What is a Retention Bonus?
A retention bonus is a financial incentive offered by a company to encourage employees to stay with the organization for a specific period of time. It is typically a one-time payment or a series of payments given to employees who meet certain criteria, such as remaining employed for a predetermined length of time or achieving specific performance goals.
Definition and Purpose
The purpose of a retention bonus is to retain valuable employees and reduce turnover. It is often used in industries where there is a high demand for skilled workers or in situations where an organization is undergoing significant changes, such as mergers or acquisitions.
Retention bonuses are designed to motivate employees to stay with the company during periods of uncertainty or transition. By offering a financial incentive, employers hope to encourage employees to remain committed and engaged, rather than seeking opportunities elsewhere.
How Does Retention Pay Work?
Retention pay works by offering employees a financial reward for staying with the company for a specified period of time. The bonus amount and the criteria for earning it are typically outlined in an employment contract or agreement.
For example, a company may offer a retention bonus of $10,000 to employees who remain with the organization for two years after a merger. The bonus may be paid out in installments, such as $5,000 after the first year and $5,000 after the second year.
In some cases, retention bonuses may be tied to performance goals or specific milestones. For example, an employee may be eligible for a bonus if they achieve certain sales targets or complete a project successfully.
Benefits of Offering Retention Bonuses
Offering retention bonuses can have several benefits for both employers and employees. For employers, retention bonuses can help reduce turnover and the associated costs of recruiting and training new employees. They can also help maintain stability and continuity during times of change.
For employees, retention bonuses provide a financial incentive to stay with the company, which can help improve job satisfaction and morale. They can also provide a sense of security and stability, knowing that they will receive a bonus if they meet the specified criteria.
Why Companies Choose to Provide Retention Pay
Companies choose to provide retention pay for a variety of reasons. Some of the common reasons include:
- Retaining key talent: Companies may offer retention bonuses to retain employees with critical skills or knowledge that are difficult to replace.
- Managing organizational changes: During periods of change, such as mergers or acquisitions, companies may use retention bonuses to keep employees engaged and committed.
- Reducing turnover: Retention bonuses can help reduce turnover by providing employees with a financial incentive to stay with the company.
- Improving employee morale: Offering retention bonuses can boost employee morale and job satisfaction, as employees feel valued and appreciated.
Considerations for Implementing Retention Bonuses
When implementing retention bonuses, companies should consider several factors:
- Cost: Retention bonuses can be expensive, so companies need to carefully consider the financial impact and whether the benefits outweigh the costs.
- Eligibility criteria: Companies should clearly define the criteria for earning a retention bonus to ensure fairness and transparency.
- Effectiveness: Companies should regularly evaluate the effectiveness of their retention bonus program to determine if it is achieving its intended goals.
The purpose of retention pay is to encourage employees to remain loyal to the organization and discourage them from seeking employment elsewhere. It is often used as a strategic tool by companies to retain their top talent and prevent the loss of valuable employees.
Retention pay is typically offered in situations where there is a high risk of employee turnover, such as during mergers and acquisitions, restructuring, or when there is a shortage of skilled workers in a particular industry. By offering a financial incentive, companies aim to motivate employees to stay with the organization and continue contributing to its success.
Companies may also use retention pay as a way to acknowledge and reward employees who have demonstrated exceptional performance or have made significant contributions to the organization. It can be seen as a way to show appreciation for their hard work and dedication.
Overall, retention pay serves as a powerful tool for companies to retain their top talent and maintain a competitive edge in the market. It helps to create a sense of loyalty and commitment among employees, which can lead to increased productivity, improved morale, and ultimately, the long-term success of the organization.
How Does Retention Pay Work?
Retention pay is typically offered to employees who are critical to the success of the organization, such as top performers, executives, or employees with specialized skills or knowledge. The purpose of retention pay is to motivate these employees to stay with the company and continue contributing their expertise.
Eligibility Criteria
The eligibility criteria for retention pay vary from company to company. Some common criteria include the length of service, performance metrics, and the employee’s role within the organization. Employers may also consider the employee’s potential to leave the company or the difficulty of replacing them.
Before offering retention pay, employers may conduct a thorough evaluation of the employee’s performance and potential. This evaluation helps determine the amount of the bonus and whether the employee meets the necessary criteria.
