Total Expense Ratio TER Definition
The Total Expense Ratio (TER) is a financial ratio that measures the total costs associated with managing and operating an investment fund. It is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets. The TER includes various expenses such as management fees, administrative fees, custodian fees, legal fees, and other operational costs.
The Total Expense Ratio is an important metric for investors as it provides insight into the overall cost of investing in a particular fund. It allows investors to compare the costs of different funds and evaluate the impact of expenses on investment returns.
The TER includes both explicit and implicit costs. Explicit costs are the fees and expenses that are directly deducted from the fund’s assets, such as management fees. Implicit costs, on the other hand, are the costs associated with trading and portfolio turnover, which can impact the fund’s performance.
How to Calculate the Total Expense Ratio

The Total Expense Ratio is calculated by dividing the total expenses of the fund by its average net assets. The formula for calculating the TER is as follows:
TER = (Total Expenses / Average Net Assets) * 100%
The total expenses include all the costs incurred by the fund during a specific period, such as management fees, administrative fees, and other operational costs. The average net assets represent the average value of the fund’s assets over the same period.
For example, if a fund has total expenses of $100,000 and an average net asset value of $1,000,000, the TER would be calculated as:
TER = ($100,000 / $1,000,000) * 100% = 10%
This means that the fund’s expenses represent 10% of its average net assets.
It is important to note that the TER is an annualized ratio and is typically reported on an annual basis. However, it can also be calculated for shorter periods, such as quarterly or monthly, to provide a more frequent assessment of the fund’s expenses.
The TER includes various costs, such as management fees, administrative expenses, legal fees, audit fees, and other operational expenses. These costs are expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets over a specific period, usually on an annual basis.
Investors should pay close attention to the TER as it directly affects their investment returns. A higher TER means that a larger portion of the fund’s returns will be used to cover expenses, reducing the overall return for investors. On the other hand, a lower TER indicates that a higher proportion of the fund’s returns will be available to investors.
How to Calculate the Total Expense Ratio

The Total Expense Ratio (TER) is a key financial ratio that measures the total costs associated with managing and operating an investment fund. It is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s total assets and represents the annual expenses incurred by the fund, including management fees, administrative costs, and other operating expenses.
To calculate the Total Expense Ratio, you need to know the total expenses of the fund and its average net assets. The formula for calculating TER is as follows:
TER = (Total Expenses / Average Net Assets) x 100
First, you need to determine the total expenses of the fund, which include management fees, administrative costs, legal fees, audit fees, and any other expenses directly related to the operation of the fund. These expenses are typically disclosed in the fund’s annual report or prospectus.
Next, you need to calculate the average net assets of the fund. This is done by taking the sum of the fund’s net assets at the beginning and end of the reporting period and dividing it by two. Net assets represent the total value of the fund’s investments minus any liabilities.
Once you have both the total expenses and average net assets, you can plug these values into the formula to calculate the Total Expense Ratio. Multiply the result by 100 to express it as a percentage.
For example, let’s say a fund has total expenses of $1 million and average net assets of $100 million. The calculation would be as follows:
TER = ($1,000,000 / $100,000,000) x 100 = 1%
Calculating the Total Expense Ratio is important for investors as it provides insight into the overall cost of investing in a particular fund. It allows investors to compare the expenses of different funds and make informed decisions based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
It’s worth noting that the Total Expense Ratio does not include certain costs, such as trading costs and transaction fees, which can also impact investment returns. Therefore, investors should consider other factors in addition to the TER when evaluating the potential returns of a fund.
Financial Ratios: TER
Definition of Total Expense Ratio

