Pro Forma Financial Statements: Definition
Pro forma financial statements are projected financial statements that are created based on assumptions and hypothetical scenarios. These statements provide an estimate of a company’s financial performance and position in the future, typically for a specific period of time. Pro forma statements are used by businesses for various purposes, such as mergers and acquisitions, financial planning, and forecasting.
What are Pro Forma Financial Statements?
Pro forma financial statements are financial statements that are prepared based on certain assumptions and hypothetical scenarios. These statements are not based on historical data but are instead projected into the future. Pro forma statements typically include an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
Pro forma financial statements are used to estimate the financial performance and position of a company under different circumstances. They can be used to evaluate the potential impact of a merger or acquisition, assess the feasibility of a new business venture, or plan for future financial needs.
Why Create Pro Forma Statements?
There are several reasons why businesses create pro forma financial statements:
1. Mergers and Acquisitions: Pro forma statements are often used in the context of mergers and acquisitions to evaluate the financial impact of the transaction. By creating pro forma statements, companies can estimate the combined financials of the two entities and assess the potential synergies and risks.
2. Financial Planning: Pro forma statements are also used for financial planning purposes. By projecting future financials, companies can identify potential gaps in funding, plan for capital expenditures, and make informed decisions about resource allocation.
3. Forecasting: Pro forma statements can be used for forecasting purposes to estimate the financial performance of a company in the future. This can help businesses make strategic decisions, set realistic goals, and evaluate the potential outcomes of different scenarios.
Steps to Creating Pro Forma Statements
Creating pro forma financial statements involves several steps:
1. Gather Data: Collect relevant financial and operational data, such as historical financial statements, market research, and industry trends.
2. Define Assumptions: Identify the key assumptions that will drive the pro forma statements, such as revenue growth rates, cost structures, and capital expenditures.
3. Project Revenue and Expenses: Use the assumptions to project future revenue and expenses. This can be done using various forecasting techniques, such as trend analysis or market research.
4. Prepare the Income Statement: Based on the projected revenue and expenses, create a pro forma income statement that shows the estimated profitability of the company.
5. Create the Balance Sheet: Use the projected revenue and expenses to estimate the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. This will provide an overview of the company’s financial position.
6. Develop the Cash Flow Statement: Estimate the company’s cash inflows and outflows based on the projected revenue and expenses. This will provide insights into the company’s liquidity and ability to meet its financial obligations.
Key Considerations for Creating Pro Forma Statements
When creating pro forma financial statements, it is important to consider the following:
1. Accuracy of Assumptions: The accuracy of the assumptions used to create the pro forma statements is crucial. It is important to base the assumptions on reliable data and market research.
2. Sensitivity Analysis: Perform sensitivity analysis to assess the impact of changes in key assumptions on the pro forma statements. This will help identify potential risks and uncertainties.
3. Realistic Projections: Ensure that the projected financials are realistic and achievable. Overly optimistic projections can lead to unrealistic expectations and poor decision-making.
4. Regular Updates: Pro forma statements should be regularly updated to reflect changes in the business environment and new information. This will ensure that the statements remain relevant and accurate.
What are Pro Forma Financial Statements?
Pro forma financial statements are projected financial statements that a company creates to provide an estimate of its future financial performance. These statements are based on assumptions and hypothetical scenarios, rather than actual historical data. Pro forma statements are typically used in situations such as mergers and acquisitions, initial public offerings, and business planning.
Why are Pro Forma Financial Statements Important?
Pro forma financial statements are important because they allow companies to forecast and evaluate the potential financial impact of certain events or decisions. By creating pro forma statements, companies can assess the feasibility of a business venture, determine the financial viability of a merger or acquisition, or evaluate the potential effects of changes in business operations.
Pro forma financial statements provide several benefits:
- Financial Planning: Pro forma statements help companies plan and set financial goals by providing a clear picture of the potential financial outcomes.
- Risk Assessment: Pro forma statements allow companies to assess the financial risks associated with certain decisions or events, helping them make more informed choices.
