Technical Indicator: Definition
A technical indicator is a mathematical calculation that is applied to a financial instrument’s price and/or volume to help identify potential trading opportunities. It is used by technical analysts to analyze historical price and volume data and make predictions about future price movements.
Technical indicators are based on the premise that historical price and volume data can provide insights into market trends and patterns. By analyzing these patterns, analysts can identify potential entry and exit points for trades.
There are various types of technical indicators, each with its own calculation method and interpretation. Some common types of technical indicators include moving averages, oscillators, and trend-following indicators.
Technical indicators are often displayed on charts alongside price data to provide visual representation of the indicator’s values. Traders can use these visual representations to make informed trading decisions.
| Indicator Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Moving Averages | Calculates the average price over a specified period of time to identify trends. | Simple Moving Average (SMA) |
| Oscillators | Measures the momentum and overbought/oversold conditions of a security. | Relative Strength Index (RSI) |
| Trend-following Indicators | Identifies the direction and strength of a trend. | Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) |
Technical indicators should not be used in isolation but rather in conjunction with other forms of analysis, such as fundamental analysis, to make well-informed trading decisions. It is important for traders to understand the limitations and potential pitfalls of using technical indicators and to use them as part of a comprehensive trading strategy.
What is a Technical Indicator?
A technical indicator is a mathematical calculation or graphical representation of price and/or volume data used to analyze and predict future price movements in financial markets. It is a tool commonly used by traders and analysts in technical analysis, which is the study of historical market data to forecast future price trends.
Technical indicators are based on the premise that historical price and volume patterns can provide insights into future market behavior. By analyzing these patterns, traders can identify potential buying or selling opportunities and make informed trading decisions.
Importance of Technical Indicators
These indicators can be used in various ways, such as confirming or contradicting other technical analysis tools, generating trading signals, identifying overbought or oversold conditions, and determining support and resistance levels.
Types of Technical Indicators
There are numerous types of technical indicators, each with its own calculation method and interpretation. Some common types include:
- Trend indicators: These indicators help identify the direction and strength of a trend.
- Momentum indicators: These indicators measure the speed and magnitude of price movements.
- Volatility indicators: These indicators measure the degree of price fluctuations in the market.
- Volume indicators: These indicators analyze the trading volume of a security.
- Oscillators: These indicators help identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
Traders often use a combination of different technical indicators to gain a comprehensive view of the market and increase the accuracy of their predictions.
Analyst Uses of Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are widely used by analysts in the field of technical analysis to make informed investment decisions. These indicators provide valuable insights into the price and volume movements of financial instruments, helping analysts identify trends, confirm market signals, and predict future price movements.
Here are some of the key analyst uses of technical indicators:
- Trend Identification: Technical indicators help analysts identify the direction and strength of a market trend. By analyzing the price movements and patterns, indicators such as moving averages, trend lines, and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can help analysts determine whether a market is trending upwards, downwards, or sideways.
- Confirmation of Market Signals: Technical indicators can be used to confirm or validate signals generated by other analysis techniques. For example, if a chart pattern suggests a potential reversal, analysts may use indicators like RSI (Relative Strength Index) or Stochastic Oscillator to confirm the signal before making a trading decision.
- Overbought and Oversold Conditions: Technical indicators can help analysts identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. Indicators like RSI and Stochastic Oscillator measure the momentum of price movements and provide insights into whether a security is overbought (potentially due for a price correction) or oversold (potentially due for a price rebound).
- Volatility Measurement: Technical indicators can also help analysts measure the volatility of a security or market. Volatility indicators such as Bollinger Bands or Average True Range (ATR) provide insights into the price fluctuations and can be used to assess the risk and potential profitability of a trade.
- Entry and Exit Points: Technical indicators can assist analysts in determining optimal entry and exit points for trades. By analyzing indicators like moving averages, MACD, or Fibonacci retracement levels, analysts can identify potential price levels where buying or selling positions may be favorable.
How Analysts Use Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are widely used by analysts to make informed decisions in the financial markets. These indicators provide valuable insights into the price movements of various securities, helping analysts identify trends, reversals, and potential trading opportunities.
