Federal Tax Filings
1. Individual Tax Return
2. Filing Deadlines
The filing deadline for federal tax returns is typically April 15th of each year. However, if the 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. It is important to file your federal tax return on time to avoid penalties and interest.
3. Electronic Filing
The IRS encourages taxpayers to file their federal tax returns electronically. This method is faster, more secure, and reduces the chances of errors. There are various software programs and online platforms available that make electronic filing easy and convenient.
4. Payment Options
If you owe taxes after filing your federal tax return, there are several payment options available. You can pay online using a credit or debit card, set up a payment plan with the IRS, or send a check or money order by mail. It is important to pay your taxes in full and on time to avoid penalties and interest.
5. Refund Options
If you are entitled to a refund after filing your federal tax return, you have several options for receiving it. You can choose to have the refund directly deposited into your bank account, receive a paper check in the mail, or use the funds to purchase U.S. savings bonds. It is important to provide accurate banking information to ensure a smooth refund process.
State Tax Filings
Why do I need to file state taxes?
Most states require their residents to file state tax returns if they meet certain income thresholds or if they earned income within the state. Filing state taxes is necessary to report your income and determine if you owe any additional taxes or are eligible for a refund.
State tax forms
State tax deductions and credits
State tax deadlines

State tax payment options
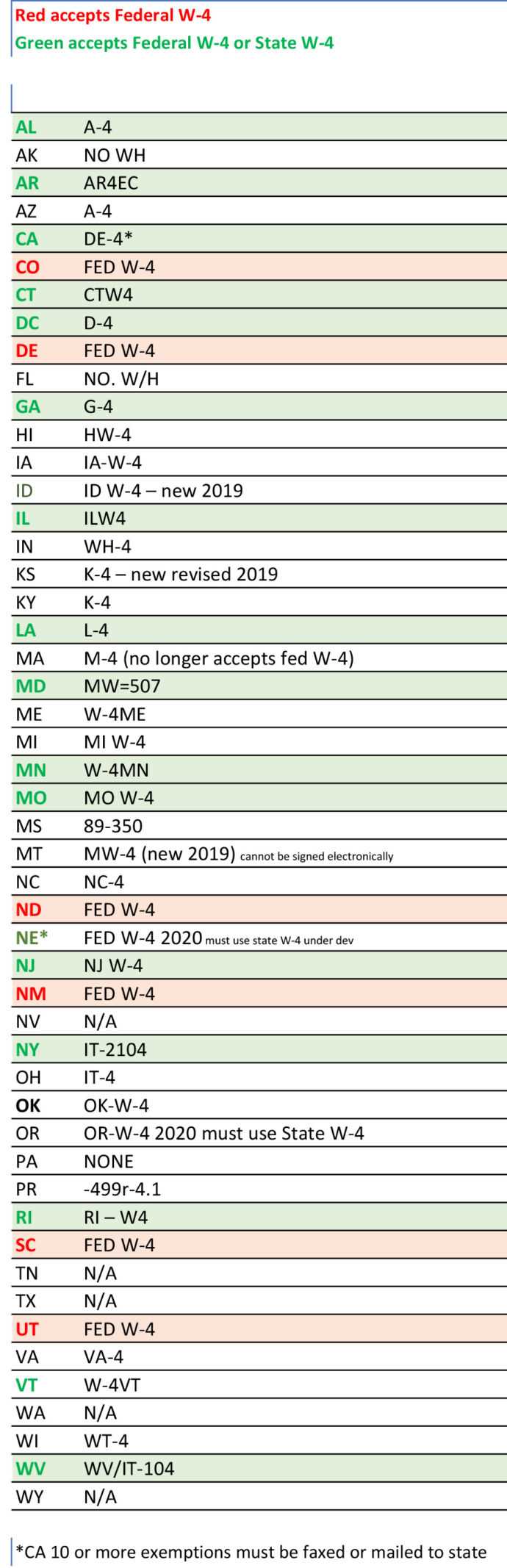
Withholding Rules for Federal Taxes
One of the key factors in determining the withholding amount is the employee’s Form W-4, which they fill out when starting a new job. This form provides information about the employee’s filing status, dependents, and any additional income or deductions. Based on this information, the employer uses the IRS withholding tables to calculate the appropriate amount to withhold from the employee’s paycheck.
The number of allowances claimed on the Form W-4 also plays a significant role in determining the withholding amount. An allowance is a monetary value that reduces the amount of income subject to withholding. The more allowances claimed, the less money will be withheld from the employee’s paycheck.
Additional Withholding Options
In addition to the allowances, employees can also choose to have additional amounts withheld from their paycheck. This can be helpful for individuals who have other sources of income or who anticipate owing more taxes than what will be withheld based on their allowances alone.
To request additional withholding, employees can fill out Form W-4 and indicate the additional amount they want to be withheld per pay period. This can help ensure that enough money is being withheld to cover their tax obligations.
Withholding Rules for State Taxes
One key difference between federal and state withholding is that states have their own tax brackets and rates. This means that the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck for state taxes may be different than the amount withheld for federal taxes.
Another important factor to consider is whether or not your state has a state income tax. Not all states impose an income tax, so if you live in one of these states, you may not have any state taxes withheld from your paycheck.
States also have their own rules regarding exemptions and deductions. These rules may differ from the federal rules, so it is important to understand how they apply to your specific situation. For example, some states may allow additional deductions or exemptions that can lower your taxable income for state tax purposes.
It is also important to note that some states have reciprocity agreements with neighboring states. These agreements allow residents who work in one state but live in another to only have taxes withheld for their state of residence. This can simplify the withholding process for individuals who commute across state lines for work.
Finally, it is crucial to stay up-to-date with any changes to state withholding rules. State tax laws can change, and it is important to be aware of any updates that may affect your withholding obligations.
Differences between Federal and State Withholding
Federal Tax Withholding

The federal tax withholding system operates on a progressive tax rate, meaning that the percentage of income withheld increases as income increases. This ensures that individuals with higher incomes pay a higher percentage of their income in taxes.
State Tax Withholding
State tax withholding works similarly to federal tax withholding, but each state has its own rules and regulations. Some states have a flat tax rate, meaning that a fixed percentage of an employee’s wages is withheld regardless of income level. Other states have a progressive tax rate similar to the federal system, where the percentage of income withheld increases as income increases.
Like federal taxes, state taxes are based on the employee’s Form W-4, or a similar state-specific form. It is important for individuals to review and update their state withholding information if they experience any changes in their personal or financial situation.
Key Differences
One key difference between federal and state withholding is that federal taxes are mandatory for all employees, while state taxes may only be required in certain states. Additionally, the tax rates and brackets for federal and state taxes can vary significantly.
Another difference is that federal tax withholding is typically more complex than state tax withholding. The federal tax code is extensive and includes various deductions, credits, and exemptions that can impact an individual’s tax liability. State tax codes may be simpler and have fewer deductions and credits available.
It is important for individuals to understand the differences between federal and state withholding to ensure that they are properly withholding the correct amount of taxes. Failing to do so can result in underpayment or overpayment of taxes, which can have financial consequences.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