- Investor Communication: Pro forma statements are often used to communicate financial projections and potential investment opportunities to investors and stakeholders.
- Decision Making: Pro forma statements provide valuable insights for decision-making processes, allowing companies to evaluate the potential financial impact of different scenarios.
Components of Pro Forma Financial Statements
Pro forma financial statements typically include the following components:
- Income Statement: This statement projects the company’s revenues, expenses, and net income for a specific period.
- Balance Sheet: The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity at a specific point in time.
- Cash Flow Statement: This statement shows the inflows and outflows of cash during a specific period, providing insights into the company’s liquidity.
Guide to Creating Pro Forma Statements
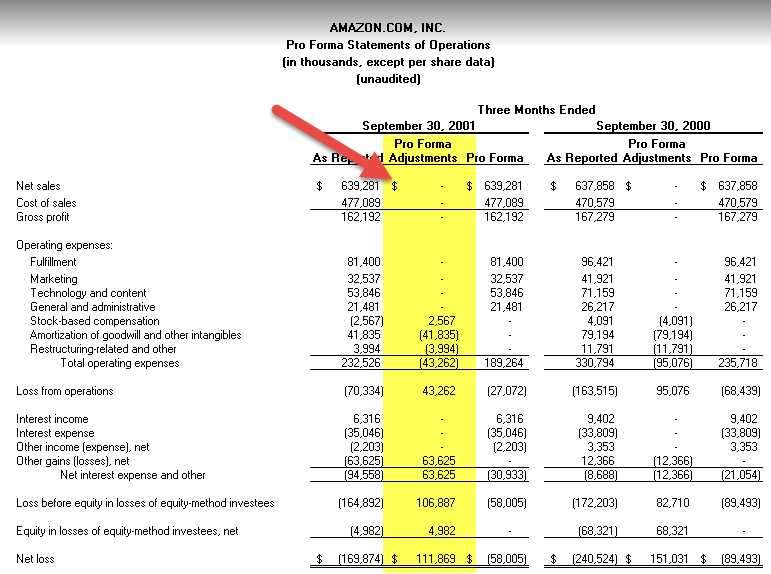
Creating pro forma financial statements is an essential step in the financial planning process for businesses. These statements provide a projected view of a company’s financial performance and position based on certain assumptions and hypothetical scenarios. Here is a step-by-step guide to creating pro forma statements:
1. Determine the Purpose
Before creating pro forma statements, it is important to determine the purpose for which they are being prepared. Are they needed for internal planning and decision-making or for external stakeholders such as investors or lenders? The purpose will dictate the level of detail and accuracy required in the statements.
2. Gather Historical Data
The next step is to gather historical financial data for the company. This includes income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the past few years. This data will serve as a starting point for creating the pro forma statements.
3. Identify Assumptions
Pro forma statements are based on assumptions about future business conditions and performance. These assumptions can include factors such as sales growth rates, pricing changes, cost fluctuations, and investment plans. It is important to clearly identify and document these assumptions to ensure transparency and accuracy in the pro forma statements.