Payment Structure
The payment structure of retention pay can vary. It can be a one-time lump sum payment or divided into multiple installments over a specified period. The payment may be contingent on the employee’s continued employment with the company for a certain duration.
Retention pay is typically separate from the employee’s regular salary and may be subject to different tax regulations. Employers may also include clawback provisions in the retention pay agreement, which allow them to recover the bonus if the employee leaves the company before a specified period.
Communication and Transparency
When implementing retention pay, it is essential for employers to communicate the purpose and criteria of the bonus clearly to the eligible employees. This helps create transparency and ensures that employees understand the expectations and requirements for receiving the bonus.
Exploring the Mechanics of Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses are a type of financial incentive offered by companies to encourage employees to stay with the organization for a specified period of time. These bonuses are typically given as a lump sum payment or as a series of payments over a set period.
There are several key factors to consider when implementing retention bonuses:
1. Eligibility Criteria:
Companies need to establish clear eligibility criteria for retention bonuses. This may include factors such as job title, length of service, performance, or criticality of the employee’s role within the organization. By defining these criteria, companies can ensure that the bonuses are awarded to employees who are most likely to contribute to the long-term success of the company.
2. Bonus Amount:
The amount of the retention bonus should be carefully determined to strike a balance between motivating employees to stay and the financial feasibility for the company. It should be a significant enough sum to be enticing, but not so high that it becomes unsustainable for the company to offer.
3. Payment Structure:
Retention bonuses can be paid out in various ways. Some companies choose to provide a lump sum payment at the end of the retention period, while others prefer to distribute the bonus in installments over the course of the specified period. The payment structure should be designed to align with the company’s financial capabilities and the employee’s preferences.
4. Retention Period:
The length of the retention period is an important consideration. Companies need to determine how long they want employees to stay in order to receive the bonus. This period can vary depending on the industry, job role, and the company’s specific goals and needs.
5. Communication and Transparency:
It is crucial for companies to communicate the details of the retention bonus program clearly and transparently to employees. This includes explaining the eligibility criteria, bonus amount, payment structure, and retention period. Clear communication helps employees understand the value of the bonus and motivates them to stay with the company.
Retention bonuses can be an effective tool for companies to retain top talent and reduce turnover. By carefully considering the mechanics of retention bonuses and implementing them strategically, companies can create a win-win situation for both the organization and its employees.
Benefits of Offering Retention Bonuses
Retention bonuses can provide several benefits for both employers and employees. Here are some key advantages of offering retention bonuses:
1. Employee Loyalty: Retention bonuses can help foster a sense of loyalty among employees. By offering a financial incentive for staying with the company, employees are more likely to remain committed and dedicated to their work.
2. Talent Retention: In competitive industries, attracting and retaining top talent is crucial for business success. Retention bonuses can help companies retain their best employees by providing them with an additional incentive to stay.
3. Increased Productivity: When employees feel valued and appreciated, they are more likely to be motivated and productive. Retention bonuses can serve as a reward for hard work and can encourage employees to continue performing at their best.
4. Cost Savings: Hiring and training new employees can be costly and time-consuming. By offering retention bonuses, companies can reduce turnover rates and save on recruitment and training expenses.
5. Competitive Advantage: Offering retention bonuses can give companies a competitive edge in the job market. Candidates may be more inclined to choose a company that offers attractive retention bonuses over one that does not.
6. Employee Satisfaction: Retention bonuses can contribute to overall employee satisfaction. When employees feel appreciated and rewarded for their loyalty, they are more likely to have a positive attitude towards their work and the company.
7. Long-Term Planning: Retention bonuses can help companies with long-term planning by ensuring that key employees remain with the organization. This stability allows for better succession planning and continuity in leadership roles.
8. Employee Engagement: Retention bonuses can enhance employee engagement by creating a sense of investment in the company’s success. When employees feel valued and recognized, they are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work.
Why Companies Choose to Provide Retention Pay
Retention pay, in the form of retention bonuses, is a strategic tool that companies use to incentivize and retain their top-performing employees. There are several reasons why companies choose to provide retention pay:
1. Retaining Key Talent:
2. Minimizing Turnover Costs:
Employee turnover can be costly for companies. When an employee leaves, the company must invest time and resources into recruiting, hiring, and training a replacement. By providing retention pay, companies can reduce turnover rates and the associated costs, ultimately saving money in the long run.
