What is an Account Statement?
An account statement is a document that provides a summary of the financial transactions and balances for a specific period of time in a person’s or business’s bank account. It is typically issued by the bank or financial institution where the account is held.
Definition and Purpose
The account statement serves as a record of all the deposits, withdrawals, and other activities that have occurred in the account during the specified period. It provides important information about the account holder’s financial transactions and helps them keep track of their balance and spending.
The primary purpose of an account statement is to provide transparency and accountability. It allows the account holder to verify the accuracy of the transactions and ensure that there are no unauthorized or fraudulent activities taking place in their account.
Importance in Banking
For the bank, account statements help in maintaining accurate records of their customers’ accounts and provide a basis for customer service and dispute resolution. They also serve as a legal document in case of any disputes or investigations related to the account.
Types of Account Statements
There are different types of account statements based on the type of account and the purpose. Some common types include:
- Checking Account Statement
- Savings Account Statement
- Credit Card Statement
- Loan Statement
- Investment Account Statement
Each type of statement provides specific information related to the respective account, such as balances, transactions, interest earned or charged, fees, and other relevant details.
How to Read an Account Statement
Reading an account statement may seem overwhelming at first, but it becomes easier with practice. Here are some key steps to follow:
- Review the opening and closing balances to understand the change in the account balance during the period.
- Check for any discrepancies or errors in the transactions listed.
- Look for any fees or charges that have been applied to the account.
- Review the transaction details to ensure they match your records.
- Keep track of any interest earned or charged on the account.
- Compare the statement with your own records to ensure accuracy.
If you notice any discrepancies or have any questions about the account statement, it is important to contact your bank or financial institution for clarification.
Examples of Account Statements
Account statements can vary in format and layout depending on the bank or financial institution. However, they generally include the following information:
- Account holder’s name and contact information
- Account number
- Statement period
- Opening and closing balances
- List of transactions with dates, descriptions, and amounts
- Interest earned or charged
- Fees and charges
- Summary of the account
Here is an example of a typical account statement:
[Insert example of account statement]
It is important to review your account statement regularly and keep them in a safe place for future reference.
Definition and Purpose
An account statement is a document that provides a summary of the financial transactions and activities that have occurred within a specific period of time for a particular bank account. It is typically issued by a bank or financial institution to its customers, and it serves as a record of all the deposits, withdrawals, transfers, and other transactions that have taken place in the account.
In addition to serving as a record of financial transactions, account statements also serve as a proof of account activity. They can be used as supporting documents for various purposes, such as applying for loans, filing insurance claims, or resolving disputes. Account statements are often required by financial institutions, government agencies, and other organizations as part of their verification and documentation processes.
Overall, account statements are a vital component of the banking system, providing transparency, accountability, and convenience to account holders. They enable individuals and businesses to stay informed about their financial standing, make informed decisions, and maintain accurate financial records.
Importance in Banking
The account statement plays a crucial role in banking as it provides a comprehensive overview of a customer’s financial transactions. It serves as a record of all the deposits, withdrawals, and other activities related to the account.
One of the key reasons why account statements are important in banking is that they help customers keep track of their finances. By reviewing the statement, customers can easily identify any discrepancies or errors in their transactions. This allows them to promptly report any issues to the bank and ensure that their accounts are accurate and up to date.
Account statements also serve as a proof of transaction for customers. In case of any disputes or legal matters, having a detailed account statement can be crucial in providing evidence of the transactions that have taken place. This can help resolve any conflicts and protect the rights and interests of both the customer and the bank.
Furthermore, account statements are essential for financial planning and budgeting. By analyzing the statement, customers can gain insights into their spending patterns, identify areas where they can save or cut back on expenses, and set financial goals. This information can be invaluable in helping individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their finances.
In addition to serving the needs of customers, account statements also play a significant role in regulatory compliance. Banks are required by law to provide accurate and timely statements to their customers. These statements serve as a means of transparency and accountability, ensuring that banks adhere to the regulations and standards set by regulatory authorities.
Overall, account statements are a vital tool in banking that provides customers with a clear and concise summary of their financial activities. They offer transparency, help in financial management, and serve as a legal document when needed. Therefore, it is essential for both customers and banks to recognize the importance of account statements and ensure their accuracy and accessibility.
Types of Account Statements
An account statement is a document that provides a summary of the financial transactions and balances in a particular account over a specific period of time. There are several types of account statements that are commonly used in banking and financial institutions. These statements serve different purposes and provide different levels of detail.
