What is a Put Option?
Put options are typically used as a form of insurance or protection against a decline in the price of an underlying asset. They allow investors to profit from a decrease in the value of the asset without actually owning it. Put options are commonly used in stock trading, but they can also be used for other types of assets such as commodities, currencies, and indices.
When an investor purchases a put option, they are essentially betting that the price of the underlying asset will decrease. If the price does indeed decrease below the strike price, the investor can exercise the option and sell the asset at the higher strike price, thereby making a profit. However, if the price of the asset remains above the strike price, the investor is not obligated to exercise the option and can let it expire worthless.
Put options have several key components that determine their value and potential profitability. These include the strike price, the expiration date, the premium (the price paid for the option), and the underlying asset. The strike price is the price at which the asset can be sold, the expiration date is the date by which the option must be exercised, and the premium is the cost of purchasing the option.
How Does a Put Option Work?
When an investor purchases a put option, they are essentially betting that the price of the underlying asset will decrease. If the price does indeed fall below the strike price, the investor can exercise their option and sell the asset at the higher strike price, thereby making a profit.
For example, let’s say an investor purchases a put option on 100 shares of XYZ stock with a strike price of $50 and an expiration date of one month. If the price of XYZ stock falls below $50 within that month, the investor can exercise their option and sell the shares at $50, even if the market price is lower. This allows the investor to profit from the decline in the stock price.
Overall, put options provide investors with the opportunity to profit from a decline in the price of an asset, while also providing a form of insurance against potential losses. They can be a valuable tool in a well-diversified investment strategy.
Put Option: Trading Strategies
Protective Put Strategy
For example, suppose an investor holds 100 shares of a stock that is currently trading at $50 per share. The investor is concerned about a potential decline in the stock price and decides to implement a protective put strategy. They buy a put option with a strike price of $45 and an expiration date of one month. If the stock price falls below $45, the put option will increase in value and offset the losses on the stock position.
Long Put Strategy
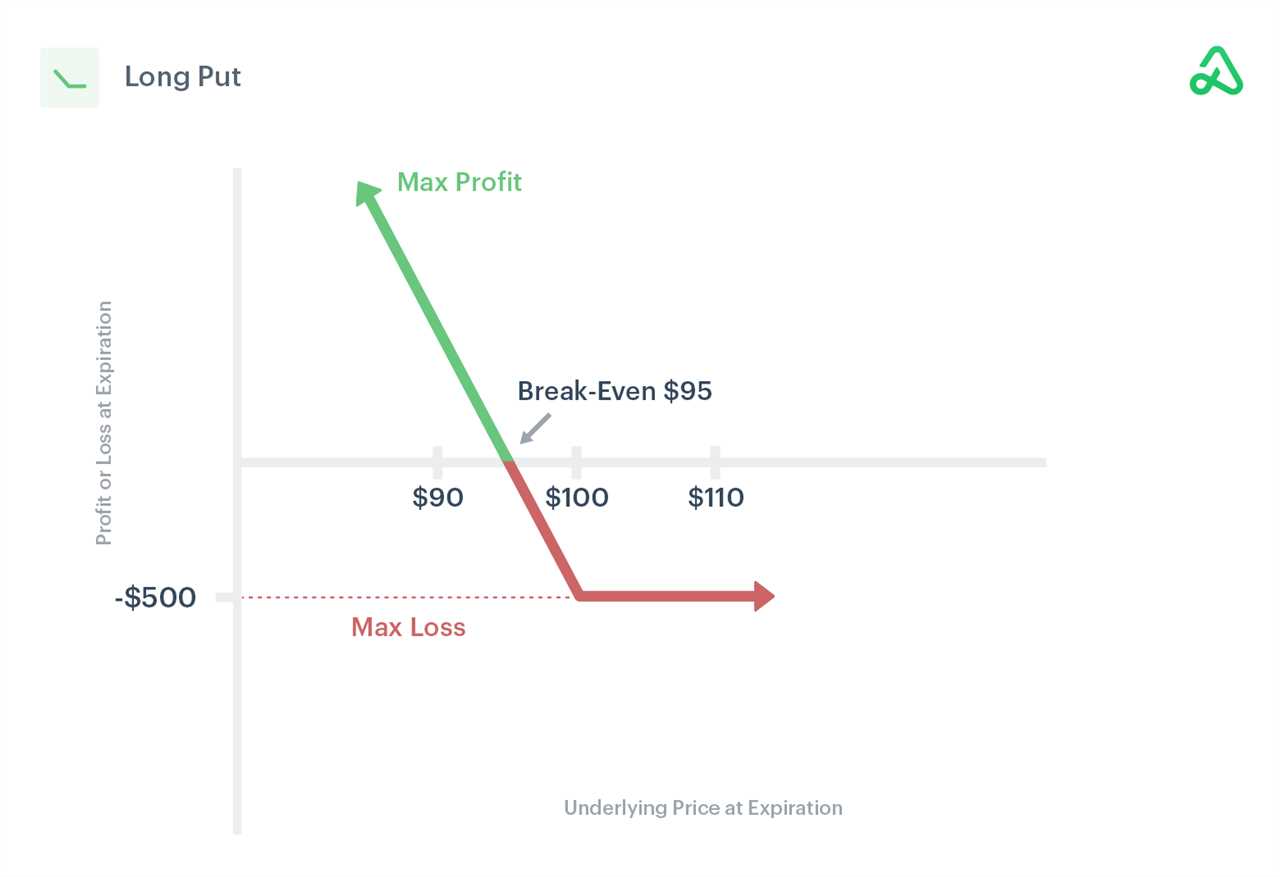
For example, suppose an investor believes that the price of a stock, currently trading at $100 per share, will decline in the near future. They decide to implement a long put strategy by buying a put option with a strike price of $90 and an expiration date of one month. If the stock price falls below $90, the put option will increase in value, allowing the investor to profit from the decline.