4. Project Revenues
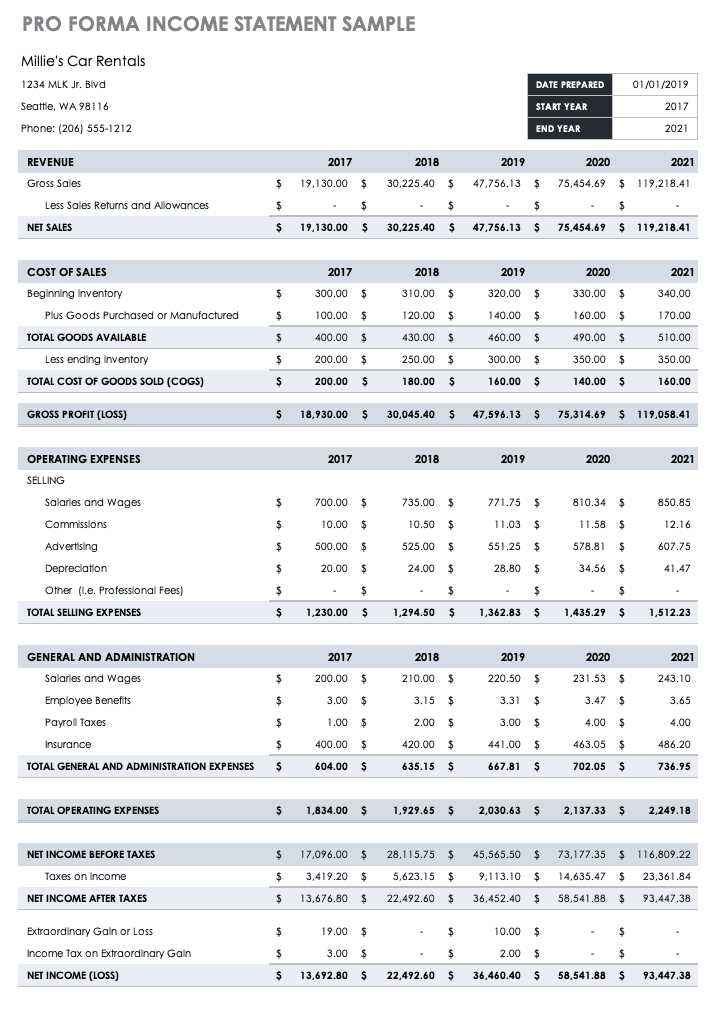
One of the key components of pro forma statements is projecting future revenues. This involves analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and industry forecasts to estimate future sales growth. Various methods such as trend analysis, market research, and expert opinions can be used to make these projections.
5. Forecast Expenses
After projecting revenues, the next step is to forecast expenses. This includes estimating costs for materials, labor, overhead, marketing, and other operating expenses. It is important to consider any expected changes in costs due to factors such as inflation, new investments, or changes in business strategy.
6. Calculate Net Income
Once revenues and expenses have been projected, the next step is to calculate the net income. This is done by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. It is important to consider any non-operating income or expenses that may affect the net income figure.
7. Prepare the Balance Sheet
After calculating the net income, the next step is to prepare the balance sheet. This involves projecting the company’s assets, liabilities, and equity based on the projected net income and other assumptions. It is important to ensure that the balance sheet balances and reflects the financial position of the company.
8. Create the Cash Flow Statement
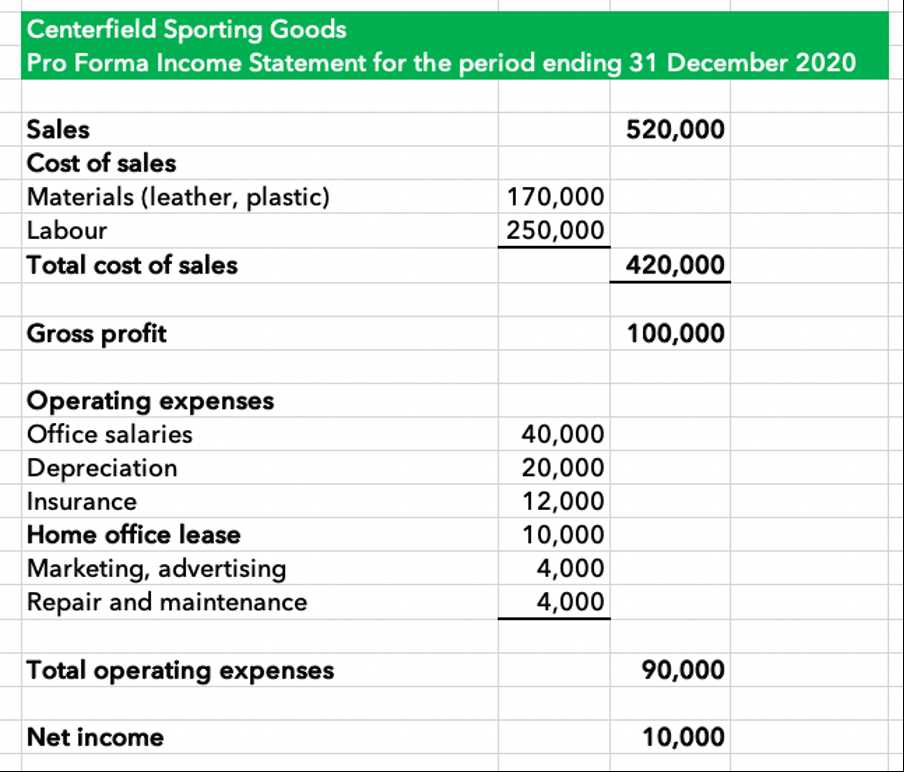
The final step is to create the cash flow statement. This statement shows the inflows and outflows of cash for the projected period. It includes cash from operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. It is important to ensure that the cash flow statement is accurate and reflects the company’s ability to generate and manage cash.
