What Are Expenses?
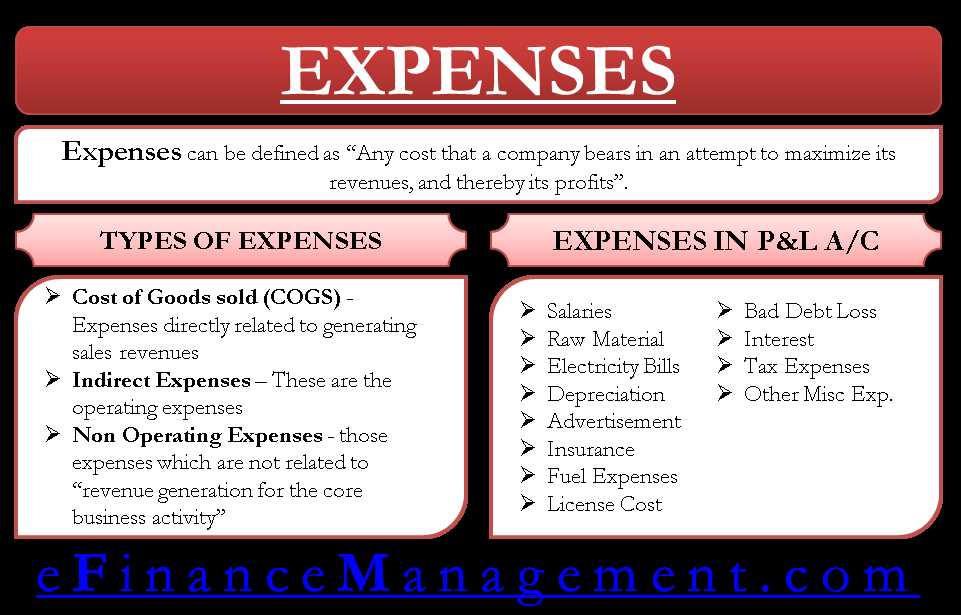
Expenses are the costs incurred by a business in order to generate revenue and operate effectively. They are the outflows of resources or obligations to other entities that result in a decrease in the company’s assets or an increase in its liabilities.
Expenses can be categorized into different types based on their nature and purpose. These categories help businesses track and analyze their spending, make informed financial decisions, and manage their budgets effectively.
Types of Expenses
There are several types of expenses that businesses commonly encounter:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Operating Expenses | These are the day-to-day expenses incurred in the normal course of business operations. They include costs such as rent, utilities, salaries, office supplies, and marketing expenses. |
| 2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing the goods or services that a business sells. It includes the cost of raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. |
| 3. Non-Operating Expenses | These are expenses that are not directly related to the core operations of the business. Examples include interest expenses, taxes, and losses from the sale of assets. |
| 4. Depreciation and Amortization | Depreciation refers to the allocation of the cost of tangible assets over their useful lives, while amortization is the allocation of the cost of intangible assets. These expenses recognize the wear and tear or the expiration of the asset’s value over time. |
| 5. Research and Development (R&D) Expenses | R&D expenses are incurred in the process of developing new products, improving existing products, or conducting research activities. These expenses are crucial for innovation and growth. |
It is important for businesses to accurately record and track their expenses to maintain financial transparency and ensure compliance with accounting standards. This allows them to assess their profitability, identify areas for cost reduction, and make informed financial decisions.
Types of Expenses
1. Fixed Expenses
2. Variable Expenses
3. Semi-Variable Expenses
4. Direct Expenses
Direct expenses are costs that can be specifically attributed to the production of a particular product or service. These expenses are directly tied to a specific project or department within a company. Examples of direct expenses include the cost of raw materials used in manufacturing, wages of production workers, and packaging costs. Tracking direct expenses is crucial for businesses to accurately determine the profitability of individual products or services.