Put Spread Strategy
For example, suppose an investor believes that the price of a stock, currently trading at $50 per share, will decline slightly in the near future. They decide to implement a put spread strategy by buying a put option with a strike price of $45 and selling a put option with a strike price of $40, both with an expiration date of one month. If the stock price falls below $45, the put option with the higher strike price will increase in value, while the put option with the lower strike price will decrease in value, resulting in a net profit.
These are just a few examples of trading strategies involving put options. It is important for investors to carefully consider their risk tolerance, investment goals, and market outlook before implementing any options trading strategy.
Protective Put Strategy
The protective put strategy is a risk management technique used by investors to protect their stock holdings from potential downside risk. It involves buying a put option on a stock that an investor already owns. This put option acts as insurance against a decline in the stock price.
How It Works
For example, let’s say an investor owns 100 shares of a stock that is currently trading at $50 per share. They are concerned that the stock price may decline in the future, so they decide to buy a put option with a strike price of $45 and an expiration date of one month. This put option gives them the right to sell their 100 shares of stock at $45 per share within the next month.
If the stock price falls below $45, the investor can exercise the put option and sell their shares at the higher strike price of $45, limiting their losses. However, if the stock price remains above $45, the investor can simply let the put option expire worthless and continue to hold onto their shares.
Benefits and Risks
The protective put strategy provides investors with downside protection and allows them to limit their losses if the stock price declines. It acts as an insurance policy against potential market downturns and can help investors sleep better at night knowing that their portfolio is protected.
However, there are some risks associated with the protective put strategy. First, buying a put option requires paying a premium, which can eat into potential profits. Additionally, if the stock price remains above the strike price, the put option will expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
Furthermore, the protective put strategy is not foolproof and does not guarantee that an investor will avoid losses. It only protects against declines in the stock price up to the strike price of the put option. If the stock price falls below the strike price, the investor may still experience losses.
Conclusion
The protective put strategy is a useful tool for investors looking to protect their stock holdings from potential downside risk. By buying a put option, investors can limit their losses if the stock price declines, providing them with peace of mind and risk management capabilities.
Long Put Strategy
The long put strategy is a popular options trading strategy that allows investors to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset. It involves buying a put option, which gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset at a specified price (strike price) within a certain period of time (expiration date).
How Does the Long Put Strategy Work?
When an investor believes that the price of an asset will decrease, they can implement the long put strategy. Here’s how it works:
- The investor buys a put option on the underlying asset.
- The put option has a strike price and an expiration date.
- If the price of the underlying asset decreases below the strike price before the expiration date, the put option becomes profitable.
- The investor can then exercise the put option and sell the underlying asset at the higher strike price, making a profit.
The long put strategy is often used as a hedging tool to protect a portfolio against potential losses. By buying put options, investors can limit their downside risk if the price of the underlying asset declines.
Advantages of the Long Put Strategy
There are several advantages to using the long put strategy:
- Profit potential: If the price of the underlying asset decreases significantly, the investor can make a substantial profit.
- Downside protection: The long put strategy provides downside protection by limiting potential losses if the price of the underlying asset declines.
Risks of the Long Put Strategy
While the long put strategy offers potential benefits, it also carries some risks:
- Time decay: As time passes, the value of the put option decreases, which can erode the investor’s profits.
- Limited profit potential: The investor’s profit is limited to the difference between the strike price and the price of the underlying asset, minus the premium paid for the put option.
- Loss of premium: If the price of the underlying asset does not decrease below the strike price before the expiration date, the put option may expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
Conclusion
The long put strategy is a popular options trading strategy that allows investors to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset. It provides downside protection and offers the potential for significant profits. However, it also carries risks, such as time decay and limited profit potential. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and trading objectives before implementing the long put strategy.
Put Spread Strategy
The put spread strategy is a popular options trading strategy that involves buying and selling put options with different strike prices. It is a limited-risk strategy that can be used by traders to profit from a decline in the price of the underlying asset.
In a put spread strategy, the trader buys a put option with a higher strike price and sells a put option with a lower strike price. The goal is to profit from the difference in the premiums of the two options. The trader expects the price of the underlying asset to decrease, causing the value of the put options to increase.
There are two types of put spread strategies: the bear put spread and the bull put spread. The bear put spread is used when the trader believes that the price of the underlying asset will decrease. The bull put spread is used when the trader believes that the price of the underlying asset will remain above the lower strike price.
When implementing a put spread strategy, it is important to consider the maximum profit and maximum loss potential. The maximum profit is limited to the difference in the strike prices minus the net premium paid, while the maximum loss is limited to the net premium paid.
The put spread strategy can be a useful tool for traders looking to profit from a decline in the price of an underlying asset. It allows traders to limit their risk while still potentially earning a profit. However, like any options trading strategy, it is important to carefully consider the risks and rewards before implementing the strategy.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