Analysts use technical indicators in a variety of ways, depending on their trading strategies and goals. Here are some common ways analysts utilize technical indicators:
| 1. Trend Identification: | Technical indicators can help analysts identify the direction of a trend. By analyzing the price movements and patterns, indicators such as moving averages, trendlines, and the Average Directional Index (ADX) can provide insights into whether the market is trending upwards, downwards, or sideways. |
| 2. Entry and Exit Points: | Technical indicators can assist analysts in determining optimal entry and exit points for trades. Indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Stochastic Oscillator, and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) can signal overbought or oversold conditions, indicating potential reversal points. |
| 3. Confirmation of Price Patterns: | Technical indicators can confirm the validity of price patterns. For example, if a chart shows a bullish reversal pattern, analysts may use indicators like the Moving Average or the Volume Oscillator to confirm the strength of the pattern before making trading decisions. |
| 4. Volatility Analysis: | Technical indicators can help analysts assess the volatility of a security. Indicators such as Bollinger Bands, Average True Range (ATR), and the Chaikin Volatility Indicator provide insights into the price range and potential price movements, helping analysts manage risk and set appropriate stop-loss levels. |
| 5. Divergence Analysis: | Technical indicators can be used to identify divergences between the price and the indicator itself. Divergences occur when the price and the indicator move in opposite directions, indicating a potential trend reversal. Analysts often use indicators like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to spot these divergences. |
Overall, technical indicators provide analysts with valuable information about the price movements and trends in the financial markets. By incorporating these indicators into their analysis, analysts can make more informed trading decisions and improve their chances of success.
Types of Technical Indicators
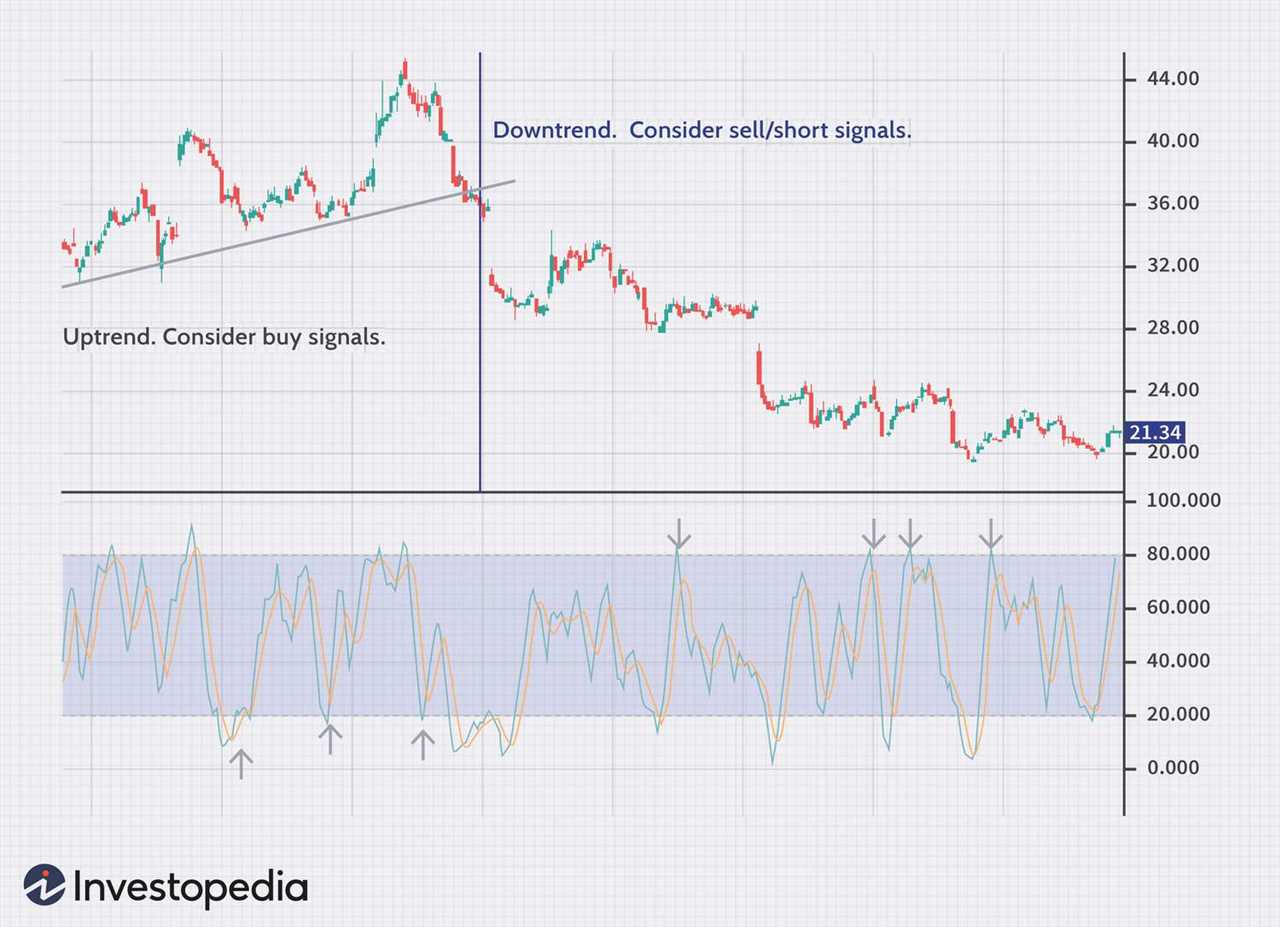
Technical indicators are essential tools used by analysts to analyze price movements and predict future market trends. These indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price data and are used to identify patterns, trends, and potential trading opportunities.
