforms provide users with access to real-time market data, research tools, and trading functionalities. They have made investing more accessible to a wider audience and eliminated the need for traditional intermediaries.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
