Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Guide: Essential Information
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is a federal law that provides eligible employees with unpaid, job-protected leave for certain family and medical reasons. This guide provides essential information about the FMLA and its provisions.
Overview of the Family and Medical Leave Act

The FMLA was enacted in 1993 to help employees balance their work and family responsibilities. It allows eligible employees to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period for the following reasons:
- Birth and care of a newborn child
- Placement of a child for adoption or foster care
- Care for a spouse, child, or parent with a serious health condition
- Employee’s own serious health condition that makes them unable to perform their job
The FMLA also provides up to 26 weeks of unpaid leave to care for a covered servicemember with a serious injury or illness.
Eligibility for Family and Medical Leave
To be eligible for FMLA leave, an employee must meet certain requirements:
- Work for a covered employer, which includes private sector employers with 50 or more employees, public agencies, and public or private elementary or secondary schools
- Have worked for the employer for at least 12 months
- Have worked at least 1,250 hours in the 12 months prior to taking FMLA leave
Employees who meet these requirements are entitled to take FMLA leave without fear of losing their job or facing retaliation from their employer.
Benefits and Protections under the Family and Medical Leave Act
While FMLA leave is unpaid, employees may be able to use accrued paid leave during their FMLA leave. The FMLA also provides certain protections for employees, including:
- Continuation of group health insurance coverage during FMLA leave
- Restoration of the same or an equivalent position after returning from FMLA leave
- Prohibition of interference, retaliation, or discrimination based on an employee’s exercise of FMLA rights
| Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) Guide: Essential Information |
|---|
| Overview of the FMLA |
| Eligibility for FMLA leave |
| Benefits and protections under the FMLA |
Overview of the Family and Medical Leave Act
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) is a federal law that provides eligible employees with job-protected leave for certain family and medical reasons. The purpose of the FMLA is to balance the demands of the workplace with the needs of employees to take time off for personal or family health issues.
Under the FMLA, eligible employees are entitled to up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave in a 12-month period. This leave can be used for various reasons, including the birth or adoption of a child, caring for a seriously ill family member, or the employee’s own serious health condition.
It is important to note that the FMLA applies to employers with 50 or more employees within a 75-mile radius. Additionally, employees must meet certain eligibility requirements to qualify for FMLA leave. These requirements include having worked for the employer for at least 12 months and having worked at least 1,250 hours during the previous 12-month period.
During FMLA leave, eligible employees are entitled to maintain their group health insurance coverage. However, they may be required to continue paying their share of the premium. Upon returning from FMLA leave, employees are generally entitled to be reinstated to their previous position or an equivalent position with the same pay, benefits, and terms of employment.
The FMLA also provides certain protections for employees who take leave under the Act. It prohibits employers from interfering with an employee’s FMLA rights or retaliating against an employee for exercising their FMLA rights. If an employer violates the FMLA, employees may file a complaint with the Department of Labor or pursue a private lawsuit.
Eligibility for Family and Medical Leave
Under the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), certain employees are eligible to take unpaid leave for specific family and medical reasons. To be eligible for FMLA leave, an employee must meet certain criteria:
1. Work for a covered employer:
The FMLA applies to employers who have 50 or more employees within a 75-mile radius. This includes private sector employers, as well as federal, state, and local government employers.
2. Have worked for the employer for at least 12 months:
An employee must have worked for the employer for at least 12 months, which do not have to be consecutive. The 12 months of employment can include both full-time and part-time work.
3. Have worked at least 1,250 hours in the past 12 months:
An employee must have worked at least 1,250 hours in the 12 months preceding the start of the FMLA leave. This equates to an average of 24 hours per week.
4. Work at a location where the employer has 50 or more employees within a 75-mile radius:
An employee must work at a location where the employer has at least 50 employees within a 75-mile radius. This ensures that the FMLA applies to employers with a significant presence in the employee’s work area.
Employers must inform their employees about their rights and responsibilities under the FMLA, including the eligibility requirements. It is also crucial for employees to understand their rights and consult with their employer’s HR department or legal counsel if they believe they are eligible for FMLA leave.