3. Maintaining Continuity:
When a key employee leaves, it can disrupt the workflow and productivity of a team or department. By offering retention bonuses, companies can ensure continuity by keeping their top performers in place. This helps maintain stability and prevents a loss of institutional knowledge and expertise.
4. Motivating and Engaging Employees:
Retention pay can serve as a powerful motivator for employees. When employees know that their hard work and dedication are recognized and rewarded, they are more likely to stay engaged and committed to their work. Retention bonuses can boost morale and create a positive work environment.
5. Fostering Loyalty:
Retention pay can foster a sense of loyalty among employees. When employees feel valued and appreciated, they are more likely to develop a strong sense of loyalty towards their employer. This loyalty can lead to increased job satisfaction, higher levels of productivity, and a lower likelihood of seeking employment elsewhere.
6. Competitive Advantage:
Offering retention pay can give companies a competitive advantage in the job market. In industries where talent is in high demand, companies that provide attractive retention bonuses are more likely to attract and retain top talent. This can give them an edge over their competitors and contribute to their overall success.
Considerations for Implementing Retention Bonuses
Implementing retention bonuses requires careful consideration and planning to ensure their effectiveness and alignment with the company’s goals and culture. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind:
1. Clear Objectives
Before implementing retention bonuses, it is crucial to define clear objectives. This includes identifying the specific goals the bonuses aim to achieve, such as reducing turnover, retaining top talent, or incentivizing employees during a critical period.
2. Budget Allocation
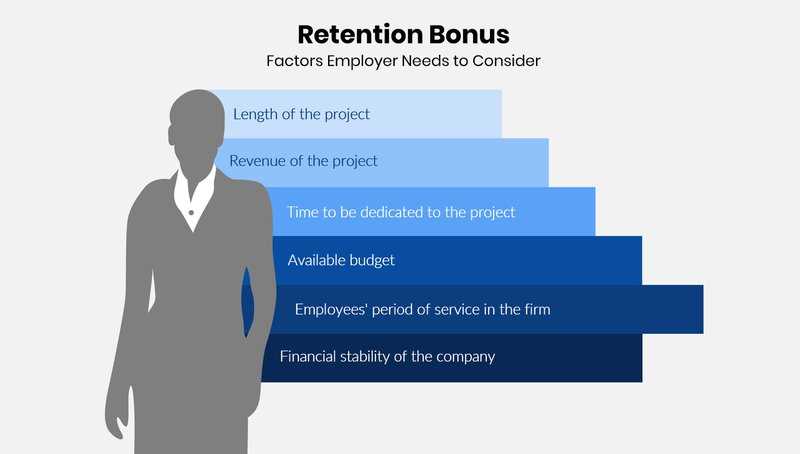
Retention bonuses should be carefully budgeted to ensure they are sustainable and do not strain the company’s finances. It is important to assess the financial impact of offering bonuses and determine the appropriate amount to allocate for each employee or group of employees.
3. Fair and Transparent Criteria
The criteria for awarding retention bonuses should be fair, transparent, and based on measurable factors. This helps to ensure that the bonuses are perceived as equitable and motivate employees to stay with the company. Examples of criteria can include length of service, performance metrics, or critical skill sets.
4. Communication and Engagement
Effective communication is essential when implementing retention bonuses. It is important to clearly communicate the purpose, eligibility criteria, and timing of the bonuses to employees. Additionally, engaging employees in the process by seeking their input and feedback can help to foster a sense of ownership and commitment.
5. Evaluation and Adjustments
Regular evaluation of the retention bonus program is necessary to assess its effectiveness and make any necessary adjustments. This includes monitoring turnover rates, employee satisfaction, and the overall impact on the company’s goals. Based on the evaluation, modifications can be made to ensure the program remains relevant and aligned with the company’s needs.
By carefully considering these factors, companies can implement retention bonuses that effectively incentivize and retain valuable employees. A well-designed retention bonus program can contribute to a positive work culture, enhance employee loyalty, and ultimately drive organizational success.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
