What is a Loan Officer?
A loan officer is a financial professional who helps individuals and businesses secure loans from banks and other lending institutions. They play a crucial role in the lending process by evaluating loan applications, assessing creditworthiness, and determining the terms and conditions of the loan.
Key Responsibilities
Loan officers have a range of responsibilities, including:
- Evaluating loan applications and determining the borrower’s creditworthiness
- Assessing the risk associated with the loan and making recommendations to the lending institution
- Reviewing financial statements, tax returns, and other relevant documents to verify the borrower’s financial position
- Working with borrowers to gather additional information or documentation as needed
- Explaining loan options and terms to borrowers and helping them choose the best loan for their needs
- Negotiating loan terms and conditions with borrowers
- Ensuring compliance with lending regulations and internal policies
- Monitoring loan performance and taking appropriate action in case of default
Skills and Qualifications
- Excellent communication and interpersonal skills
- Strong analytical and problem-solving abilities
- Attention to detail and accuracy
- Ability to work under pressure and meet deadlines
- Knowledge of lending regulations and compliance requirements
- Proficiency in financial analysis and risk assessment
- Customer service orientation
Conclusion
A loan officer plays a vital role in the lending process, helping individuals and businesses secure the financing they need. With their expertise in evaluating loan applications and assessing creditworthiness, loan officers help borrowers navigate the complex world of lending and make informed decisions about their financial future.
Responsibilities of a Loan Officer
A loan officer plays a crucial role in the lending process, acting as a bridge between borrowers and lenders. They are responsible for evaluating loan applications, determining the creditworthiness of borrowers, and ensuring that all necessary documentation is completed accurately.
Some of the key responsibilities of a loan officer include:
1. Assessing Loan Applications:
Loan officers review loan applications submitted by borrowers and assess their financial situation, credit history, and ability to repay the loan. They analyze various factors such as income, employment history, debt-to-income ratio, and collateral to determine the risk associated with lending money to the borrower.
2. Conducting Credit Checks:
Loan officers conduct thorough credit checks on borrowers to evaluate their creditworthiness. They review credit reports, credit scores, and payment history to determine the likelihood of the borrower repaying the loan on time.
3. Providing Financial Advice:
Loan officers provide guidance and advice to borrowers regarding their financial situation and loan options. They explain the terms and conditions of different loan products, help borrowers understand the implications of taking on debt, and assist them in selecting the most suitable loan for their needs.
4. Verifying Documentation:
Loan officers ensure that all necessary documentation is completed accurately and in compliance with regulatory requirements. They verify income statements, employment records, tax returns, and other supporting documents to validate the information provided by borrowers.
5. Managing Loan Portfolio:
Loan officers are responsible for managing their loan portfolio, which includes monitoring loan performance, tracking repayment schedules, and addressing any issues or concerns that may arise during the loan term. They work closely with borrowers to ensure timely repayment and provide assistance in case of financial difficulties.
Overall, loan officers play a critical role in the lending process by evaluating loan applications, assessing creditworthiness, providing financial advice, verifying documentation, and managing loan portfolios. Their expertise and attention to detail are essential in ensuring that loans are granted to qualified borrowers and that the lending process is carried out smoothly.