Benefits and Protections under the Family and Medical Leave Act
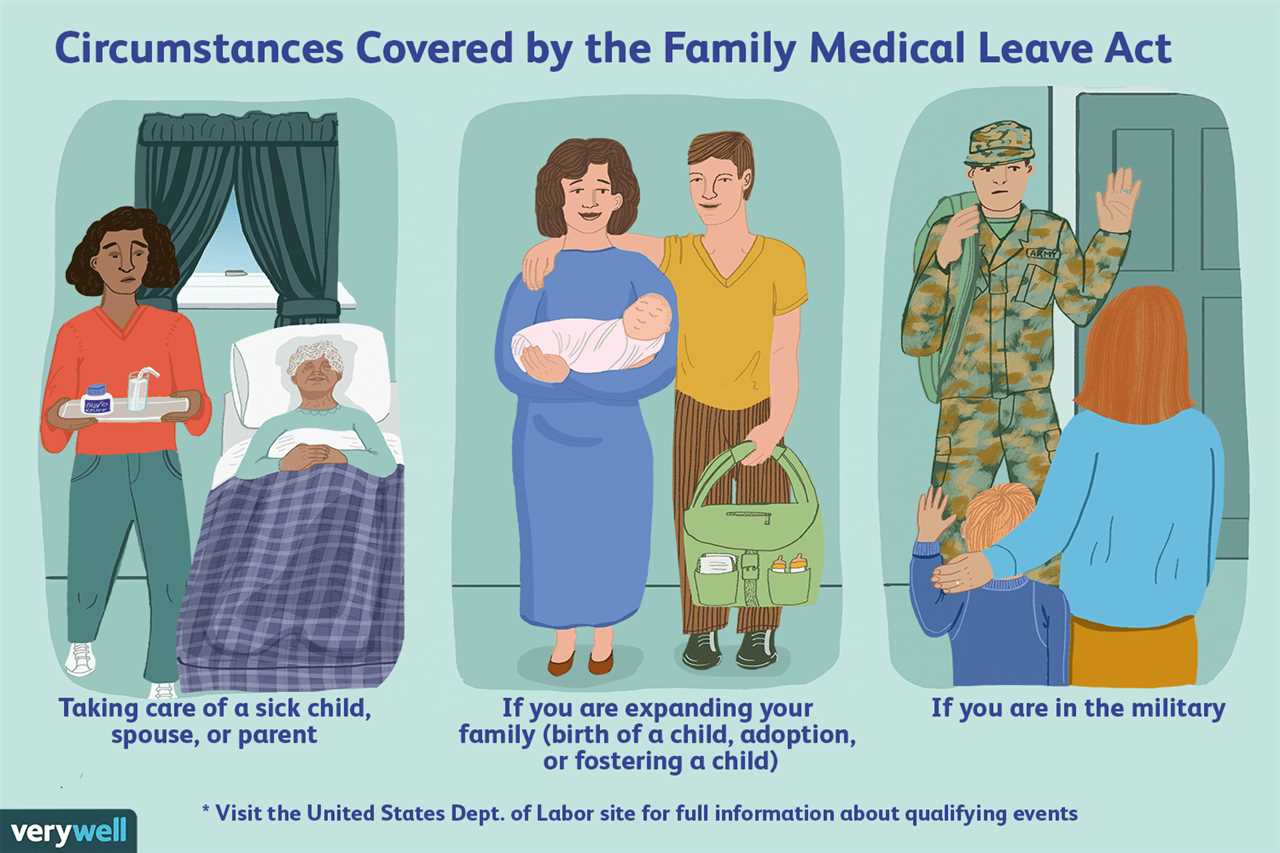
The Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) provides several benefits and protections for eligible employees who need to take time off from work due to specific family or medical reasons. These benefits and protections include:
1. Job Protection
One of the key benefits of FMLA is that it provides job protection for eligible employees who take leave under the act. This means that when an employee returns from FMLA leave, they are entitled to be reinstated to their previous position or an equivalent position with the same pay, benefits, and terms of employment. Employers are prohibited from retaliating against employees for taking FMLA leave.
2. Continuation of Health Benefits
During FMLA leave, eligible employees are entitled to continue their health insurance coverage under the same terms as if they were actively working. The employer must maintain the employee’s health benefits during the leave period, and the employee is responsible for paying their portion of the premiums.
3. Accrual of Leave and Seniority
While on FMLA leave, eligible employees continue to accrue any leave they would have earned if they were actively working. This includes vacation time, sick leave, and other forms of paid time off. Additionally, the time spent on FMLA leave does not break an employee’s continuous service or seniority with the employer.
4. Protection against Discrimination

The FMLA prohibits employers from discriminating against employees who exercise their rights under the act. It is illegal for an employer to interfere with an employee’s FMLA rights or to retaliate against them for taking FMLA leave. If an employee believes their rights have been violated, they have the right to file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Labor.
5. Military Family Leave
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, the FMLA also provides specific protections for employees with family members serving in the military. Eligible employees may take up to 12 weeks of leave to address certain qualifying exigencies arising out of the deployment of their spouse, child, or parent to a foreign country. They may also take up to 26 weeks of leave to care for a covered service member with a serious injury or illness.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Protection | Employees are entitled to be reinstated to their previous position or an equivalent position upon returning from FMLA leave. |
| Continuation of Health Benefits | Employees can maintain their health insurance coverage during FMLA leave. |
| Accrual of Leave and Seniority | Employees continue to accrue leave and maintain their seniority while on FMLA leave. |
| Protection against Discrimination | Employers are prohibited from retaliating or discriminating against employees for exercising their FMLA rights. |
| Military Family Leave | Additional protections are provided for employees with family members serving in the military. |
Overall, the FMLA provides important benefits and protections for eligible employees who need to take time off for family or medical reasons. It ensures job security, continuation of health benefits, and safeguards against discrimination. Additionally, it recognizes the unique circumstances of military families and provides specific leave provisions for them.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