By following this guide, businesses can create accurate and reliable pro forma financial statements that can be used for financial planning, decision-making, and communicating with stakeholders.
Why Create Pro Forma Statements?
Creating pro forma financial statements is an essential step in the financial planning and analysis process for businesses. Pro forma statements provide a forecast of a company’s future financial performance based on certain assumptions and projections. They are used to assess the potential impact of various business decisions, such as mergers and acquisitions, new product launches, or changes in pricing strategies.
There are several key reasons why businesses create pro forma statements:
- Financial Planning: Pro forma statements help businesses plan for the future by providing a clear picture of the expected financial outcomes. They allow companies to set realistic goals and develop strategies to achieve them.
- Investor Relations: Pro forma statements are often used to communicate financial projections to investors and stakeholders. They provide valuable information about the company’s growth potential and can help attract investment and support from external parties.
- Decision Making: Pro forma statements enable businesses to evaluate the financial implications of different decisions before implementing them. By analyzing the projected financial outcomes, companies can make informed choices and minimize risks.
- Valuation: Pro forma statements are crucial in the valuation process, especially in mergers and acquisitions. They help determine the potential value of a target company and assess the financial impact of the transaction on the acquiring company.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Pro forma statements serve as a basis for budgeting and forecasting activities. They provide a roadmap for allocating resources, setting sales targets, and managing expenses, ensuring that the company’s financial goals are aligned with its strategic objectives.
In summary, pro forma financial statements play a vital role in financial planning, decision making, investor relations, and valuation processes. By creating these statements, businesses can gain valuable insights into their future financial performance and make informed decisions to drive growth and success.
Steps to Creating Pro Forma Statements
Creating pro forma financial statements involves several steps that help businesses project their future financial performance. These steps include:
1. Gather Historical Financial Data:
The first step in creating pro forma statements is to gather historical financial data. This includes financial statements such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for a specific period, usually the past three to five years.
2. Analyze Historical Data:
3. Identify Assumptions:
Based on the analysis of historical data, assumptions need to be made about the future performance of the business. These assumptions can include factors such as revenue growth rates, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and capital expenditures.
4. Forecast Revenue:
Using the identified assumptions, revenue for future periods can be forecasted. This can be done by considering factors such as market trends, customer demand, and competitive landscape. The revenue forecast should be realistic and based on thorough market research.
5. Estimate Costs:
After forecasting revenue, the next step is to estimate costs. This includes estimating the cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other costs associated with running the business. It is important to consider factors such as inflation, changes in input costs, and efficiency improvements.
6. Project Cash Flow:
7. Prepare Pro Forma Financial Statements:
Based on the projected revenue, costs, and cash flow, pro forma financial statements can be prepared. These statements include pro forma income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Pro forma financial statements provide a snapshot of the company’s projected financial performance.
8. Review and Adjust:
Once the pro forma financial statements are prepared, they should be reviewed and adjusted if necessary. This involves comparing the projected financials with industry benchmarks, historical performance, and management’s expectations. Adjustments can be made to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the pro forma statements.
9. Communicate and Monitor:
Finally, the pro forma financial statements should be communicated to relevant stakeholders, such as investors, lenders, and management. It is important to monitor the actual financial performance against the projected performance and make adjustments as needed.