1. Bank Statement
A bank statement is a type of account statement that is provided by a bank to its customers. It typically includes information about the account holder’s name, account number, and contact details. The bank statement also provides a detailed list of all the transactions that have occurred in the account during a specific period, including deposits, withdrawals, and any fees or charges that have been applied. Bank statements are usually issued on a monthly basis and are an important tool for managing personal finances.
2. Credit Card Statement
A credit card statement is a type of account statement that is provided by a credit card company to its cardholders. It includes information about the cardholder’s name, account number, and contact details. The credit card statement provides a detailed list of all the transactions that have been made using the credit card during a specific billing cycle. It also includes information about the outstanding balance, minimum payment due, and any fees or charges that have been applied. Credit card statements are usually issued on a monthly basis and are an important tool for managing credit card expenses and monitoring spending habits.
3. Investment Account Statement
An investment account statement is a type of account statement that is provided by a financial institution to its clients who have investment accounts. It includes information about the client’s name, account number, and contact details. The investment account statement provides a detailed list of all the investment transactions that have occurred in the account during a specific period, including purchases, sales, dividends, and any fees or charges that have been applied. It also includes information about the current value of the investments and the overall performance of the account. Investment account statements are usually issued on a quarterly basis and are an important tool for tracking investment performance and making informed investment decisions.
4. Loan Statement
A loan statement is a type of account statement that is provided by a lender to its borrowers. It includes information about the borrower’s name, loan account number, and contact details. The loan statement provides a detailed list of all the loan transactions that have occurred during a specific period, including loan disbursements, repayments, and any interest or fees that have been charged. It also includes information about the outstanding balance, the amount of interest paid, and the remaining term of the loan. Loan statements are usually issued on a monthly basis and are an important tool for managing loan repayments and keeping track of the loan balance.
These are just a few examples of the types of account statements that are commonly used in banking and financial institutions. Each type of statement serves a specific purpose and provides valuable information for managing personal finances, monitoring spending habits, tracking investment performance, and managing loan repayments. It is important for individuals to carefully review their account statements and reconcile them with their own records to ensure accuracy and identify any discrepancies or errors.
How to Read an Account Statement
Reading an account statement is an important skill for managing your finances. It provides a detailed summary of your transactions, balances, and other important information related to your bank account. Here are some steps to help you read and understand an account statement:
1. Review the Header

The header of the account statement contains essential information such as your name, account number, statement period, and the date the statement was generated. Make sure to verify that the information is accurate and matches your account details.
2. Understand the Account Summary