The Total Expense Ratio is a measure of the total costs incurred by an investment fund, expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets. It includes various expenses, such as management fees, administrative costs, custodian fees, legal fees, and other operating expenses. The TER is deducted from the fund’s assets, reducing the overall return to investors.
Calculating the Total Expense Ratio
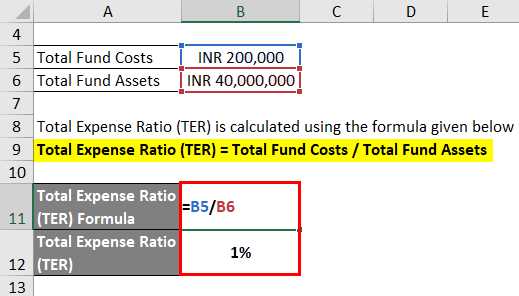
To calculate the Total Expense Ratio, you need to divide the total expenses of the investment fund by its average net assets. The formula is as follows:
TER = (Total Expenses / Average Net Assets) x 100%
The total expenses include all costs incurred by the fund during a specific period, such as a year. The average net assets represent the average value of the fund’s assets over the same period. By dividing the total expenses by the average net assets and multiplying by 100%, you can determine the TER as a percentage.
For example, if an investment fund has total expenses of $100,000 and an average net asset value of $5 million, the TER would be calculated as:
(100,000 / 5,000,000) x 100% = 2%
Importance of Total Expense Ratio in Financial Ratios
The Total Expense Ratio is an important metric for investors because it directly affects investment returns. Lower TERs indicate lower costs associated with owning the investment, which can lead to higher net returns for investors. On the other hand, higher TERs can significantly reduce investment returns over time.
Comparing the TERs of different investment options allows investors to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of each option. By choosing investments with lower TERs, investors can potentially increase their overall returns and achieve their financial goals more efficiently.
Additionally, the TER provides transparency and accountability for investment funds. It allows investors to understand the expenses associated with managing the fund and assess whether the fees charged are reasonable in relation to the fund’s performance and objectives.
Importance of Total Expense Ratio in Financial Ratios
What is the Total Expense Ratio?
The Total Expense Ratio (TER) is a measure of the total costs associated with managing and operating an investment fund. It includes all expenses, such as management fees, administrative costs, legal fees, and other operational expenses. The TER is expressed as a percentage of the fund’s average net assets.
Calculating the Total Expense Ratio
To calculate the Total Expense Ratio, the total expenses of the fund are divided by its average net assets. The formula is as follows:
Total Expense Ratio = Total Expenses / Average Net Assets
The average net assets are calculated by taking the average of the fund’s net assets at the beginning and end of a specific period, usually a year.
The Total Expense Ratio is important for several reasons:
- Costs impact investment returns: The TER directly affects the overall returns of an investment. Higher expenses result in lower net returns for investors. By comparing the TER of different funds, investors can choose options with lower costs, potentially maximizing their returns.
- Transparency: The TER provides transparency regarding the costs associated with investing in a particular fund. It allows investors to understand the impact of expenses on their investment performance and make informed decisions.
- Comparability: The TER allows investors to compare the costs of different funds. By considering the TER along with other financial ratios, investors can evaluate the cost-effectiveness of various investment options.
- Long-term impact: Even small differences in the TER can have a significant impact on investment returns over the long term. By choosing funds with lower expenses, investors can potentially increase their wealth accumulation over time.
How Total Expense Ratio Affects Investment Returns
The Total Expense Ratio (TER) is a crucial financial ratio that investors should consider when making investment decisions. The TER represents the total cost of owning and managing an investment, expressed as a percentage of the investment’s total assets. It includes various expenses such as management fees, administrative costs, and other operational expenses.
When calculating investment returns, it is vital to consider the impact of the TER on the net return. The TER is deducted from the investment’s total assets, reducing the overall value of the investment. As a result, the net return earned by investors is lower than the gross return generated by the investment.
Investors should compare the TER of different investment options before making a decision. Lower TERs indicate that a higher percentage of the investment’s returns will be retained by the investor, leading to higher overall profitability.
Additionally, the TER can vary across different types of investments, such as mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and index funds. Investors should carefully evaluate the TER of each investment option to determine which one offers the best balance between cost and potential returns.
Furthermore, it is essential to consider the long-term impact of the TER on investment returns. Even a small difference in the TER can have a significant effect on investment performance over an extended period. Therefore, investors should aim to minimize the TER to maximize their returns.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
