Projected Benefit Obligation Definition
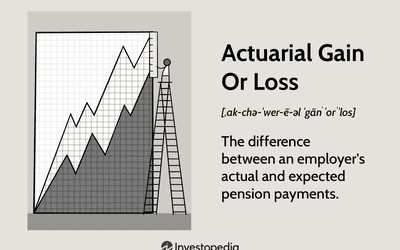
The projected benefit obligation (PBO) is a financial term used in the field of financial analysis. It refers to the estimated amount of money that a company will need to set aside in order to fulfill its future pension obligations to its employees. The PBO is an important metric for companies to consider when evaluating their financial health and long-term sustainability.
The PBO is an important metric for both companies and investors. For companies, it represents a liability on their balance sheet and can impact their financial statements and overall financial health. It is also a key consideration for companies when making decisions about pension plan funding and investment strategies.
For investors, the PBO provides insight into a company’s long-term financial obligations and its ability to meet those obligations. It can also impact the company’s valuation and stock performance.
| Benefits of Projected Benefit Obligation in Financial Analysis |
|---|
| 1. Provides an estimate of future pension obligations |
| 2. Helps companies assess their financial health and sustainability |
| 3. Guides decision-making on pension plan funding and investment strategies |
| 4. Provides insight for investors into a company’s long-term financial obligations |
Projected Benefit Obligation (PBO) is a financial term that refers to the estimated amount of money a company will need to pay to its employees as retirement benefits in the future. It is an important concept in financial analysis as it helps assess the financial obligations and liabilities of a company.
When a company offers retirement benefits to its employees, it creates a long-term financial obligation. The projected benefit obligation is the present value of these future retirement benefits that the company expects to pay to its employees. It takes into account factors such as employee salaries, years of service, expected retirement age, and expected lifespan after retirement.
The PBO is calculated using actuarial assumptions and techniques. Actuaries use statistical models and data to estimate the future cash flows required to meet the retirement benefit obligations. These assumptions include factors such as mortality rates, salary growth rates, and discount rates.
Importance of Projected Benefit Obligation in Financial Analysis
Projected Benefit Obligation is an important metric for financial analysis as it helps assess the financial health and sustainability of a company. By calculating the PBO, analysts can evaluate the long-term liabilities and obligations of a company and determine its ability to meet these obligations.
How It Works
The concept of projected benefit obligation (PBO) is an important aspect of financial analysis, particularly in the field of pension accounting. PBO refers to the estimated amount of money that a company will need to pay out in pension benefits to its employees over the course of their retirement.
When calculating PBO, several factors are taken into consideration. These include the number of employees, their ages, their years of service, and the expected length of their retirement. Additionally, the projected investment returns on the pension fund assets are also factored in.
Once all of these variables are determined, a company can calculate its PBO using actuarial assumptions and techniques. This calculation provides a snapshot of the company’s future pension obligations and helps to determine the funding requirements for the pension plan.
Actuarial Assumptions
Actuarial assumptions play a crucial role in the calculation of PBO. These assumptions include the expected rate of return on pension assets, the discount rate used to calculate the present value of future pension payments, and the mortality rates of the plan participants.
The expected rate of return on pension assets is an important assumption because it affects the amount of money that needs to be contributed to the pension plan. A higher expected rate of return will result in lower contributions, while a lower expected rate of return will require higher contributions.
The discount rate, on the other hand, is used to calculate the present value of future pension payments. A higher discount rate will result in a lower present value, while a lower discount rate will increase the present value of future pension obligations.
Mortality rates are also taken into account when calculating PBO. These rates reflect the likelihood of plan participants living to a certain age. The longer participants are expected to live, the higher the projected benefit obligation will be.
Importance in Financial Analysis
The projected benefit obligation is an important metric for financial analysis because it provides insights into a company’s long-term financial obligations. It helps investors and analysts assess the financial health and sustainability of a company’s pension plan.
Furthermore, the projected benefit obligation can also impact a company’s financial statements. It is reported as a liability on the balance sheet, which affects the company’s overall financial position and can impact its creditworthiness.
Calculating Projected Benefit Obligation
Projected Benefit Obligation (PBO) is a crucial concept in financial analysis, particularly in the field of pension accounting. It represents the estimated amount of money that a company will be required to pay to fulfill its future pension obligations to its employees.
To calculate the Projected Benefit Obligation, several factors need to be taken into consideration:
1. Employee Salary and Service
The first step is to determine the average salary of the employees who are eligible for the pension plan. This includes considering factors such as years of service, salary growth, and potential promotions. The longer an employee has been with the company and the higher their salary, the greater their projected benefit obligation.
2. Expected Retirement Age and Life Expectancy
The next factor to consider is the expected retirement age of the employees and their life expectancy. This helps in estimating the duration for which the company will need to provide pension benefits. If employees are expected to retire earlier or have a longer life expectancy, the projected benefit obligation will be higher.
3. Discount Rate
The discount rate is an important factor in calculating the projected benefit obligation. It represents the rate at which the future pension obligations are discounted to their present value. A higher discount rate will result in a lower projected benefit obligation, while a lower discount rate will lead to a higher projected benefit obligation.
4. Expected Return on Plan Assets
Another factor to consider is the expected return on the plan assets. This represents the anticipated rate of return on the investments made by the pension plan. A higher expected return will reduce the projected benefit obligation, while a lower expected return will increase it.
Once all these factors have been taken into account, the projected benefit obligation can be calculated using actuarial methods and financial models. It is important for companies to regularly review and update their projected benefit obligation to ensure accurate financial reporting and planning.
Financial Analysis
In the field of finance, projected benefit obligation (PBO) plays a crucial role in financial analysis. It is a measure used to determine the future pension obligations of a company or organization. By calculating the PBO, analysts can assess the financial health and stability of a company’s pension plan.
Financial analysis involves evaluating various aspects of a company’s financial performance, including its assets, liabilities, and cash flow. The projected benefit obligation is an important component of this analysis, as it provides insight into the long-term financial commitments a company has towards its employees.
Analysts use the projected benefit obligation to assess the financial impact of a company’s pension plan on its overall financial position. It helps them understand the potential liabilities that may arise in the future and evaluate the company’s ability to meet these obligations.
Furthermore, the projected benefit obligation is also used in financial reporting. Companies are required to disclose their pension obligations in their financial statements, including the projected benefit obligation. This information is important for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to evaluate the financial health and sustainability of a company.
Importance of Projected Benefit Obligation in Financial Analysis
One of the primary reasons why the PBO is important in financial analysis is that it provides a clear picture of a company’s long-term financial liabilities. By estimating the future pension benefits that employees are entitled to, businesses can assess the potential impact on their financial health and plan accordingly. This information is especially critical for companies that offer defined benefit pension plans, where the employer guarantees specific retirement benefits to employees.
Moreover, the PBO is a key component in determining a company’s pension expense, which is recorded in the financial statements. By accurately calculating the PBO, businesses can ensure that their financial statements reflect the true cost of providing pension benefits to employees. This, in turn, enables investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate financial information.
The PBO also plays a significant role in assessing a company’s ability to meet its pension obligations. By comparing the PBO to the company’s assets, businesses can determine if they have sufficient funds to cover future pension payments. This analysis is crucial for evaluating the financial stability and sustainability of a company, as well as its ability to attract and retain talented employees.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