By following these steps, businesses can create accurate and reliable pro forma financial statements that help in making informed financial decisions and planning for the future.
Key Considerations for Creating Pro Forma Statements
When creating pro forma financial statements, there are several key considerations that should be taken into account. These considerations will help ensure the accuracy and reliability of the statements, as well as provide valuable insights into the financial performance and potential risks of a business.
1. Historical Data
One of the most important considerations when creating pro forma statements is the use of accurate and reliable historical data. This data should include financial statements from previous years, as well as any relevant industry benchmarks or market trends. By analyzing this historical data, businesses can make informed projections and assumptions about future performance.
2. Assumptions and Projections
Pro forma statements are based on assumptions and projections about future events and circumstances. It is important to clearly state and justify these assumptions, as well as provide supporting evidence or data. This will help stakeholders understand the basis for the projections and assess their reasonableness.
3. Sensitivity Analysis
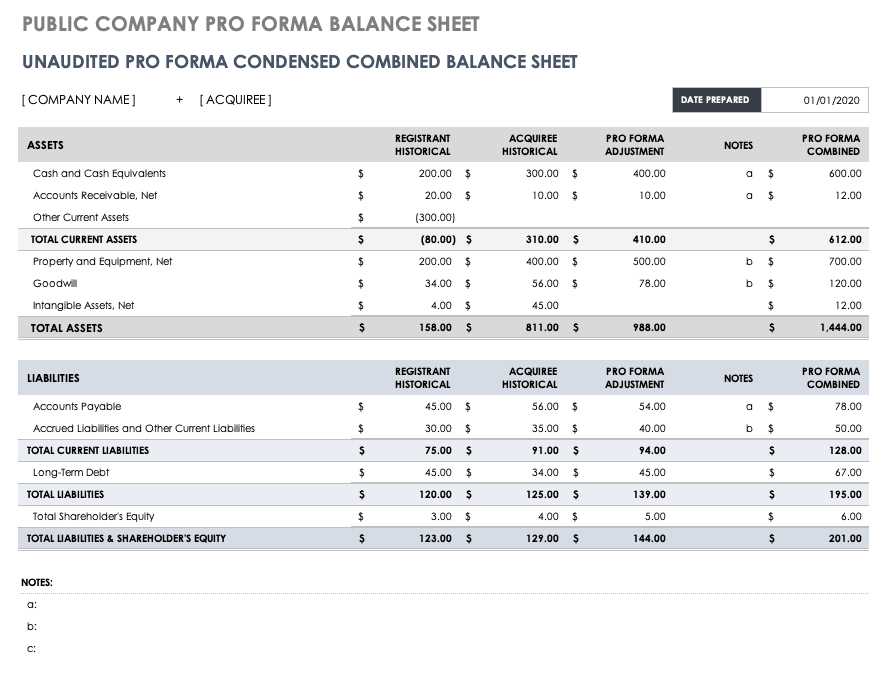
Pro forma statements should include a sensitivity analysis that assesses the impact of different scenarios or variables on the financial projections. This analysis can help identify potential risks and uncertainties, as well as provide a range of possible outcomes. By considering different scenarios, businesses can better prepare for potential challenges and make more informed decisions.
4. Realistic and Achievable Goals
When creating pro forma statements, it is important to set realistic and achievable goals. Overly optimistic projections can lead to unrealistic expectations and potential financial difficulties. By setting goals that are based on thorough analysis and market research, businesses can ensure that their pro forma statements reflect a reasonable and achievable financial outlook.
5. Review and Validation
Before finalizing pro forma statements, it is crucial to review and validate the accuracy and reliability of the data and assumptions used. This can be done through internal reviews, external audits, or consultations with financial experts. By ensuring the integrity of the statements, businesses can enhance their credibility and provide stakeholders with a more accurate representation of their financial position.
| Key Considerations for Creating Pro Forma Statements |
|---|
| 1. Historical Data |
| 2. Assumptions and Projections |
| 3. Sensitivity Analysis |
| 4. Realistic and Achievable Goals |
| 5. Review and Validation |

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
