Definition of Long-Term Liabilities
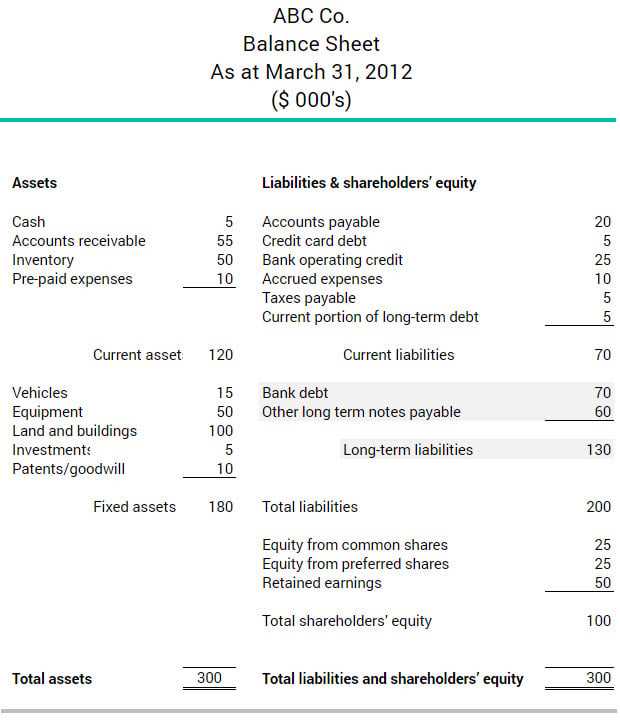
Long-term liabilities refer to the financial obligations or debts that a company is expected to repay over a period of more than one year. These liabilities are typically recorded on the balance sheet under the long-term liabilities section.
Characteristics of Long-Term Liabilities

- Maturity Period: Long-term liabilities have a maturity period of more than one year. This means that the company has a longer time frame to repay the debt compared to short-term liabilities.
- Fixed Repayment Schedule: Long-term liabilities often have a fixed repayment schedule, which means that the company is required to make regular payments over the term of the loan or debt.
- Interest Payments: Long-term liabilities typically involve interest payments. The interest rate is agreed upon at the time of borrowing and is added to the principal amount, increasing the total amount to be repaid.
- Examples: Common examples of long-term liabilities include long-term loans, bonds, mortgages, pension obligations, and lease obligations.
Importance of Long-Term Liabilities
Long-term liabilities play a crucial role in a company’s financial health and stability. They provide a source of funding for long-term investments and expansion projects. Additionally, they allow companies to spread out their debt repayment over a longer period, reducing the immediate financial burden.
Examples of Long-Term Liabilities
Long-term liabilities are financial obligations that extend beyond one year and are typically used to finance a company’s operations or investments. These liabilities represent the amount of money that a company owes to external parties and are an important component of a company’s overall financial health.
Here are some examples of long-term liabilities:
1. Bonds: Bonds are a form of long-term debt that companies issue to raise capital. They are typically sold to investors and pay a fixed interest rate over a specified period of time. Companies use the proceeds from bond issuances to fund various projects or operations.
2. Loans: Loans are another common form of long-term liability. Companies may borrow money from banks or other financial institutions to finance their operations or investments. These loans usually have a fixed repayment schedule and include interest payments.
3. Mortgages: Mortgages are long-term loans used to finance the purchase of real estate. Companies may take out mortgages to acquire office buildings, manufacturing facilities, or other properties. The mortgage is secured by the property itself, and the company makes regular payments over a specified period of time.
4. Lease Obligations: Lease obligations are long-term liabilities that arise from leasing assets such as equipment, vehicles, or real estate. Companies enter into lease agreements to use these assets without having to purchase them outright. The lease payments are made over the term of the lease agreement.
These are just a few examples of long-term liabilities that companies may have. It is important for businesses to carefully manage their long-term liabilities to ensure they have the necessary funds to meet their obligations and maintain financial stability.
Applications of Long-Term Liabilities
Long-term liabilities play a crucial role in the financial management of businesses. They are used by companies to finance long-term projects, investments, and operations. Here are some key applications of long-term liabilities:
1. Financing Capital Expenditures
One of the primary applications of long-term liabilities is to finance capital expenditures. These expenditures include the purchase of property, plant, and equipment, which are essential for the long-term growth and expansion of a business. By taking on long-term debt, companies can spread out the cost of these investments over time, making it more manageable and allowing them to invest in growth opportunities.
2. Funding Research and Development
Research and development (R&D) activities are crucial for companies to stay competitive and innovate in their industries. However, R&D can be costly and may not generate immediate returns. Long-term liabilities provide a source of funding for R&D initiatives, allowing companies to invest in new technologies, product development, and process improvements. This enables businesses to stay ahead of the curve and adapt to changing market demands.
3. Acquiring Other Businesses
Long-term liabilities can also be used to finance mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activities. When a company wants to acquire another business, it may need additional funds to complete the transaction. By issuing long-term debt, companies can raise the necessary capital to finance the acquisition. This allows businesses to expand their operations, enter new markets, and gain a competitive advantage.
4. Managing Working Capital

While long-term liabilities are typically used for long-term investments, they can also be utilized to manage working capital needs. Working capital refers to the funds required for day-to-day operations, such as paying suppliers, covering payroll, and managing inventory. By using long-term debt, companies can ensure they have sufficient liquidity to meet their short-term obligations and maintain smooth operations.
5. Enhancing Shareholder Value
Long-term liabilities can be strategically used to enhance shareholder value. By leveraging long-term debt, companies can invest in projects and initiatives that have the potential to generate higher returns than the cost of borrowing. This can lead to increased profitability, higher stock prices, and ultimately, greater shareholder wealth. However, it is important for companies to carefully manage their debt levels to avoid excessive risk and maintain financial stability.
Corporate Debt and Long-Term Liabilities
Corporate debt refers to the borrowing of funds by a company from various sources to finance its operations or investments. Long-term liabilities, on the other hand, are the obligations that a company expects to settle over a period of more than one year. Corporate debt is a common form of long-term liability for businesses.
Long-term liabilities can include loans, bonds, mortgages, and other forms of debt that have a maturity date of more than one year. These liabilities are typically recorded on a company’s balance sheet and are an important indicator of its financial health and stability.
Companies may choose to issue corporate debt to fund expansion projects, acquisitions, or to meet other long-term financial needs. By issuing debt, companies can raise capital without diluting ownership or giving up control of the business. However, taking on debt also comes with risks, such as interest payments and the potential for default if the company is unable to meet its financial obligations.
Corporate debt can be classified as either secured or unsecured. Secured debt is backed by specific assets of the company, such as property or equipment, which can be seized by the lender in the event of default. Unsecured debt, on the other hand, is not backed by specific assets and relies solely on the company’s ability to generate cash flow to repay the debt.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