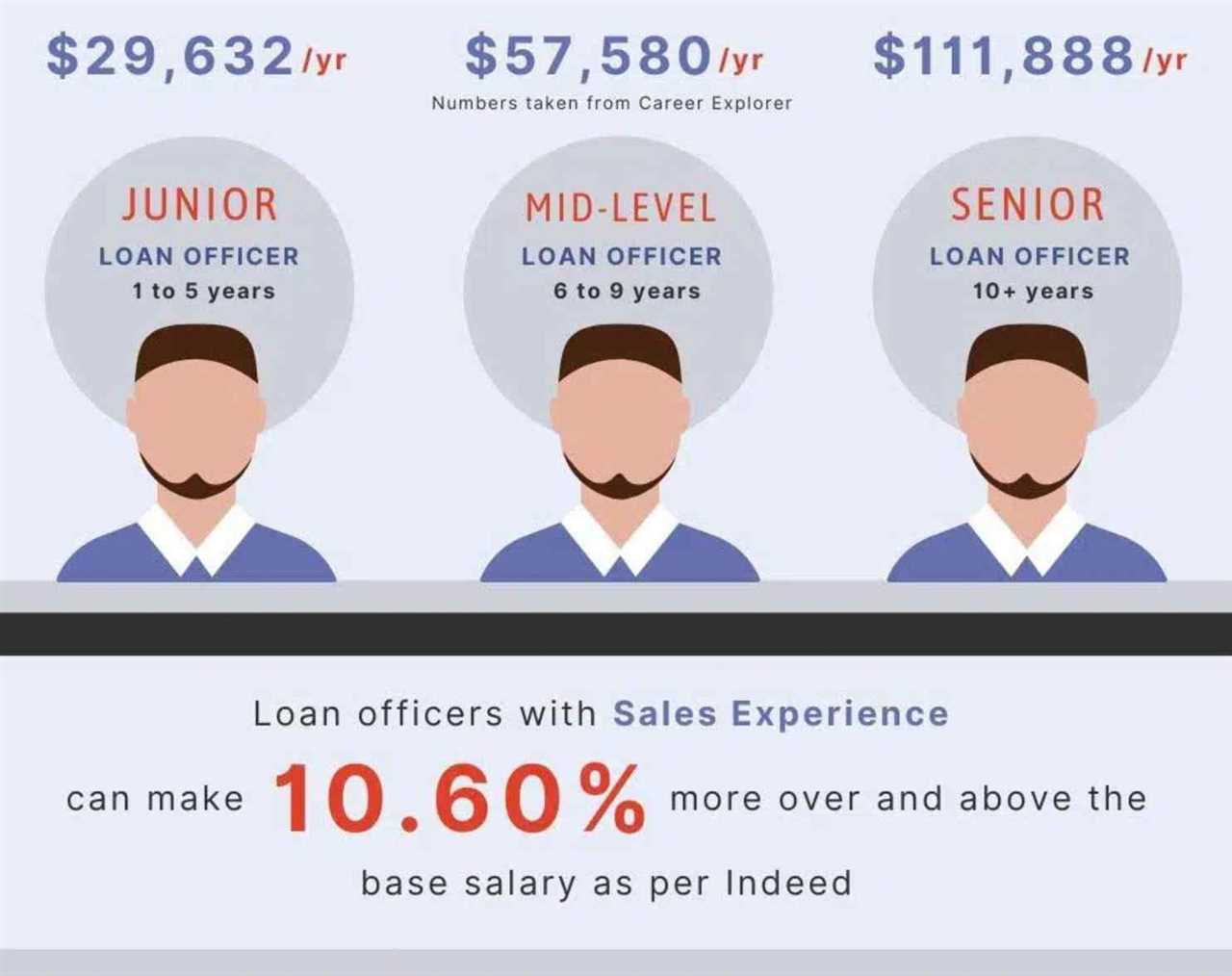
Benefits and Compensation for Loan Officers
Being a loan officer can be a rewarding career choice, as it offers a range of benefits and competitive compensation. Here are some of the key advantages of working as a loan officer:
1. Competitive Salary
Loan officers typically receive a competitive base salary, which can vary depending on factors such as experience, location, and the size of the lending institution. In addition to the base salary, loan officers often have the opportunity to earn commission based on the number and value of loans they originate.
2. Performance-Based Bonuses
Many lending institutions offer performance-based bonuses to loan officers who meet or exceed their targets. These bonuses can provide a significant boost to a loan officer’s overall compensation and serve as a strong incentive to excel in their role.
3. Comprehensive Benefits Package
Loan officers typically enjoy a comprehensive benefits package that may include health insurance, dental and vision coverage, retirement plans, and paid time off. These benefits can contribute to a loan officer’s overall financial security and well-being.
4. Professional Development Opportunities
Lending institutions often provide loan officers with opportunities for professional development and growth. This can include access to training programs, industry conferences, and certifications that can enhance a loan officer’s skills and marketability.
5. Job Stability
The demand for loan officers remains steady, as individuals and businesses continue to seek financing for various purposes. This job stability can provide loan officers with a sense of security and confidence in their career choice.

Emily Bibb simplifies finance through bestselling books and articles, bridging complex concepts for everyday understanding. Engaging audiences via social media, she shares insights for financial success. Active in seminars and philanthropy, Bibb aims to create a more financially informed society, driven by her passion for empowering others.