There are various types of technical indicators, each with its own unique formula and purpose. Here are some common types of technical indicators:
Trend Indicators:
Trend indicators are used to identify the direction and strength of a market trend. They help traders determine whether the market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or ranging. Examples of trend indicators include moving averages, trendlines, and the Average Directional Index (ADX).
Momentum Indicators:
Momentum indicators are used to measure the speed and strength of price movements. They help traders identify overbought or oversold conditions and potential trend reversals. Examples of momentum indicators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Stochastic Oscillator, and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
Volume Indicators:
Volume indicators are used to analyze the trading volume of a security. They help traders understand the level of market participation and confirm the strength of a trend. Examples of volume indicators include On-Balance Volume (OBV), Chaikin Money Flow (CMF), and Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP).
Volatility Indicators:
Volatility indicators are used to measure the volatility or price fluctuations of a security. They help traders identify potential breakouts or trend reversals. Examples of volatility indicators include Bollinger Bands, Average True Range (ATR), and Standard Deviation.
Oscillators:
Oscillators are used to identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. They help traders determine when a security is likely to reverse its direction. Examples of oscillators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and the Stochastic Oscillator.
Each type of technical indicator has its own strengths and weaknesses, and traders often use a combination of indicators to make informed trading decisions. It is important to understand the characteristics and limitations of each indicator before using them in your analysis.
Common Types of Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are widely used by analysts to analyze price movements and identify potential trading opportunities in financial markets. There are various types of technical indicators, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Here are some common types of technical indicators:
1. Trend Indicators: These indicators are used to identify the direction of the market trend. They help traders determine whether the market is in an uptrend, downtrend, or ranging phase. Examples of trend indicators include moving averages, trendlines, and the Average Directional Index (ADX).
2. Oscillators: Oscillators are used to identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. They provide signals when the market is likely to reverse or consolidate. Examples of oscillators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Stochastic Oscillator, and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD).
3. Volume Indicators: Volume indicators measure the trading volume in a market. They help traders analyze the strength of price movements and identify potential reversals or continuations. Examples of volume indicators include the On-Balance Volume (OBV), Chaikin Money Flow (CMF), and the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP).
4. Momentum Indicators: Momentum indicators measure the speed and strength of price movements. They help traders identify potential trend reversals or continuations. Examples of momentum indicators include the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and the Average True Range (ATR).
5. Volatility Indicators: Volatility indicators measure the volatility or price fluctuations in a market. They help traders identify potential breakouts or reversals. Examples of volatility indicators include Bollinger Bands, Average True Range (ATR), and the Moving Average Envelope.
6. Support and Resistance Indicators: These indicators help traders identify key levels of support and resistance in a market. They provide insights into potential price reversals or breakouts. Examples of support and resistance indicators include pivot points, Fibonacci retracement levels, and the Ichimoku Cloud.
7. Pattern Recognition Indicators: Pattern recognition indicators help traders identify chart patterns that can indicate potential trend reversals or continuations. Examples of pattern recognition indicators include the Head and Shoulders pattern, Double Top/Bottom, and the Cup and Handle pattern.
It is important to note that technical indicators should not be used in isolation but rather in conjunction with other forms of analysis. Traders should also consider the specific characteristics of the financial instrument being traded and adjust their strategies accordingly.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