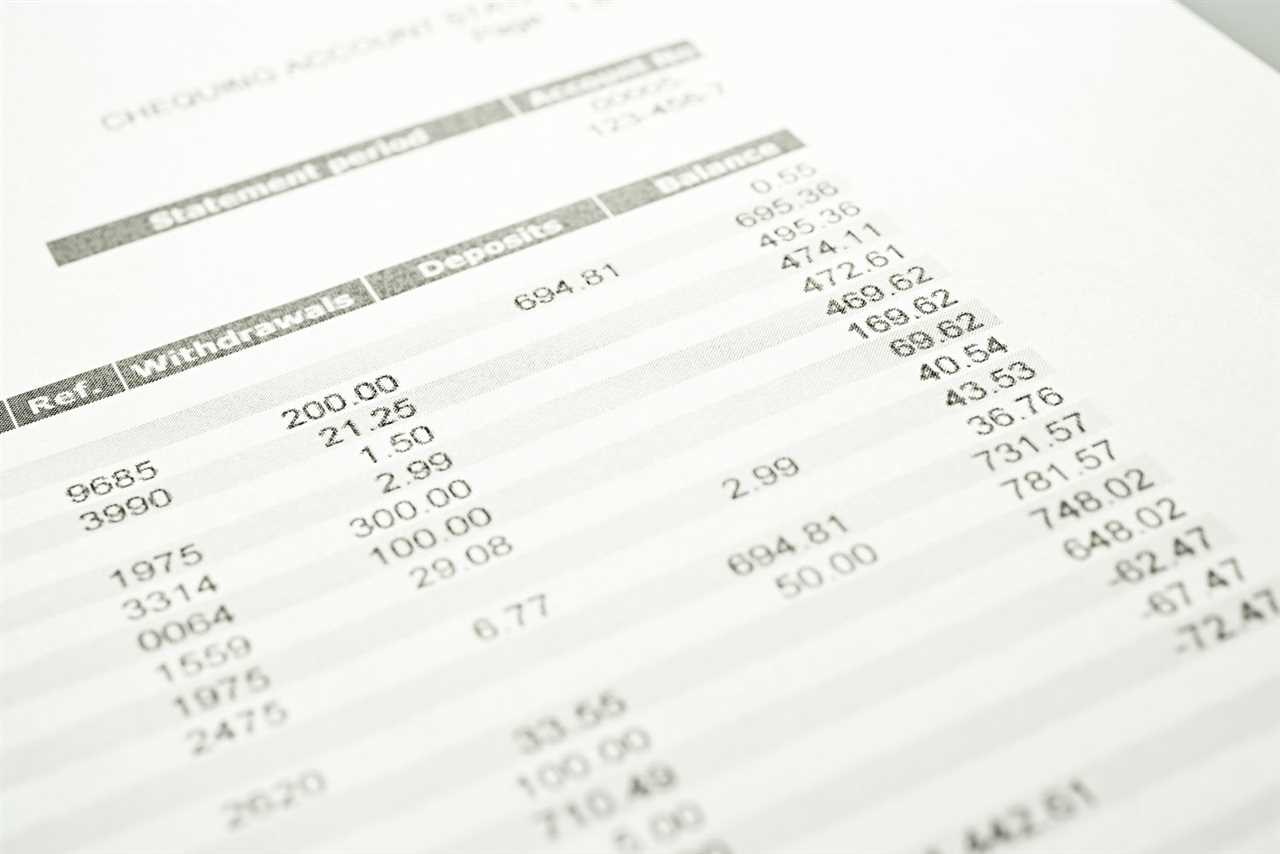
The account summary section provides an overview of your account’s financial activity during the statement period. It includes the beginning and ending balances, as well as any deposits, withdrawals, or fees incurred. This section gives you a snapshot of your account’s financial health.
3. Analyze Transaction Details
4. Check for Errors or Discrepancies
While reviewing your account statement, keep an eye out for any errors or discrepancies. This could include duplicate transactions, incorrect amounts, or unauthorized charges. If you notice any discrepancies, contact your bank immediately to resolve the issue.
5. Understand Fees and Charges

Account statements often include a section that outlines any fees or charges associated with your account. Take the time to understand these fees and charges and ensure that they are reasonable and expected. If you have any questions or concerns, reach out to your bank for clarification.
6. Keep Track of Account Balances
As you review your account statement, make note of your current balance and compare it to previous statements. This will help you track your account’s financial progress and identify any unusual activity or discrepancies.
By following these steps, you can effectively read and understand your account statement, allowing you to stay informed about your financial transactions and maintain control over your finances.
Examples of Account Statements
Account statements provide a detailed summary of a customer’s financial transactions within a specific period. These statements are essential for individuals and businesses to keep track of their finances and monitor their financial health. Here are a few examples of account statements:
1. Bank Account Statement: A bank account statement is a document provided by a bank to its customers, which shows the transactions made in the account during a specific period. It includes details such as deposits, withdrawals, interest earned, fees charged, and the account balance at the end of the period. Bank account statements are crucial for reconciling transactions, detecting any errors or fraudulent activities, and managing personal or business finances effectively.
2. Credit Card Statement: A credit card statement is a monthly statement provided by the credit card issuer to the cardholder. It includes details of all the transactions made using the credit card, such as purchases, cash advances, balance transfers, and payments. The statement also shows the outstanding balance, minimum payment due, interest charged, and any fees or penalties. Credit card statements help cardholders keep track of their spending, manage their credit card debt, and detect any unauthorized transactions.
3. Investment Account Statement: An investment account statement is provided by financial institutions or brokerage firms to their clients who have investment accounts. It includes details of the investments held, such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or other securities. The statement shows the current value of the investments, any dividends or interest earned, capital gains or losses, and transaction history. Investment account statements help investors monitor the performance of their investments and make informed decisions regarding buying or selling securities.
These are just a few examples of account statements that individuals and businesses may encounter. Each type of account statement serves a specific purpose and provides valuable information for managing finances effectively. It is important to review account statements regularly, reconcile transactions, and report any discrepancies or fraudulent activities to the respective financial institution.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