5. Indirect Expenses
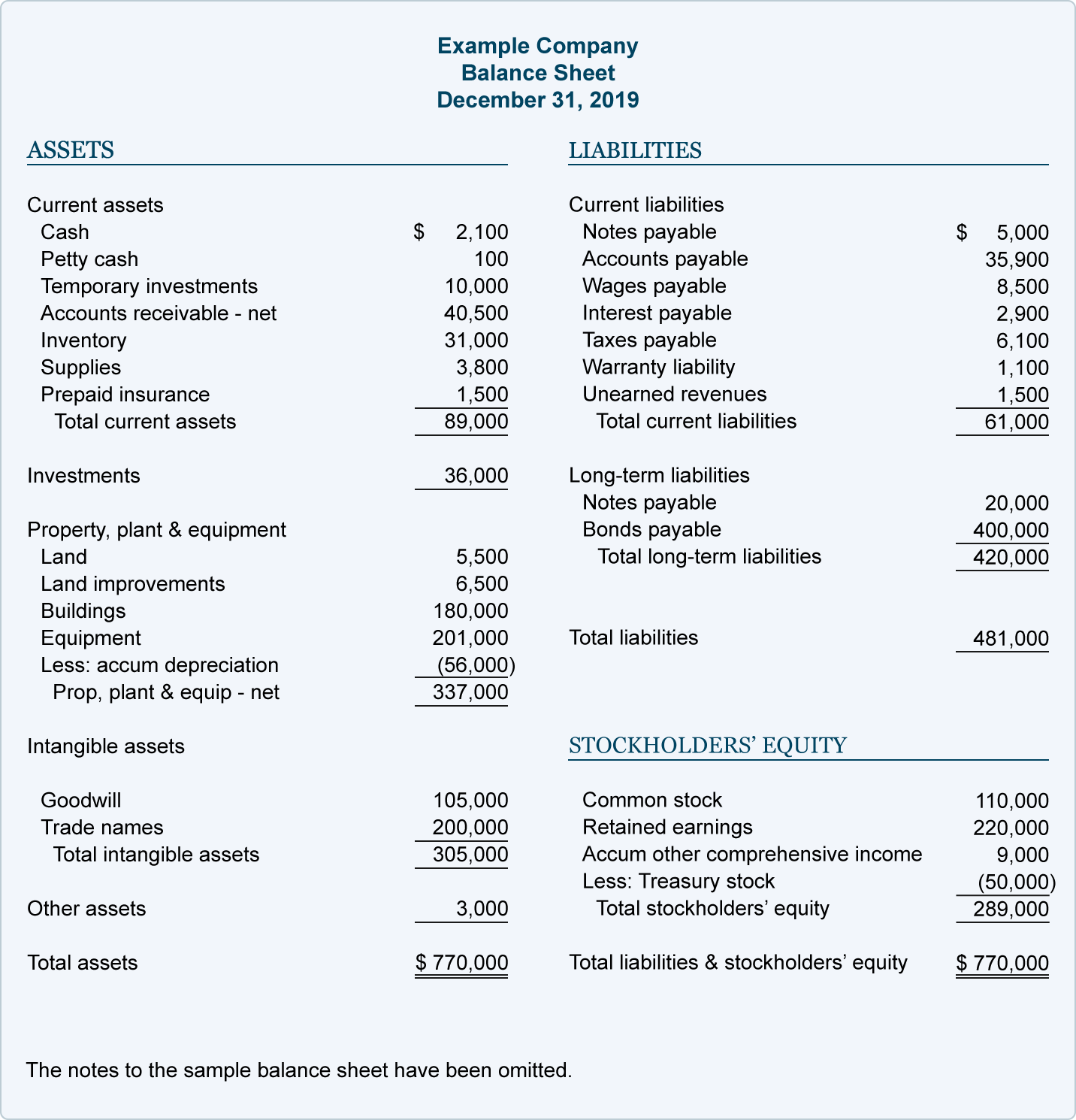
How Expenses Are Recorded
Recording expenses accurately is crucial for businesses to maintain financial transparency and make informed decisions. Here are some common methods used to record expenses:
1. Manual Recordkeeping
One way to record expenses is through manual recordkeeping. This involves keeping physical copies of receipts, invoices, and other relevant documents. Businesses can use spreadsheets or accounting software to enter the expense details manually. This method allows for greater control and customization but can be time-consuming and prone to human error.
2. Electronic Recordkeeping
With the advancement of technology, many businesses now opt for electronic recordkeeping. This involves using accounting software or cloud-based platforms to track and record expenses. Electronic recordkeeping allows for automation, easy access, and real-time updates. It also reduces the risk of losing important documents and provides better organization.
3. Expense Reports
4. Accounting Systems
Accounting systems play a vital role in recording and managing expenses. These systems integrate various financial processes, including expense recording, invoicing, and financial reporting. They provide a centralized platform where businesses can track, categorize, and analyze expenses. Accounting systems also allow for easy integration with other financial software and provide valuable insights into the financial health of the business.
5. Bank and Credit Card Statements
Bank and credit card statements can also be used to record expenses. Businesses can review these statements and categorize the transactions accordingly. This method is convenient as it eliminates the need for manual data entry. However, it may require additional reconciliation to ensure accuracy and completeness.
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Recordkeeping | Greater control and customization | Time-consuming and prone to human error |
| Electronic Recordkeeping | Automation, easy access, real-time updates | Initial setup and potential technical issues |
| Expense Reports | Systematic tracking and analysis | Dependency on employee submission |
| Accounting Systems | Centralized platform, integration, insights | Cost of implementation and maintenance |
| Bank and Credit Card Statements | Convenient, eliminates manual data entry | Requires additional reconciliation |
Choosing the most suitable method for recording expenses depends on the size and nature of the business, as well as its financial management practices. It is essential to establish clear procedures and guidelines to ensure accurate and consistent expense recording.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
