History and Formation of the Arab League
The formation of the Arab League was a response to the growing desire for Arab unity and the need to address common political, economic, and social issues faced by Arab nations. The league’s founders sought to strengthen Arab identity and foster cooperation in various fields, including politics, economics, culture, and education.
The Arab League’s structure consists of several bodies, including the Council, the General Secretariat, and specialized committees. The Council is the league’s highest decision-making body, composed of representatives from each member state. The General Secretariat, headed by the Secretary-General, is responsible for implementing the decisions of the Council and coordinating the league’s activities.
Throughout its history, the Arab League has faced various challenges, including internal divisions, conflicts among member states, and external pressures. However, it has also achieved notable successes in areas such as economic cooperation, cultural exchange, and joint defense efforts.
Objectives and Functions of the Arab League
One of the main objectives of the Arab League is to safeguard the independence and sovereignty of its member states. It seeks to protect the interests of Arab countries and promote their common goals and aspirations. The League also aims to strengthen Arab solidarity and foster cooperation in various fields, such as politics, economics, culture, and social development.
The Arab League has several functions that contribute to achieving its objectives. One of its key functions is to coordinate political positions and policies among member states. Through regular meetings and consultations, the League works towards consensus on regional and international issues, with the aim of presenting a unified Arab stance.
Another important function of the Arab League is to promote economic integration and cooperation among Arab countries. It seeks to enhance trade relations, facilitate investment, and promote economic development in the region. The League also works towards the establishment of a common market and the removal of trade barriers among member states.
Furthermore, the Arab League plays a significant role in addressing regional conflicts and promoting peace and stability in the Middle East. It supports peaceful resolution of disputes and encourages dialogue among member states. The League also cooperates with other regional and international organizations to address common challenges, such as terrorism and extremism.
In addition, the Arab League is committed to promoting Arab culture and heritage. It encourages cultural exchange and cooperation among member states, with the aim of preserving and promoting Arab identity and heritage. The League also supports educational and scientific cooperation to enhance the capabilities and knowledge of Arab nations.
Role of the Arab League in the Middle East
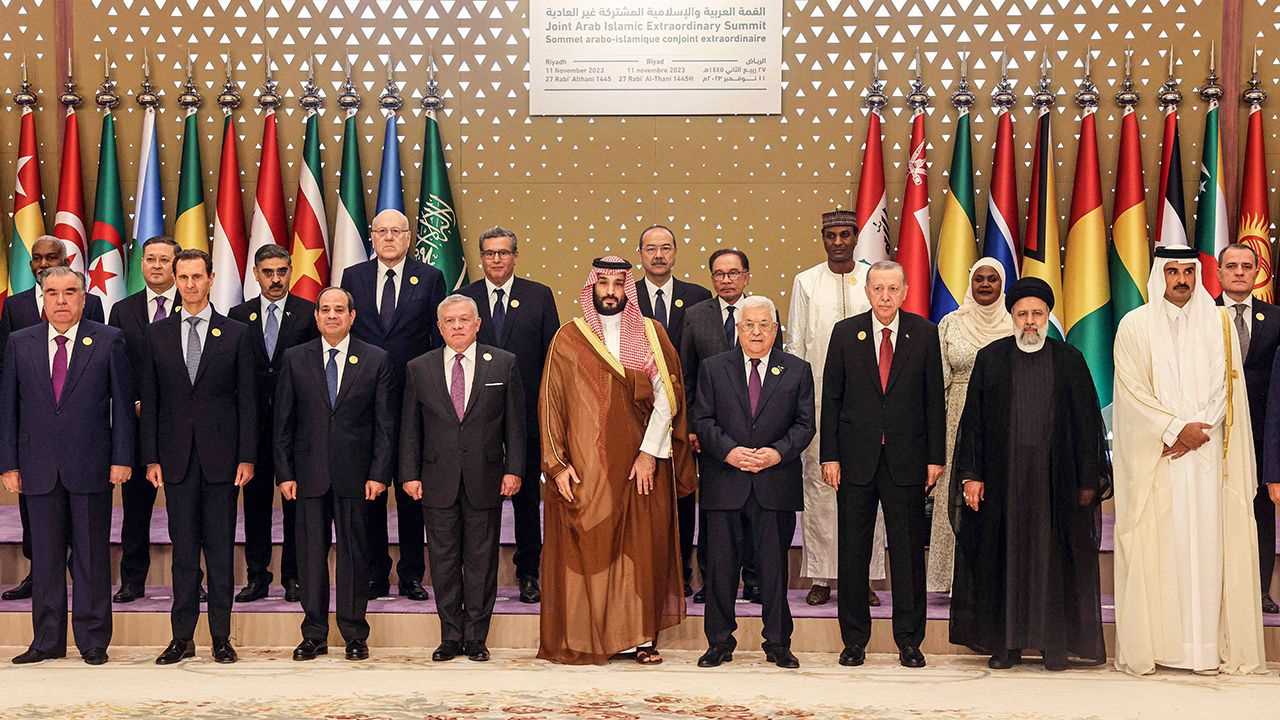

The Arab League plays a significant role in the Middle East region, working towards promoting unity, cooperation, and coordination among its member states. It serves as a platform for dialogue and collaboration on various political, economic, social, and cultural issues.
Political Role
Economic Role
The Arab League works towards enhancing economic cooperation and integration among its member states. It aims to promote economic development, trade, and investment within the Arab world. The League facilitates the establishment of joint economic projects, encourages intra-Arab trade, and supports initiatives to reduce trade barriers and promote economic diversification.
Furthermore, the Arab League plays a role in coordinating economic policies and positions among its member states. It addresses economic challenges and works towards developing common strategies to tackle issues such as poverty, unemployment, and sustainable development.
Social and Cultural Role
The Arab League recognizes the importance of social and cultural cooperation among its member states. It aims to preserve and promote Arab culture, heritage, and identity. The League supports initiatives that foster cultural exchange, education, and scientific research among Arab countries.
Moreover, the Arab League plays a role in addressing social issues and promoting human rights within the Arab world. It works towards enhancing social welfare, gender equality, and the rights of marginalized groups. The League also supports initiatives to combat terrorism, extremism, and radicalization.
Challenges and Future Prospects for the Arab League
The Arab League, like any other international organization, faces numerous challenges in its efforts to promote unity and cooperation among its member states. These challenges stem from both internal and external factors and have a significant impact on the effectiveness and relevance of the organization in addressing the issues facing the Middle East.
Internal Challenges
- Political Divisions: One of the major challenges facing the Arab League is the political divisions among its member states. These divisions often hinder the ability of the organization to reach consensus and take collective action on regional issues. The differing political ideologies, interests, and priorities of member states make it difficult to formulate a unified stance on critical matters.
- Lack of Cooperation: Another internal challenge is the lack of effective cooperation among member states. Despite the shared cultural and historical ties, many Arab countries have struggled to work together towards common goals. This lack of cooperation undermines the Arab League’s ability to address regional conflicts, promote economic integration, and effectively respond to crises.
- Resource Constraints: Many Arab League member states face economic and resource constraints that limit their ability to actively participate in the organization’s initiatives. Limited financial resources and infrastructure hinder the implementation of projects and programs aimed at promoting development and stability in the region.
External Challenges
- Regional Conflicts: The Middle East is plagued by various conflicts, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the Syrian civil war, and the ongoing instability in Yemen and Libya. These conflicts pose significant challenges to the Arab League’s efforts to maintain peace and stability in the region. The organization often struggles to mediate and resolve these conflicts due to the complex nature of the issues and the involvement of external actors.
- Changing Dynamics: The Middle East is undergoing significant geopolitical shifts, with new power dynamics emerging in the region. The rise of non-Arab actors, such as Turkey and Iran, has altered the balance of power and influence. The Arab League must adapt to these changing dynamics to remain relevant and effective in addressing the region’s challenges.
Despite these challenges, the Arab League continues to play a crucial role in the Middle East. To overcome these obstacles and enhance its effectiveness, the organization needs to foster greater unity among member states, strengthen cooperation mechanisms, and address the root causes of regional conflicts. Additionally, the Arab League should actively engage with external actors and forge strategic partnerships to better navigate the complex geopolitical landscape. By doing so, the Arab League can work towards achieving its objectives of promoting peace, stability, and development in the Middle East.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
